The healthcare landscape is adapting to new demands, such as virtual care, which has become increasingly essential. Among these advancements, Electronic Health Records (EHRs) have been one of the most significant tools in Internet of Things healthcare, consolidating various functions into a single system. However, challenges remain, such as integrating dispersed patient data and addressing usability issues contributing to clinician burnout.
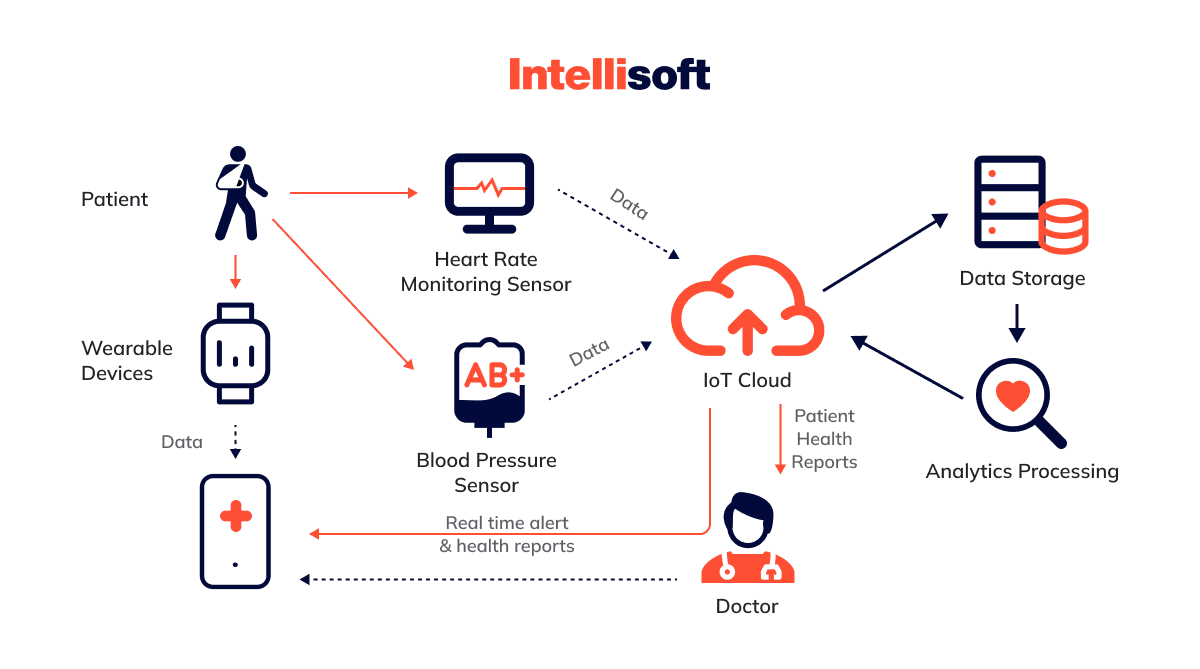
Amid these challenges, the Internet of Things in healthcare is a game-changer, extending healthcare capabilities beyond traditional clinical settings. Remote patient monitoring (RPM) technologies use IoT sensors to provide real-time health data, reducing the need for unnecessary in-person visits. As the demand for remote care continues to grow, IoT-driven innovations are shaping the future of healthcare, enhancing accessibility, and transforming patient monitoring.
In this article, we’ll explore the core advantages of the Internet of Things for healthcare, examine the most common Internet of Things healthcare applications, and share tips for overcoming the challenges that may arise along the way.
Table of Contents
What Is IoMT?
What is the Internet of Things in healthcare? It is an infrastructure of internet-connected medical smart devices, systems, software, and hardware. All these elements can collect data (whether about the health of patients or the state of medical assets) and share it in real-time. Experts say that such data is critical for medicine in 2022.
Internet of Things in healthcare applications solves many problems at different levels:
1. Hospitals: facility management
- Equipment monitoring and fault warning.
- Room control (temperature in rooms, laboratories, and freezers).
- Maintenance of appropriate temperature and pressure in shipping containers.
- Accounting of equipment, medicines, and consumables.
- Determining the location of equipment (wheelchairs, defibrillators, nebulizers, etc.).
- Personnel performance analysis.
- rRegulation of the flow of patients.
2. Doctors: Improving the efficiency of medical care with the Internet of Healthcare things
- Monitoring the vital signs of patients’ health in operating and postoperative wards.
- Round-the-clock monitoring of severely ill patients in intensive care units, cardiology, and epileptology.
- Online diagnostics through telemedicine solutions during treatment and rehabilitation at home.
- Formation of statistics of patients and their medical records based on the collected data.
3. Patients: self-diagnosis using wearable devices, maintaining communication with doctors
- Checking health indicators during the day with fitness bracelets, glucometers, and cuffs for measuring pulse.
- Automatic reminders for activities, medications, or doctor visits.
- Notification of changes in vital signs with data sent to doctors and family Members.
4. Insurance companies: making insurance decisions based on monitoring data
- Monitoring compliance with precautionary measures.
- Detection of fraud with insurance payments.
- Assessment of the feasibility of issuing insurance in particular cases.
The work of medical institutions is reaching a new level. The performance of administrative and management tasks becomes much more simple. Here are some Internet of Things healthcare examples: controlling the supply of medical assets, keeping records, monitoring the movement of personnel, or processing data. More advantages are related to the service quality. It is vital for patients with limited mobility, for example, after spinal surgery. Also, IoT has proven itself in orthopedics during COVID-19.
Wearable devices allow patients to independently control their wellbeing and adjust their daily routine, activity, and nutrition according to current indicators. Such sensors automatically notify healthcare workers about reaching critical values, which reduces health risks. There are many Internet of Things healthcare applications, and now we are going to look at several use cases.
Why Is Healthcare Internet of Things so Important?
Let’s start by understanding what IoT means in the medical world. The Internet of Things in healthcare is a network of smart devices and sensors that gather, transmit, and analyze health data. This approach includes wearables like fitness trackers and smartwatches, as well as medical devices such as smart glucose monitors, connected inhalers, smart hearing aids, and home monitoring systems with sensors. These interconnected devices enable real-time data sharing with healthcare professionals, allowing for proactive and personalized patient care.
But just how significant are these technologies? Here is the Internet of Things in healthcare an overview:
- In 2023, the global Internet of Things market in the healthcare sector was valued at $44.21 billion and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 21.2% from 2024 to 2030.
- By 2026, the number of IoT mobile connections worldwide is expected to more than double from 2021 levels.
- By 2025, the US is projected to have 70.6 million remote patient monitoring (RPM) users, a 56.5% increase from 2022.
Even though the pandemic has passed, the impact of the Internet of Things in healthcare market is lasting, particularly in the increased demand for IoT devices. These technologies enable healthcare providers to remotely monitor patients’ vital signs and health data, helping to detect potential issues early, improve disease management, and reduce hospital readmissions. Let’s review Internet of Things healthcare examples in the following section.
IoT in Healthcare: 5 Excellent Examples
1. Wellbeing monitoring
It is perhaps one of the most common Internet of Things healthcare applications. As we mentioned above, such devices can automatically collect essential health data: pulse, blood pressure, temperature, glucose levels, etc. They are sent to healthcare professionals to make informed treatment decisions. It’s possible to track the status of any disease, including Parkinson’s syndrome, mental disorders, heart problems, and diabetes.
Let’s give a couple of the Internet of Things healthcare examples from the practice of market players. The DexCom system integrates with third-party apps to help control diabetes as part of non-intensive insulin therapy. Boston Scientific’s mCRM solution manages a patient’s heart rate. Such technologies are valuable for the elderly and people with disabilities.
Eugene, back-end/front-end developer @IntelliSoft:
When it comes to IoT in healthcare, I can draw up one of our cases, Cambio Device Connectivity (CDC), known as Medical Device Information Collection (MDIC). We took part in creating the platform for gathering, storing, and disseminating data from medical devices in real-time. The idea is that MDIC connects with the built-in data interface of medical devices via device-manufacturer-provided software across the hospital network.
IntelliSoft has also worked on various wearables that a patient could use at home. Applying such tools to different parts of the body, it is possible to measure pulse, blood pressure, temperature, glucose levels, and then report data to the CDC solution. Thus, this app is helpful for both patients and clinical labs, especially nowadays, when many people are forced to or prefer to stay at home.
2. Compliance with sanitary standards
Medical internet of things and big data in healthcare help maintain optimal sanitation conditions in hospitals and clinics. How? For instance, by reminding staff to wash and sanitize their hands upon entering the room and immediately after contact with the patient. Such sensors are installed on soap dispensers and disinfectants. They check if the doctor has entered the room and send a voice reminder of hygiene procedures.
The sensors can even recommend disinfection methods according to each patient’s needs. Experts believe that it reduces the risk of infection by more than 60%. This approach also strengthens patients’ trust in healthcare professionals, as they see that the hospital cares about their protection and follows the rules.
3. Mood tracking
It is another type of patient data that is problematic to collect and process. Doctors usually just ask their patients how they feel. The problem is that they often cannot accurately describe their condition and mood. Moreover, it is impossible to quickly determine mood swings, especially associated with psychiatric disorders.
Wearable sensors come to the rescue. They analyze the state based on various data like a heartbeat, blood pressure, and even eye movement. And since anxiety symptoms affect not only thoughts and feelings but also behavior and the whole body, it is possible to draw conclusions about a person’s emotions. Of course, it does not predict depression, but it gives an idea of the general mood.
4. Smart Pills
Completely new ways of monitoring health are being introduced thanks to the IoT. There are pills with built-in miniature sensors that begin their own examinations when ingested. They collect the necessary information from the digestive system and others.
It helps avoid invasive procedures such as colonoscopy and inserting a nasogastric tube into the stomach. Doctors can check the acidity of the patient’s stomach, identify internal bleeding, or determine irritable bowel syndrome and even cancer. As a rule, such pills just dissolve or pass through the entire body.
5. Medication control
If the treatment is provided at home, the doctor cannot control the medication. Non-compliance with the prescriptions of patients leads to deterioration, relapses, and repeated hospitalizations. With the help of IoT, the doctor (or another person responsible for patient care) can track the medication schedule remotely while the patient is at home.
A smart pillbox is another way to control medication. For example, smart technology from AdhereTech automatically sends information about medication time. If a person misses it, they receive a notification in the form of an automatic call or text message.
And now let’s look at the main advantages of the technology and highlight a few problems that may arise in each of the Internet of Things in healthcare applications.
Related readings:
- 9 Technological Trends in Healthcare in 2023
- Telemedicine App Development: Features and Key Phases
- Main Benefits of AI in Healthcare: How AI Brings New Solutions to the Industry
- Automation in the Industry of Healthcare: Main Benefits for Business
- Understanding the New Rules: MDD vs. MDR
What Are the Advantages of IoMT?

- Real-time monitoring. Medical professionals can respond to emergencies timely and reduce the risk of death, such as heart failure. It is also the basis for telemedicine, when diagnostics and treatment are provided remotely without visiting a doctor.
- Medication compliance guarantee. Doctors can no longer rely on patient responses about how they feel. IoT provides info on activity, daily routines, and medication schedules, allowing for out-of-hospital treatment monitoring.
- Increased patient engagement. Wearable sensors are used for self-diagnosis and assessment of wellbeing. A person receives more health information and, based on it, can make informed decisions, for example, about adjusting the daily routine or nutrition.
- Convenient asset management. Smart sensors help you check your equipment and alert you when repairs are needed, keep track of medicines and consumables, and even see the current location of devices.
- Reduced costs. Automated data collection eliminates the human factor. Constant monitoring and timely assistance prevent repeated hospitalizations and improve treatment quality. All this reduces the cost of hospitals when dealing with a large flow of patients.
- Research accuracy. Devices generate large amounts of data, which creates a solid foundation for research activities. Doctors can better understand the causes of diseases, identify patterns, and find new methods of prevention and treatment.
What Are the Challenges Regarding IoMT?
Like any technology, Internet of Things healthcare has weaknesses and limitations. First of all, they relate to the disclosure of data. The devices operate wirelessly and collect a lot of information, including personal data. To solve the problem, encryption and security protocols must be implemented. However, it is difficult due to the large number of devices. It is also necessary to protect them from physical manipulation and software, hardware, and network attacks.
There may be difficulties with constant access to the Internet or integration with devices from other manufacturers. Moreover, doctors need time to understand the algorithms and start using the technology effectively. There is only one way to avoid problems: entrust it to IoT software development specialists with experience in health care.
There may be difficulties with constant access to the Internet or integration with devices from other manufacturers. Moreover, doctors need time to understand the algorithms and find their unique application of Internet of Things in healthcare. There is only one way to avoid problems: entrust it to IoT software development specialists with experience in health care.
Why Security Matters for IoT in Healthcare
To fully harness the potential of the Internet of Things healthcare, we must tackle critical security challenges head-on.
First and foremost, developers, managers, and healthcare providers need to ensure the data collected by IoT devices is securely protected. Many medical devices collect data classified as protected health information under HIPAA and similar regulations. Without proper security measures, these IoT devices could become gateways for cybercriminals to steal sensitive data. Alarmingly, 82 percent of healthcare organizations have reported attacks on their IoT devices. Therefore, using healthcare internet of things security software is a must.
Creating secure IoT hardware and software is a crucial step in addressing this challenge. Equally important is the proper management of these devices to prevent unmonitored data from falling into the wrong hands. For instance, a patient monitoring device with outdated software or one that isn’t properly decommissioned after use can provide an entry point for attackers to infiltrate networks or steal protected health information.
Identifying and classifying all IoT devices on a healthcare provider’s network is essential in mitigating this risk. Once these networks are properly identified, classified, and secured, managers can monitor device behavior for anomalies, perform risk assessments, and separate vulnerable devices from mission-critical ones. This comprehensive approach ensures you can effectively solve the Internet of Things in healthcare interoperability and security issues.
Conclusion
IoMT is a valuable technology for all parties: public hospitals, private clinics, medical professionals of various profiles, insurance companies, and, of course, patients. Involve professionals in IoT software development to reduce costs, ensure data security, and simplify Internet of Things healthcare setup and deployment! For instance, you can ask for help at the official website of IntelliSoft!