Looking For Healthcare Developers?
Data security is one of the most sensitive issues of our time, especially when it comes to healthcare. So, who is responsible for keeping a patient’s medical information safe these days?
According to the World Health Organization, there are up to 7 billion mobile phone users in the world, with mobile networks covering more than 85% of the world’s population. This global coverage of cellular communications, along with the ever-increasing technical capabilities of mobile phones, is contributing to the emergence of a new trend in public health, mHealth. It’s related to the use of smartphones for healthy lifestyles, disease prevention, and medical treatment.
The greatest development in research in the field of mobile health took place in the US and EU countries, where health experts in cooperation with IT specialists began to use mobile phones as a tool for shaping a healthy lifestyle, encouraging physical activity and healthy eating, sending reminders about when to take medications and visits the doctor, monitoring symptoms of cardiovascular and lung diseases, supporting users in quitting smoking, etc.
Table of Contents
What Makes It Different?
If you’ve ever discussed technology, business strategies, or your own experiences with a friend who works in healthcare, you’ve probably heard the phrase, “That’s not the case with health care.” That’s a perfectly reasonable statement, given the many challenges inherent in the industry and the high expectations of patients. The technological and organizational demands of healthcare are special. They now come to the forefront as the industry enters an exciting growth period, inevitably facing severe challenges.
Strict regulatory requirements, hectic business conditions, the sensitive nature of management, and the exercise of humanity in the delivery of medical treatment to the patient are all extraordinary variables found only in the context of healthcare. They require that we use a special lens to examine the various challenges the industry faces today.
Emerging Threats
Because health data is highly attractive to cybercriminals, it’s not surprising that healthcare organizations have experienced a number of large-scale and widely discussed leaks in recent years. As the Ponemon Institute’s May 2016 report on healthcare data security and privacy shows, while 2015 was the worst year in terms of inappropriate disclosures of healthcare data, there was no major breakthrough in cybersecurity. Since then, not so many things have changed.
According to the study, 89% of medical executives surveyed admitted that their organization had experienced at least one leak in the past two years. Nearly half of respondents (45%) said their institution had experienced more than five leaks. In 2015, 112 million medical data records were compromised in the United States alone. Ransomware attacks have also become a serious threat to the medical industry.
Healthcare cybersecurity professionals have a tough time. They are caught between two fires: on the one hand, they need to simplify and make the exchange of medical data more transparent to meet the demands of the times; on the other hand, they need to implement tools to protect data, devices, and networks from leaks and hacker attacks.
The problem is that in the era of digital medicine, people who don’t have even a basic understanding of information security are gaining access to sensitive patient data. To make matters worse, healthcare IT infrastructures are often rife with vulnerabilities.
The easiest way to guarantee safety and anonymity to every healthcare app user today is hiring a team of dedicated engineers who know how to create secure solutions. One example of a reliable partner is IntelliSoft. It is an outsource software development company, experienced in healthcare project development that can build or help create a medical system that would comply with all data protection regulations.
As proof of our competence, you can check the Cambio case study.
This e-healthcare company uses state-of-art technologies, and needed our assistance with some solutions. We make sure that our client meets The European Medical Device Regulation (MDR), as well as The Medical Devices Directive. IntelliSoft also implemented standards for healthcare data storage and transfer: HL7, openEHR, SNOMED CT, IHE XDS, etc. So, somehow, we served as a health protection app development company.
This perspective redirects us to the topic of privacy and data security in healthcare. Patient medical data is now widespread among numerous companies and is quickly becoming one of the most valuable forms of data. In addition to data, the medical devices we entrust our lives and health to are becoming increasingly digital, consequently exposed to threats in the form of hackers and malware.
In the world of commerce, identity theft can cause great inconvenience and cost thousands of dollars, but what is that compared to the potential damage caused by a compromised medical device? The stakes go up when a patient’s well-being depends on a properly functioning heart rate monitor, for instance.
In addition to life and health, there is another important component of the patient’s relationship with the healthcare system, Protected Health Information (PHI). Transmitted between patient, provider, and payer, PHI is generated throughout a patient’s interaction with the healthcare system. Generally, this data is handled by the healthcare companies. These companies should keep the patient’s health information confidential, available, and unchanged. It’s easier said than done, but the time for “saying instead of acting” is over. As patients, medical companies and government regulators have already learned, breaches that occur in PHI can not only be costly, but also cause tremendous inconvenience.
Security Technologies Basics in Healthcare
The benefits of mobile health are based on the ability to provide ongoing physician-patient communication. Two tracks can be distinguished: distance learning and remote symptom monitoring, which ensure that health care providers are informed about the patient’s condition in a timely manner.
The question is how to guarantee security so that patient’s data remain strictly confidential. We have several suggestions.
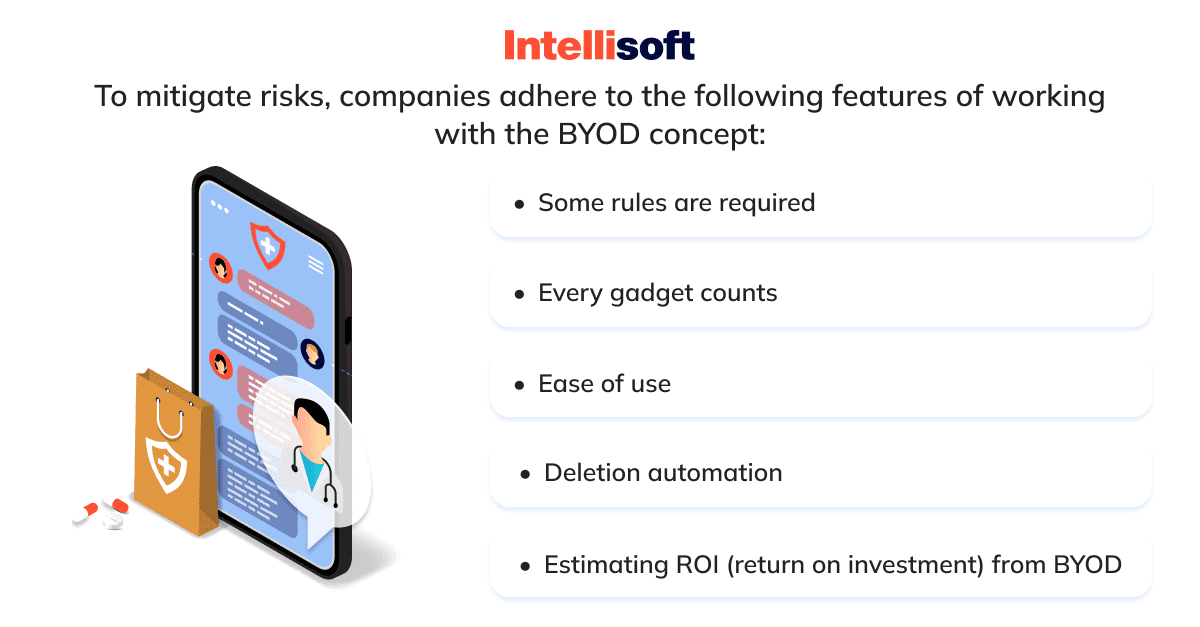
Bring Your Own Device (BYOD)
In healthcare cybersecurity, BYOD (an acronym for “Bring Your Own Device”) is an information technology policy based on the idea of taking your personal device to office instead of using the local equipment. That is, the manager gives unlimited access to non-sensitive company systems and data to the employee’s smartphone, tablet, or laptop. This happens with IT control over the gadgets themselves, installed applications, and stored data.
This is the essence of BYOD technology (or rather, IT policy in business). This type of healthcare cybersecurity reduces costs and increases productivity. At the same time, the company assumes risks due to possible violations in digital security because of other users’ gadgets.
Encryption
Encryption is the reversible transformation of information in order to conceal it from unauthorized users, while, at the same time, allowing authorized users to access data. This feature is necessary to make your app HIPAA compliant. The main purpose of encryption is to maintain the confidentiality of transmitted info. An important feature of any encryption algorithm is the use of a key, which states the choice of a particular transformation from the set of possible for a given algorithm.
With encryption, you can encode a simple and clear message (e.g., “Dropbox is cool!”) into an encrypted message that will be incomprehensible to those who see it encoded (“9itQg7nbV781+f55eXC1Lk.!”).
The encrypted message is transmitted over the web, and once delivered, the recipient must in some way (usually with an encryption key) convert the encrypted message to its original format (“Dropbox is cool!”).
Any organization that wants to use mobile and cloud technologies for patient care and staff must ensure the highest degree of data security and meet stringent regulatory requirements. Information leaks are not getting any smaller, so learning how to develop a healthcare project with ultimate cyber security is twice as important. You can read more about it in our exclusive eBook, How to Develop a Healthcare Project with Ultimate Security.
Need To Integrate HL7 To Your Product?
Healthcare organizations, especially their IT departments, must implement comprehensive, high-performance digital security measures that properly manage and protect data not just for fear of fines and reputational costs, but so that patients begin to see the benefits of sharing information in healthcare, confident that their data is secure. The methods discussed above prove that making patients feel safe in the 21st century is not that complicated.
Comprehensive Healthcare Security Environment
The number of tools to track patient data has increased dramatically over the past few years, largely due to the development of cloud technology, mobile devices, and the ability to store massive amounts of data online. In addition, wearable electronics are gaining popularity in the medical field. For example, the FitBit and Nike Fuel Band fitness trackers provide biometric data, on the basis of which physicians can develop more effective treatment regimens. As with mobile technology, such devices are both a boon and a risk. Healthcare providers need to understand where and how the information generated by IoT gadgets is stored.
These technologies’ development reinforces new trends in preventive healthcare and remote medicine. However, complex rules of information security in healthcare imposed on the industry by regulators and patient care priorities are affecting the pace of industry innovation.
So, the idea is to provide a comprehensive healthcare security environment by any means. The question is how.
VMware—Virtual Machine Risk Mitigation
VMware is a server virtualization technology developed by an American company of the same name. VMware digital health innovations are created to consolidate enterprise-level servers and maintain their continuous operation. Virtualization is required to divide the server into many virtual dedicated servers isolated from each other.
This tech creates several scapegoats to deal with cyberattacks or multiple backup databases/desktops. For instance, if a cyberattack against an EHR system occurs, the company develops a decoy EHR to reflect the attack or retrieve data from other VMs. In other words, this technology significantly minimizes risks and losses for healthcare institutions.
Industry Integrated Solution
Most of medical workers have no idea how to support and guarantee data security. World-known IT providers such as Cisco and Oracle create safety packages to meet the expectations of a medical institution. Developing video surveillance, distant third-party control, staff checks, and more are all cases that go beyond the healthcare info security of a certain device or data. In fact, those spying and damaging the physical data tech infrastructure are as threatening as intruders attacking in cyberspace. Industry-integrated solutions are there to handle security regarding threats that can be generated within the land-based premise.
The growth of the digital health market is also driving the sharing of medical data for clinical trials. For example, patients may agree to send their data for subsequent analysis, and physicians may agree to share new types of health information (genetic research data, etc.).
So far, the healthcare industry has not proven that it protects digital health data in a truly trustworthy way. Apparently, it has yet to earn the trust of patients.
Related readings:
- Healthcare in the Cloud: Transforming Patient Care and Data Management
- A Step-by-Step Guide to Developing HIPAA-compliant Medical Apps
- Transforming Healthcare Communication: Integration of HL7 Interface Engine
- Healthcare App Developers for Hire: Which Option to Choose
- Best Examples Of Successful Healthcare IT Start-Ups From Denmark
Approaches to keeping patients, visitors, and staff safe
Technical safeguards
Software developers should focus on tech safeguards in the first turn. Without safeguard, it would be impossible to achieve compliance with a specific app later.
| Safeguard | How to implement |
| Access controls | Unauthorized users should not be able to access protected health information (PHI). That is why engineers should apply such methods of data protection as tokens, passcodes, PIN codes, voice recognition, keys, or fingerprints. At least a couple of methods at once guarantee almost perfect security. |
| Audit controls & activity logs | Make sure that a compliance software logs all actions. That is the way to keep an eye on what is going on with protected health information. Think about procedural mechanisms or special hardware/software to track activities and assess them. |
| Integrity controls | Try to detect all authorized/unauthorized access efforts and come up with the effective integrity policy. You may need safety procedures to defend information from modifications or damage. |
| Data transmission protection | Data transmission security measures are necessary to forbid unauthorized users when protected health information is transmitted. |
Physical safeguards
It is necessary to implement physical safeguards. Let the team of technicians with corresponding experience do that. In general, those are safeguards associated with physical access to electronic protected health information (e.g., workstation, storage location, mobile safety).
| Safeguard | How to implement |
| Facility access monitoring & control | Just authorized users may have access to the objects of a covered institution. |
| Workstation & device safety | A company must limit the usage of workstations and mobile solutions with access to protected health information. The most effective practices for doing so include safety systems, video surveillance, deletion of information, door/window locks, etc. |
Administrative safeguards
To implement administrative safeguards, organizations should assign a security officer, who will have to assess threats and restrict access.
| Safeguard | How to implement |
| Data access management | The employees should be able to access protected health information just in cases when they demand information to provide services. In other words, it’s vital to ensure minimum necessary usage of PHI. Access controls must be flexible. |
| Risk evaluation | Medical and fitness app developers should provide the future users and owners of software with a full understanding of info use practices. Moreover, companies should define the ways PHI must be managed, along with evaluating threats. |
| Security staff training | A company should hire a person responsible for security issues – the so-called security official. It is also necessary to educate staff on how to detect and handle various risks associated with safety. |
| Info security evaluation | Regular security audit is a must. In the end, the entity should ensure meeting the The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) software requirements. |
Healthcare & medicine is the field for people with a great sense of responsibility. Organizations that deal with health protection software development should be aware of all standards set by HIPAA. Administrative and physical safeguards are heavily impacted by tech and HIPAA compliance app providers.
HL7 and FHIR Data Sharing Standards in Medical Fields
Currently, the statistics are not comforting at all. Statista admits that roughly 1,500 mln data breaches take place every year in the United States alone. Medical information is often under the threat. HIPAA Journal adds that up to 9,7 mln medical records were compromised monthly in 2020. So how should healthcare representatives deal with this problem?

HL7 is the first set of global standards healthcare organizations should memorize and apply. It is also known as Health Level Seven. It was offered to help monitor e-health data management and integration.
There is also the so-called FHIR. It stands for the Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources. It is a simpler analogy of HL7. This standard possesses way better interoperability than outdated HL7. In the FHIR-based apps, the resources share a common set of metadata, method of representation, interpretation, and a readable part. Both HL7 and FHIR are actively applied in health protection system development, but more and more companies switch to FHIR.
More Data Standards to Keep in Mind
ICD-10, EVV, XDS/XDS-I are other measures one can stick to to make software more secure. Here are some details:
- The ICD-10 was designed to create an infrastructure capable of crafting a medical system where hospitals, labs, and pharmacies can safely share the patient’s information. This disease categorization coding system was suggested as an update to the 9th edition of the international classification of diseases. This version has more categories.
- XDS was designed to interpret how medical entities must share healthcare data with staff. The patient’s info is retrieved from the source system. The primary idea of this approach to cross-enterprise doc sharing is that the healthcare docs are indexed in a registry with various attributes. A professional who demands access to a certain file has an opportunity to look through the index and get/use the required data. Then, there is another version, XDS-I. It is actually an extension for sharing pictures instead of textual content. Retrieving images of the full quality happens safely right from source PACS to the workstation.
- EVV stands for electronic visit verification. The app should check the service name, patient’s name, location, date and time, etc. In other words, collect everything about the visit. It is mostly used for home visits. GPS tracking tools usually help with such checks and data collection.
Thanks for the Diagnosis, but What Is the Treatment?
Of course, some work should be done to improve the privacy of patient data. It’s quite possible that the rapid development of healthcare technologies will eventually leave security somewhere by the wayside. With PHI slowly becoming “digital gold,” the focus on information privacy will only increase in the coming years. Are we doing enough to keep up?
How To Develop Secures Healthcare Software?
Efforts by federal and privatized health care institutions are paying off, so it’s likely that data security practices will continue to evolve and improve. It’s important to note that organizations should try to get the attention of both employees and their patients.
Remember that we all have a responsibility to be educated about healthcare security. As we receive services, we must understand how our data will be used (and what might happen to it if it is leaked), as well as critically and carefully evaluate medical providers. By broaching the topic of privacy, we begin to cultivate respect for our data and make sure that healthcare is as much about care as it is about trust.
Overall, the good news is that the diagnosis is not fatal. It’s just that when you start working on an EHR, telehealth solution, healthcare compliance software, or any other compliance app, you must know the rules. Otherwise, you will need to assemble a team with the relevant experience or hire a software development vendor. Whereas in-house recruitment takes a lot of time, outsourcing enables you to initiate HIPAA compliant software development as soon as you find the right company. If you are interested in creating safe products and services for your users, send a quote to our team of experts so that we can help you.
AboutKosta Mitrofanskiy
I have 25 years of hands-on experience in the IT and software development industry. During this period, I helped 50+ companies to gain a technological edge across different industries. I can help you with dedicated teams, hiring stand-alone developers, developing a product design and MVP for your healthcare, logistics, or IoT projects. If you have questions concerning our cooperation or need an NDA to sign, contact info@intellisoftware.net.