You can think about data management strategy this way: picture navigating a ship through the boundless ocean of digital information without some kind of navigational chart. That sounds impossible, right? That is exactly what running a business without data management strategies might look like.
At IntelliSoft, we understand that data is not a set of numbers and text – it forms the foundation of strategic decision-making procedures. With our experience in software development and dealing with data-related solutions, we can help you navigate your complex maze of info processes, be it collection, organization, protection, or insightful use.
We have mastered the art of integrating seamless strategic data management systems that synchronize perfectly with business needs, ensuring every byte of data matters. Whether you look to patch gaps, eliminate redundancies, or enhance data efficacy, we have a solution.
Let’s dive in together and discover the data strategy definition, how can data management create value, and why a proactive, strategic approach to info management is essential for staying competitive in the market.
Table of Contents
Understanding Data Management and Its Crucial Role in Business Growth
So, what is a data management strategy? The data management approach is often seen as the backbone of a successful enterprise. It’s crucial for transforming raw info into valuable insights for strategic decision-making. This comprehensive discipline includes the practices and processes used to handle, safeguard, and utilize an organization’s information. Why is this important? When info is well-managed, it enhances business clarity and foresight.
Productivity Boosts Across the Board
Effective data management sharpens an organization’s efficiency. Organizing information meticulously reduces unnecessary information movement and streamlines operations, making critical info easily accessible. Such organizational efficiency boosts productivity and helps identify and address performance issues quickly, ensuring smooth business operations.
Cost Efficiency: Saving More Than Just Money
A robust big data strategy helps reduce redundant efforts and resources. It eliminates the need for repetitive tasks and redundant storage, saving on operational costs. This efficiency allows employees to focus on unique, value-adding activities instead of repetitive information-related tasks.
Agility in Responding to Market Changes
A company’s ability to adapt quickly is crucial. Well-organized data streamlines decision-making, enabling faster responses to market shifts and competitor actions. This responsiveness helps seize opportunities quickly and mitigate risks.
Enhancing Decision-Making Accuracy
The quality of information directly affects the quality of business decisions. High-quality, well-managed info provides a comprehensive view of the business landscape, leading to more informed and accurate decisions. On the other hand, poor info quality can result in misguided decisions that harm the business.
As we explore the components of info management further, remember its essence: treating information, not just as numbers, but as a strategic asset. This approach drives business growth and innovation. This foundational understanding positions companies like yours to harness the full potential of their data, turning info into a powerful competitive advantage.
Key Components of Data Management
Let’s discuss the building blocks of a sophisticated info management strategy. All types of data management play vital roles in shaping how information serves an organization’s goals. From architecture defining the blueprint to modeling crafting the finer details, these data management steps combine to transform raw info into strategic assets.

Data Architecture: Crafting the Blueprint for Data Utilization
The crucial role of data architecture is at the core of any information management strategy. This discipline is the foundation for how info is systematically collected, integrated, transformed, stored, and utilized across the organization. A data architect’s role is paramount. They are tasked with constructing a robust infrastructure that aligns info processes with broader business objectives.
Their responsibilities are extensive. They select optimal software and hardware solutions and decide on information storage deployment, whether cloud-based or on-premises. Additionally, data architects ensure that the designed system allows stakeholders easy access, which enables swift and efficient decision-making. This alignment ensures that the cloud data management strategy and architecture support enhances business operations, turning information into a strategic asset that delivers real business value.
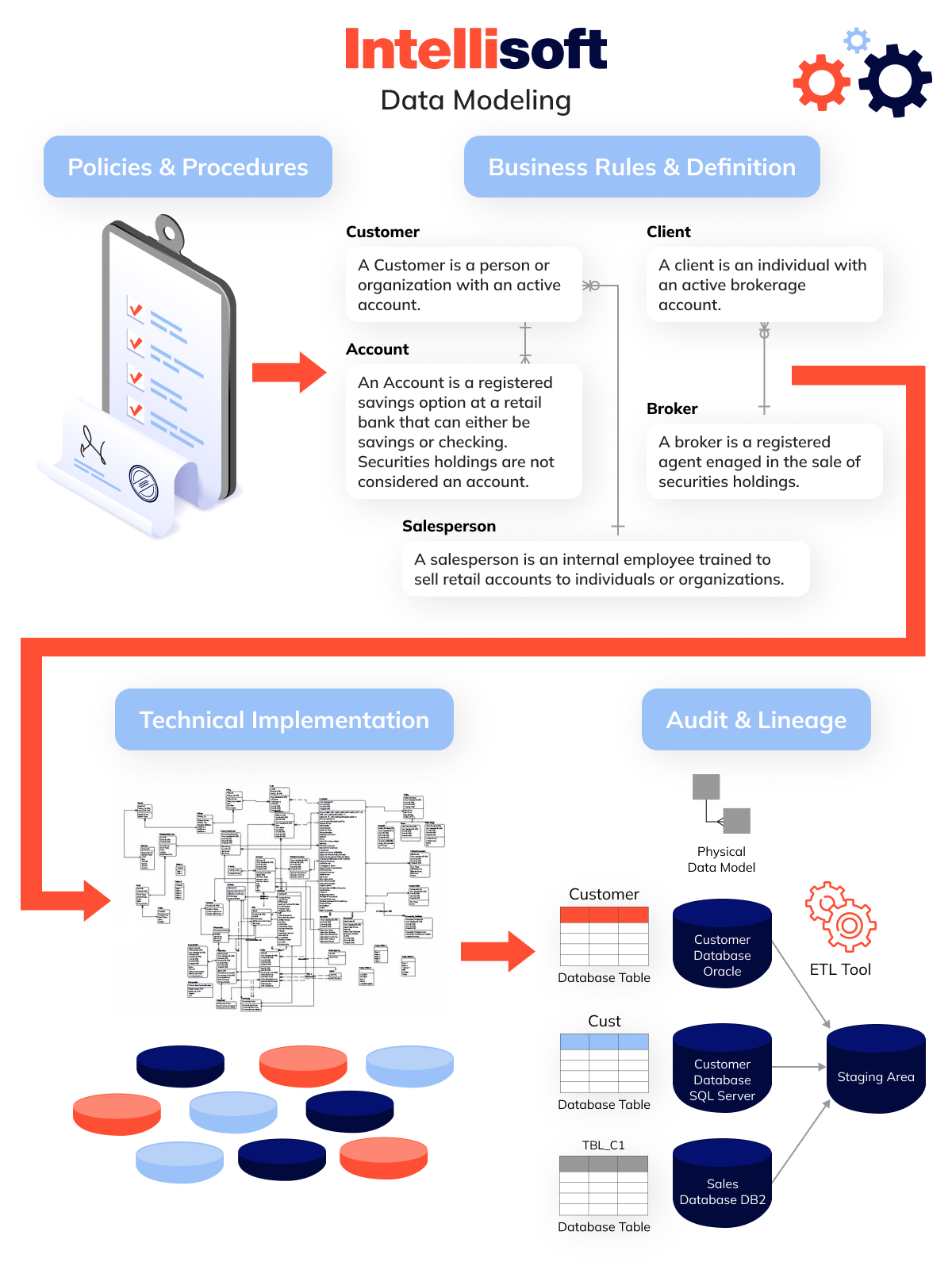
Data Modeling: Sculpting Information into Business Insights
Following the architectural framework set by data architects, the next pivotal component is information modeling. DAMA defines info modeling as the process through which information requirements are discovered, analyzed, represented, and communicated. Data modeling transforms abstract info into concrete models that reflect core business concepts such as products, customers, and their interrelationships.
Data modelers and scientists work closely with stakeholders to determine the most valuable info for the organization. They sculpt this information into well-defined models that accurately represent business entities and their attributes. These comprehensive models are conducive to efficient storage, retrieval, and sharing. This meticulous crafting of info models ensures that information does not remain mere numbers but evolves into meaningful assets, which can significantly influence business strategies and outcomes.
Database Administration: Ensuring Continuous Data Accessibility
Database administration is crucial in managing and maintaining an organization’s infrastructure—the databases. Database administrators handle various tasks to ensure information is always available and accessible. They monitor database performance closely, making necessary adjustments to optimize data access strategy and query response times.
Their duties include designing the database architecture, implementing updates, and maintaining strict information security measures. They automate many tasks using sophisticated Database Management Systems, ensuring the database strategy remains robust, secure, and operational.
Data Integration and Interoperability: Unifying Disparate Data Sources
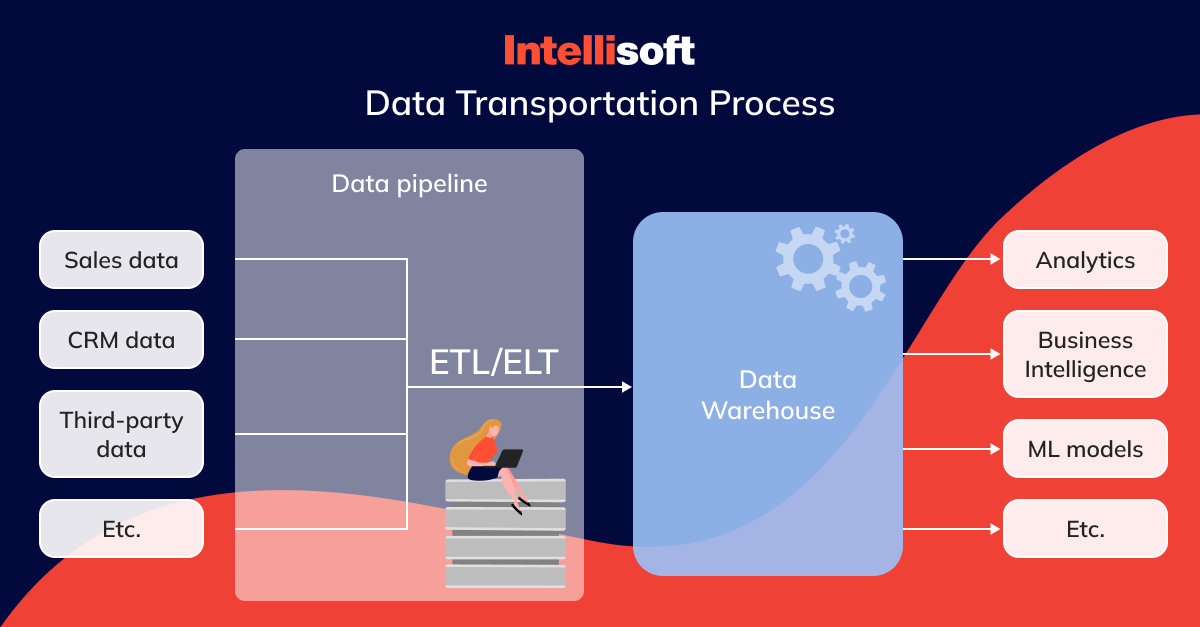
Today, information is often spread across various platforms and formats—from IoT devices and social media to CRM systems and e-commerce platforms. Data integration bridges these gaps, ensuring info from different sources can be consolidated into a coherent dataset.
This consolidation is vital for accurate analysis and reporting. Data architects, engineers, and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) developers play key roles here. They use ETL processes to batch, transform, and move information to a warehouse. Virtualization data management techniques then provide a unified view of the info, regardless of its original format or location, enhancing the system’s overall interoperability.
Data Analytics and Business Intelligence: Extracting Actionable Insights
Data analytics and business intelligence (BI) transform information into strategic assets. Specialists like data analysts, BI analysts, and scientists deploy tools to analyze vast datasets. These tools of data management help identify patterns and extract actionable insights for strategic decision-making and operational improvements. Business intelligence summarizes historical information and visualizes it in ways that prompt immediate action, enhancing current operational efficiencies.
Data analytics involves developing algorithms that delve deep into info to uncover hidden insights. This approach ensures well-informed decisions and protection against potential risks. Together, these practices empower organizations to leverage their information to enhance business outcomes significantly.
Data Quality Management: Sustaining the Integrity of Information
Data Quality Management (DQM) is vital for maintaining an organization’s overall information health and integrity. Led by information quality engineers, this continuous and proactive process involves careful observation, analysis, and improvement of info at every stage of its lifecycle. Instead of just fixing issues after they occur, DQM focuses on preventing problems from happening in the first place. This proactive approach ensures that info stays accurate, reliable, and ready for strategic use, effectively supporting the organization’s goals.

Information Security: Fortifying Against Data Breaches
Information security acts as a shield that protects an organization’s valuable information from unauthorized access and breaches. Data architects, security specialists, and database administrators work together to implement robust security measures. These include encryption, tokenization (which turns sensitive information into non-sensitive tokens), strict access controls, and advanced threat detection systems to identify network anomalies.
Regular backups are also crucial to prevent information loss. A comprehensive security strategy involves safeguarding info and managing its lifecycle carefully. You retain information only as long as necessary and securely dispose of it to avoid redundancy and archiving risks.
Data Governance and Master Data Management: Upholding Information Consistency and Efficiency
Data governance ensures consistent and efficient info use across an organization. Managed by data governance analysts, this practice sets the framework for info usage policies, processes, and standards that comply with legal regulations like the EU’s GDPR and California’s CCPA. An essential part of info governance is Master Data Management (MDM), which focuses on managing key enterprise data related to customers, products, staff, and other critical resources.
MDM works to eliminate data duplicities, inaccuracies, and inconsistencies, ensuring uniformity across various departments such as sales, customer service, and logistics. Effective governance and MDM prevent potential info misuse and ensure that all business units operate with a unified, accurate view of critical data, thereby avoiding internal conflicts and enhancing organizational efficiency. Explore all these types of data management to identify which methods best align with your business goals and enhance your strategic capabilities.
Related readings:
- Legal Requirements for Storing Data: Key Insights for Storing User Data
- Making Sense of Databases: How to Choose the Right One
- Vendor Management IT: Definition, Features, Advantages, and More
- Big Data Security Intelligence: What You Need to Know
- Top 10 Data Warehouse Software Tools for Your Business
Strategic Approaches to Building an Information Management Strategy
An effective information management strategy is crucial for organizations handling vast information. This strategy serves as a guide, ensuring all collected info aligns with and supports the business’s broader objectives. Let’s explore the foundational steps for crafting a strategy that addresses current needs and positions your business for future success.
Setting Clear Business Objectives
The first step in creating a robust big data strategy is to delve into your business objectives. What are your company’s core goals and challenges? Understanding these will guide the effective collection and utilization of information. Start by engaging with organizational stakeholders to gather insights and determine the critical areas where information can significantly impact. These collaborative efforts of data management help develop a focused strategy that acts as a compass, directing all efforts toward fulfilling the identified business objectives.
Pinpointing Information Requirements
Once your goals are set, the next step is to identify precisely what information is necessary to achieve these objectives. This involves determining whether you need internal or external information, structured or unstructured, or a combination thereof. When considering which statement is true about designing a data strategy, it’s essential to recognize that a well-designed strategy must be adaptable to evolving business needs and technological advancements.
Each type of information serves different purposes and may require a different data management methodology for collection and processing. By clarifying what information is essential, you can create a targeted approach for gathering it, ensuring that every piece of information serves a strategic purpose.
Establishing a Sustainable Information Processing Framework
With a clear understanding of the necessary information, the next stage involves setting up a structured framework for processing this info. This framework should provide a systematic approach to filling in any gaps in your current information. It includes outlining how each type of info will be collected, whether through direct methods like surveys and analytics or indirect methods such as purchasing from third-party vendors.
This structured approach simplifies the collection process and ensures that information management is sustainable and scalable, adapting to the business’s changing needs over time.
Establishing Robust Information Governance
As the volume of organizational information grows, establishing robust information governance becomes essential. This involves creating and enforcing policies related to quality, security, privacy, transparency, ethics, access, and ownership of information. These policies must be communicated across the entire organization, not just within specialized teams. Effective governance ensures that everyone in the organization understands and adheres to these guidelines, facilitating the efficient and ethical use of info.
Choosing Suitable Technological Tools
The backbone of any effective big data strategy is the technology that supports it. The right technological tools are vital for efficiently gathering, storing, and analyzing information. Organizations must carefully evaluate their technological needs against their strategic goals, selecting tools that enhance their ability to derive meaningful insights from the info collected. Ensuring these tools are powerful and compatible with the organization’s existing systems is crucial for seamless operations.
Cultivating a Knowledgeable Team
A successful information management strategy heavily relies on the skills and knowledge of the team handling it. Cultivating a culture that values continuous learning and information literacy across the organization is imperative. Leaders should provide opportunities for team members to enhance their understanding and skills in managing and utilizing info effectively. Organizations can maximize their strategy’s impact by fostering a team well-versed in information management principles.
Strategy Deployment and Adaptation
The final step in cementing your information management strategy is its implementation and ongoing adaptation. This phase involves identifying potential obstacles that delay the strategy and designating leadership roles to guide necessary adjustments. Monitoring the strategy’s effectiveness in real time allows for timely modifications in response to changing organizational needs or external factors. Continuously refining your approach ensures that the info management strategy remains aligned with the business’s goals and adapts to new challenges and opportunities.
Navigating Common Information Management Challenges
Certain challenges recur across industries in information management, impeding the seamless flow and utilization of organizational knowledge. Understanding these challenges is the first step toward crafting a robust management strategy that anticipates and mitigates potential setbacks.
Breaking Down Information Silos
One of the most significant hurdles in the data management process is the existence of silos within an organization. These silos occur when information is isolated within specific departments or systems, restricting access to other areas of the organization. Such fragmentation can severely hamper efforts to integrate various sources of information, making it challenging to achieve a holistic view of the enterprise’s knowledge assets.
Safeguarding Against Security Breaches
Security remains a paramount concern in managing sensitive information. Organizations must ensure robust protections are in place to shield their info from unauthorized access and cyber threats. This includes adopting stringent governance policies and deploying secure management software and platforms, which are critical in maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of information.
Integrating Diverse Information Systems
Another prevalent challenge is integrating disparate information systems, especially when legacy systems coexist with modern technologies. Achieving seamless integration requires a well-conceived architectural plan and efficient management platforms. Such integration is vital for maintaining consistent quality and availability of info across the enterprise.
Maintaining Information Quality
High-quality information is the cornerstone of reliable decision-making and operational efficiency. Establishing a meticulous data management process to ensure information accuracy, completeness, and timeliness is essential. Regular audits and standardized models are crucial in maintaining info consistency across the board.
Mastering Information Governance
Effective governance is key to successful information management. It involves defining clear roles and responsibilities, often under the leadership of a chief information officer. Governance ensures regulatory compliance, addresses privacy concerns, and establishes usage and storage standards, facilitating responsible info handling.
Choosing Between Decentralized and Centralized Management
Organizations face the challenge of choosing between decentralized and centralized information management approaches. A centralized method offers greater control and uniformity, whereas a decentralized approach allows for increased flexibility and quicker responsiveness. The most suitable structure depends on aligning with the organization’s strategic goals and each approach’s inherent value.
Need Help with Information Management Strategy Implementation?
Implementing an efficient corporate data strategy is crucial for any business aiming to maximize the value derived from its vast volumes of knowledge and insights. Recognizing and understanding your needs is the first step towards leveraging this strategy to drive your business objectives.
However, if you’re unsure how to craft an effective strategy or struggling with the complexities of info management, IntelliSoft is here to assist you. We specialize in engineering top-tier solutions that transform your information into your most valuable asset. Our expert team is dedicated to helping you structure, manage, and optimize your info to enhance operational efficiency and accelerate your business growth.
Don’t let the challenges of data management process hold your business back. Contact IntelliSoft today, and let us provide customized solutions that address your unique needs and challenges. We can turn your information into a strategic powerhouse driving your business forward.