Medical devices significantly enhance the health and quality of life for many people worldwide. Their effectiveness, however, relies heavily on stringent standards in their design, manufacturing, and maintenance. This underscores the crucial role of a medical device QMS to ensure these devices are safe, effective, and perform optimally within the industry.
IntelliSoft has been a key player in the healthcare sector for more than 14 years, contributing to pioneering projects like the Daintel Clinical Information System (CIS). IntelliSoft not only helped this start-up develop its Minimum Viable Product (MVP) but also successfully launched it in the market. Our team was also instrumental in integrating medical devices with the Cambio Electronic Medical Record System (EMR).
In this blog, we’ll delve into QMS medical device. We’ll discuss its importance, the key benefits it offers, its essential requirements, and more. Ready to dive in? Let’s get started!
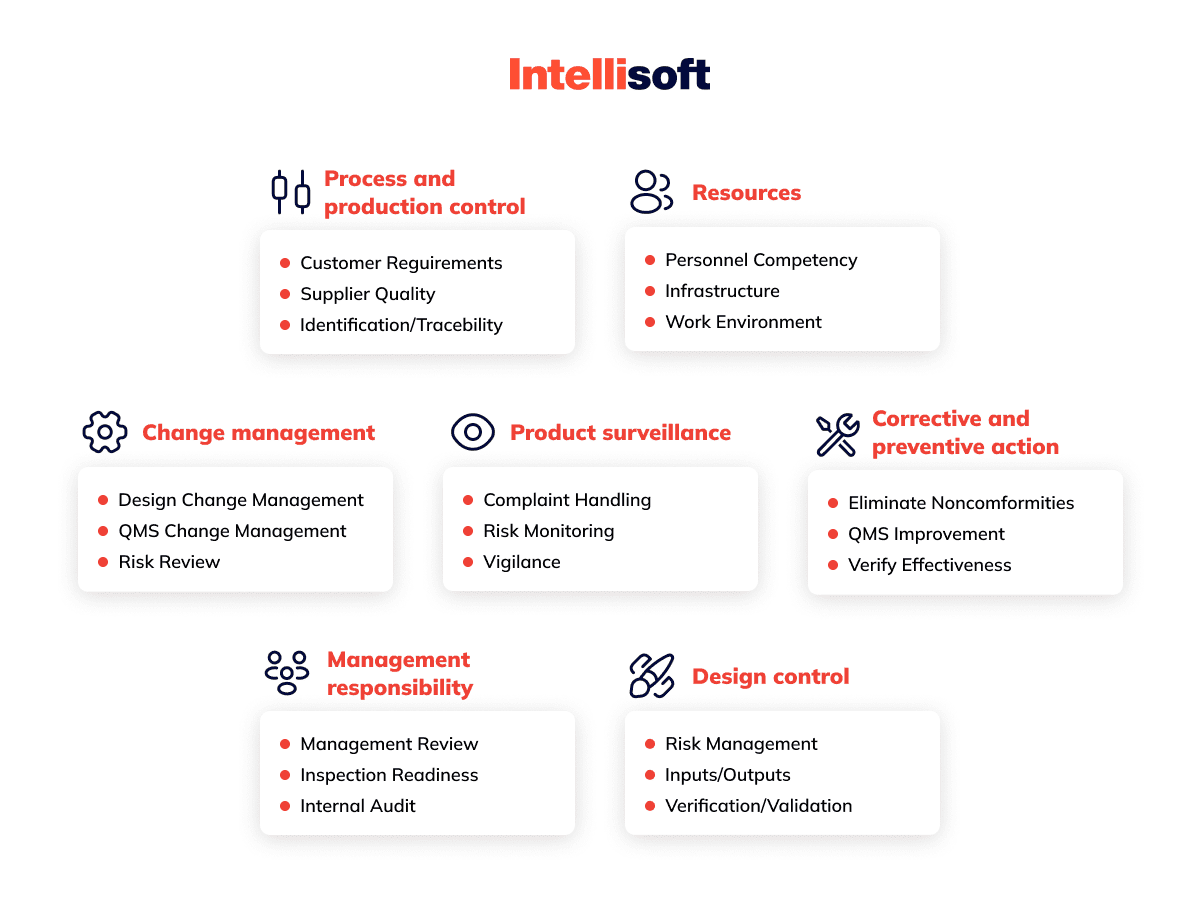
Table of Contents
What Is QMS?
What is QMS in medical devices? The Quality Management System (QMS) is an enterprise management style in which managers, engineers, and technicians strive to improve product quality and the enterprise management system. The QMS requirements are outlined in the international standard ISO 9001:2008, which is called Quality Management System Requirements. The standard was developed by the international organization for standardization (ISO). It summarizes the best world experience in management practices.
The Medical Device Quality Management System (QMS) is a part of the overall company management system, which ensures consistent quality of products and services.
The QMS methodology is based on the principles of system and process approaches. The principle of consistency is implemented in the company’s management as a system of interrelated processes aimed at achieving business goals.
The process approach allows identifying the procedures that have the most significant impact on achieving the goals. In this case, inputs and outputs of processes, internal and external customers, suppliers, and other interested parties are determined and assessed. Thus, the processes performed within the product lifecycle determine the enterprise’s organizational structure. All processes execution for all elements of the organizational structure is documented.
The organization of the QMS for medical devices involves the creation of the following documentation structure:
- Quality manual
- Quality policy and objectives
- Mandatory documented procedures
- Regulations of processes and procedures, work instructions
- Quality records

Why You Need an Industry-Specific Medical Device QMS
The quality of medical care is a set of qualities that confirm the compliance of the rendered medical care with the existing needs of the patient, their expectations, the current level of medical science, technology, and standards. The following qualities of the medical care quality are distinguished:
- Professional competence. It implies theoretical knowledge and practical skills of medical workers and support staff, as well as how they use them and follow clinical guidelines, protocols, and standards. If we talk about a manager’s competence, it is, above all, professional skills in developing and making managerial decisions.
- Accessibility. This feature means that medical care should not depend on geo, economic, social, cultural, organizational, or linguistic barriers.
Interpersonal relationships. This health care quality refers to the relationship between healthcare staff and patients, medical personnel and their management, the health care system, and the population.
Efficiency. Efficiency is the ratio of the achieved economic effect to the costs. The importance of this ratio is determined by the fact that healthcare resources are usually limited, and an effectively functioning medical system should provide optimal quality of medical care through the rational use of available resources. - Continuity. This characteristic means that the patient receives all necessary medical care without delays or tiring waiting lines, unjustified interruptions, or unwarranted repetitions in the diagnosis and treatment.
Safety. As a quality characteristic, safety means minimizing the risk of adverse effects of diagnosis, treatment, and other iatrogenic manifestations. It applies to both healthcare providers and patients. Safety measures are critical in providing both specialized and primary health care. - Convenience. This trait means a system of measures aimed at creating an optimal therapeutic and protective regime, such as ensuring comfort and order in medical institutions, rational placement of wards and therapeutic/diagnostic units, equipping them with modern equipment, organization of the patient’s daily routine, reduction of exposure to unfavorable environmental factors, etc.
- Compliance with patient expectations. For patients in a particular medical institution, medical care quality is defined by the extent to which it meets their needs and expectations. Do they get treatment on time? Patients most often pay attention to the convenience, efficiency, accessibility, continuity of health care, their relationship with the medical staff. Patients’ satisfaction with medical care depends on assessing health-related quality of life.
You should also understand why it is necessary to implement a quality system that meets the requirements of ISO 9001.
Having a certified quality management system is a formal requirement for state accreditation of a medical institution.
The unified approach to the recognition of the QMS compliance with the ISO 9001 requirements all over the world creates advantages for the higher educational establishments interested in attracting international students or building commercial relations with other countries.
Having a certified QMS guarantees the quality of the medical process in the eyes of existing and potential patients.
An effective QMS for medical devices creates a competitive advantage for medical institutions.
How to Develop QMS
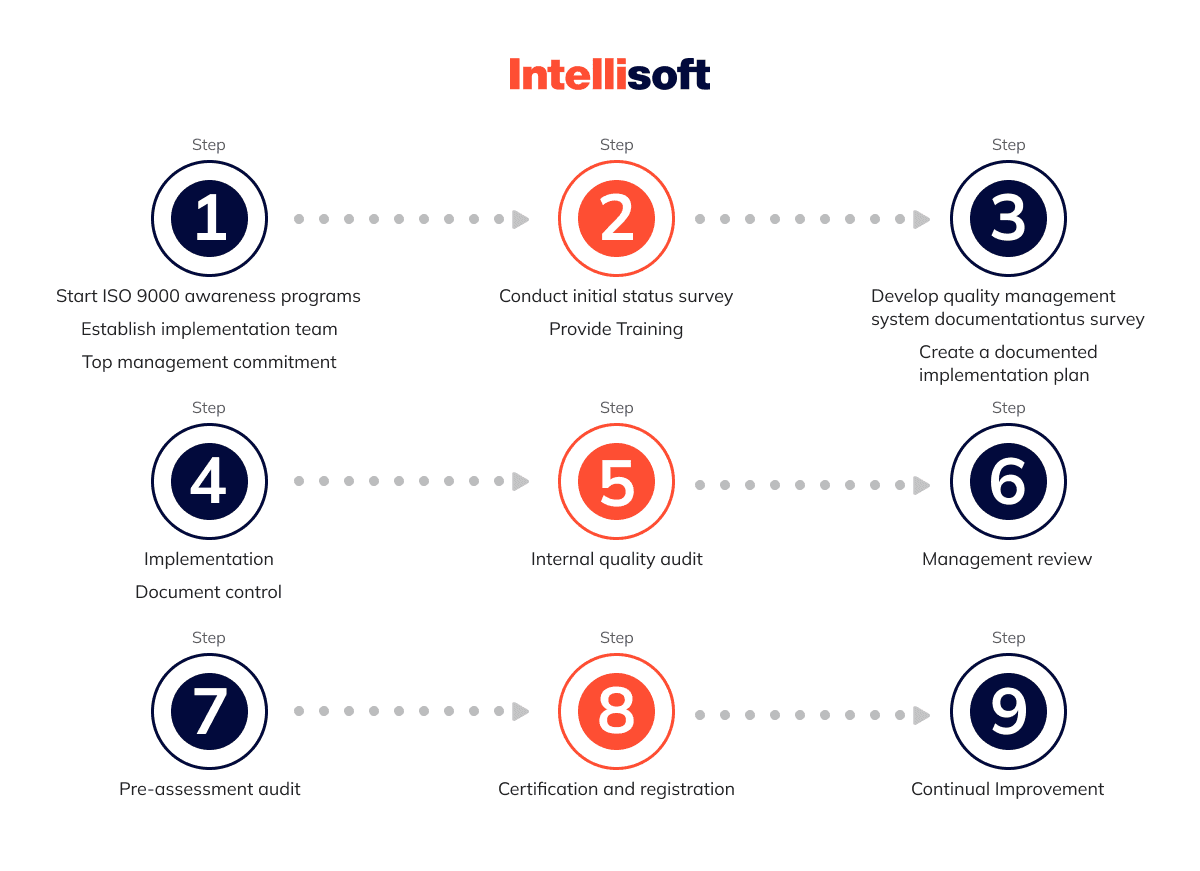
- 1. The first stage of QMS implementation: Analysis of the current situation in the organization and staff training.
Step 1: Development and implementation of the quality management system is a project with goals, deadlines, and certain resources. Therefore, the management must have the ability to support the administratively
the quality system project, as well as allocate appropriate resources.
An order is issued in the beginning, and it should specify several things.

For a large medical institution (100 employees and above), several members may be needed to form a group. The team leader is the head of the organization’s quality service. This person should devote almost 100% of their time to the issues related to building a QMS medical device.
Other group members are the employees of the quality service, who devote more than 50% of their time to the relevant questions.
Step 2: Training the working group members, informing them about the requirements of ISO-9001 series standards.
The team leader has to be trained just like less experienced members. The analysis of the status quo and the development of a quality system are their primary tasks.
Step 3: Analyze the current situation. In order to understand how much current business activities deviate from the requirements of
ISO-9001:2008 standard, it’s necessary to conduct an in-depth analysis of the current situation. Baseline data collection is mainly carried out by two methods – via questionnaires and interviews.
- 2. The second stage of QMS implementation: Development and implementation of documentation.
That is when you may face changes in the quality of employees’ work. This stage is the most labor-intensive and time-consuming. During it, such processes as the design, development, and implementation of
documentation of the quality system, as well as the implementation of changes in the medical staff work and organization, take place.
Step 1: At this phase, it’s necessary to plan how the quality system will be built, the scope of application, which processes will be included in the quality system solution, and how the quality system will be implemented.
It is essential to plan how the quality system will be implemented and disseminated.
Step 2: The basic principle of the ISO-9001:2008 standard.
To implement it, the standard requires that all organizational processes be defined and documented. To meet this requirement, the working group must first formalize the development processes. Then, it’s necessary to make changes to these processes according to the requirements specified in the standard.
Step 3: Documenting and implementing the QMS procedures.
The ISO-9001:2008 standard requires that an organization’s processes be defined and documented.
- 3. The third stage of QMS implementation: Conducting an internal audit of the quality system.
The main purpose of this stage is to check the work of the quality system before the certification audit. Additional objectives at this stage would be:
- Providing practical training of internal auditors
- Conducting audits
- Training staff before the certification audit
You Might Also Like:
- Legal Requirements for Storing Data: Key Insights for Storing User Data
- Telehealth Software Solutions: Top Trends for Telemedicine in 2022
- Main Benefits of AI in Healthcare: How AI Brings New Solutions to the Industry
- What Technologies Are Driving the Health Protection System?
- Automation in the Industry of Healthcare: Main Benefits for Business
What Regulations Govern a Medical Device QMS?
Managing the quality of medical devices extends beyond precise design and production—it demands strict compliance with international standards and regulations. The specific rules can vary depending on the device type, classification, and the markets where it is sold. Here are some key regulations that are critical for anyone in the healthcare industry to understand:
ISO 13485
ISO 13485 establishes the framework for a QMS software medical device tailored for medical devices. Building on the principles of ISO 9001, it incorporates additional requirements crucial for the medical device sector, such as risk management, design control, validation, and traceability. This standard is indispensable for any organization involved in the entire lifecycle of medical devices, from design to post-market support. Globally recognized, adherence to ISO 13485 ensures that medical products meet both customer expectations and regulatory mandates.
Medical Device Regulation (EU) 2017/745 (MDR)
The EU’s Medical Device Regulation (MDR) supersedes previous directives with a comprehensive framework aimed at enhancing patient and user safety across Europe. It introduces stringent guidelines for the classification, conformity assessment, and clinical evaluation of medical devices. Noteworthy additions to the MDR include unique device identification (UDI) systems, implant cards, and EUDAMED, the European database on medical devices. These enhancements are designed to ensure high levels of health protection and facilitate smooth market operations within the EU.
FDA 21 CFR Part 820
In the United States, the FDA enforces FDA 21 CFR Part 820, which stipulates the requirements for good manufacturing practices (CGMP) in the medical device industry. This regulation encompasses everything from design and document control to production, corrective actions, and preventive measures. Establishing a QMS medical device under this regulation involves developing comprehensive policies, objectives, manuals, plans, and audits to ensure exceptional quality and compliance.
How Long Does It Take to Implement a QMS?
The timeline can vary significantly, ranging from a few months to a couple of years, depending on the complexity and scope of your project. Here’s a breakdown of what you can expect during the implementation journey:
- Planning. Kick things off by outlining your project’s scope, goals, expected outcomes, budget, timeline, and the roles everyone will play.
Analysis. Evaluate your organization’s current state, including its products and processes. Identify any gaps that need bridging and pinpoint opportunities for enhancement. This phase also involves setting the specs for your QMS. - Design. Craft the processes, procedures, and documentation for your QMS. You’ll also choose the necessary tools, software, and hardware during this phase.
- Implementation. Put your plans into action by implementing the designed processes and setting up the selected tech tools.
- Testing. Test everything to ensure the processes and tools function as expected. This step is crucial for ironing out any kinks.
- Training. Educate your team on how to use the QMS effectively. This includes training for users, managers, and auditors.
- Deployment. Officially roll out your QMS, activating and operating the tools and processes you’ve put in place.
- Monitoring. Keep a close eye on the performance and efficiency of your QMS. Collect and analyze data to make informed decisions.
- Review. Assess the outcomes and impacts of your QMS. This is your opportunity to gauge satisfaction and ensure compliance.
- Improvement. Continuously improve your QMS by updating processes and upgrading tools as needed.
What Are the Essential QMS Requirements for Medical Devices?
Ensuring a robust medical device QMS software for medical devices is crucial for compliance and excellence. Here are the key medical device QMS requirements:
Document Control
Think of document control as the backbone of your QMS medical device. It oversees every stage of your documents’ lifecycle—creation, approval, distribution, revision, and retention. This process ensures your policies, procedures, manuals, and other essential documents are always accurate, consistent, and up-to-date. Effective document control keeps outdated or unauthorized documents from creeping into use, maintaining a high standard of quality and traceability.
Training Management
Training management is all about equipping your team with the right skills and knowledge. This involves organizing courses, workshops, webinars, and e-learning sessions tailored to your QMS needs. By ensuring everyone from users to auditors is well-trained, you boost the efficiency and effectiveness of your QMS operations. Plus, timely and relevant training keeps your team current with the latest industry standards and practices.
Audit Management
Audits are your QMS’s health check-ups. Audit management covers planning, executing, and following up on both internal and external audits. This process ensures your procedures and records meet regulatory standards and are implemented correctly. By involving qualified, independent auditors, you get unbiased insights into your system’s strengths and areas for improvement, ensuring swift resolution of any issues found.
CAPA Management
Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) management is your safeguard against recurring problems. It identifies and addresses nonconformities, deviations, and incidents like errors, defects, and recalls. CAPA management not only fixes issues but also prevents them from happening again, continuously improving the performance and quality of your Medical Device Quality Management System. Every action taken is meticulously documented, tracked, and validated, ensuring thorough and effective resolutions.
4 Approaches to a Quality Management System
A lone ranger is the first option to consider. Individual contractors possess vast experience in QMS at various device firms. You can either hire them full-time or on a fractional basis. Some of these guys may work on the so-called “use it or lose it” monthly retainer. While picking a lone ranger, decision-makers should look for a person who sees no tasks as rather menial, lest the company will be impressed when it requires doc control maintenance, for instance. It is not recommended to hire such an expert part-time or remotely.
Hiring is not a flexible way though enough businesses choose this option. This option works well in case the management has a particular individual or team in mind with whom it used to work sometime in the past. It should be a trusted person. Otherwise, preparing and placing job vacancies, interviewing applicants, onboarding, training, and retaining may take a while. In most cases, it is wiser to hire an experienced quality manager instead of a Director or Vice President (VP).
There is also the DIY approach. This abbreviation stands for “do-it-yourself.” Thus, you may guess what it means. All a business needs, in this case, is a set of standard operating procedure (SOP) templates. The responsible person will then have to fill in those templates according to the company’s data and reports. This choice is feasible for several groups of managers who have.

Those who choose the DIY approach may still demand some external help from time to time. For instance, from experts in internal or supplier auditing.
QMS expert firm is the last but not the least favored option. In the healthcare device ecosystem, many QMS specialist agencies exist. Such a model implies paying only for hours spent on the project. From doc maintenance to strategic management, entrepreneurs can pick whatever they want out of the list of services. These agencies can replicate a full-service QA department. The QMS service providers can quickly scale up and down to meet the client’s expectations ASAP. Your company obtains full support in all functional roles in this case.
Costs of Developing a QMS
How much you pay depends on the approach you choose, as well as project peculiarities and deadlines. For instance, if hiring is your choice, average annual wages can be around $164,000 for a Quality Director and as high as $258,600 for a VP. So, it makes sense to hire a Quality Manager whose typical salary is $142,000 per year. Sure, more flexible options are available, but make sure that the price corresponds to the quality of services you get.
As for the DIY approach, customizable templates can be found at prices starting from $1,000. $4,000 is usually the top price. You can check, for example, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) official website.
As for the agencies, the fee depends on the company’s size and its experience with quality management systems. The agencies typically deliver ready solutions within half a year, and it may cost you roughly 25,000-40,000 USD.
Final Words
A quality management system must be implemented as early as possible while working on a new medical device. QMS in medical devices is a guiding framework to ensure that your business has robust processes, from risk management and prevention to manufacturing procedures and vendor management.
It comes down to building a secure, effective solution that provides a smooth way to market. A properly established quality management system assists with bringing consistency. However, you may sooner or later get stuck with your QMS software development because of some issues with QMS or other stages. In this case, you can count on a dedicated development team or other types of team extension offered by Intellisoft. We are always ready to lend you a helping hand with your medical project – just let us know what the problem is, and we’ll figure it out for you!