Over the past 20 years, healthcare operations have seen revolutionary changes. In the past, access to healthcare information has been restricted, resulting in poor coordination and preventing healthcare practitioners from getting a clear picture of patients’ anamnesis.
Fortunately, with technological advancement, this issue has been solved. Nowadays, there are new standards such as HL7 and FHIR that reduce the cost of care, improve healthcare effectiveness, and allow exchanging healthcare data freely and securely. HL7 has developed standards for the transfer, retrieval, and interpretation of data, including V2 and V3, and FHIR.
Even though FHIR can be considered a part of HL7, these two standards are quite different. At IntelliSoft, we have 15 years of experience in the healthcare industry, and we’re ready to introduce a detailed comparison of HL7 vs FHIR so you can choose the best and more effective option for your healthcare organization.
Table of Contents
HL7 vs FHIR: What is Their Role in Medicine?
Revenue in the digital healthcare market is expected to reach $170.20bn in 2023, since the majority of healthcare organizations are digitizing and automating their operations with the help of advanced software solutions. In fact, if you want to release an IT solution for healthcare, it should comply with these factors:
- User-friendly interface for patients and healthcare practitioners
- Have GDPR, HIPAA, ICD-10, XDS, XDS-I, and EVV certifications
- Implement FIHR or HL7 protocols and be FHIR or HL7 compliant
The reason why digital healthcare solutions should implement these protocols is that they facilitate information sharing, provide support for mobile apps, and support use cases that benefit patients and providers. Most importantly, these protocols facilitate healthcare interoperability – the ability of healthcare systems and devices to exchange, integrate, and use data in a coordinated manner within an organization.
If you want to find a reliable provider for implementing these protocols, you need to learn about their key features and differences first.
What is HL7?
HL7 V2 was released in 1989. Back then, it was the one and only healthcare standard, and the majority of healthcare companies applied it. In 2005, its next version was released. It was an updated version with more capabilities, and it was supposed to deal with V2’s drawbacks. There are also two other versions: CDA and FIHR.
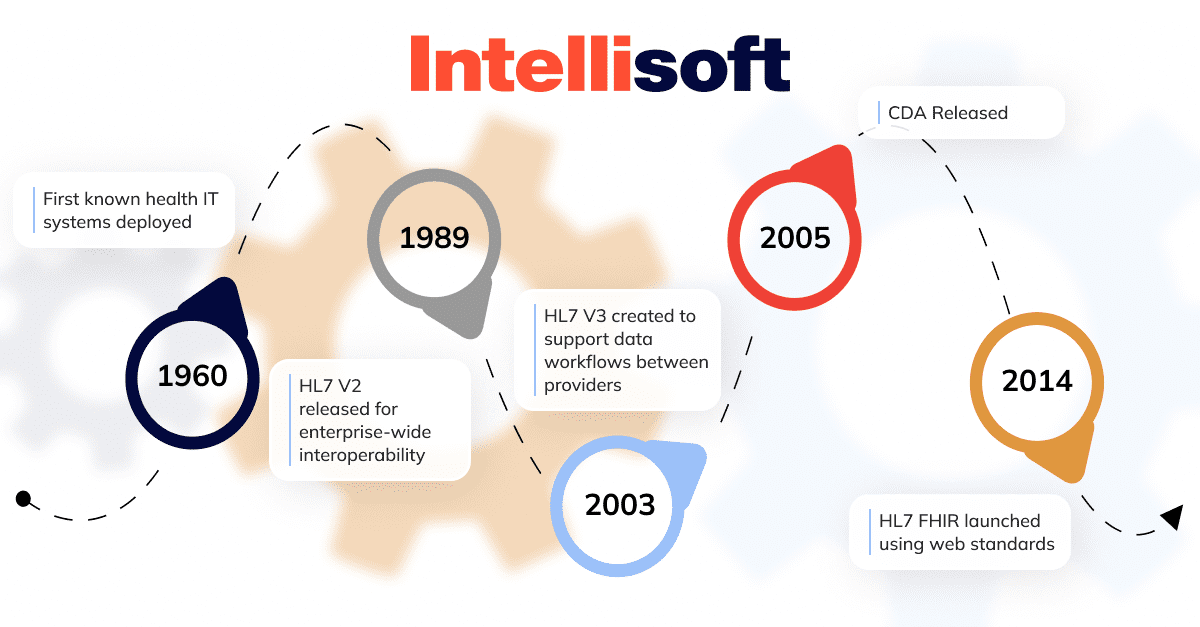
In its essence, Healthcare Level Seven is an app layer of the ISO model used to interchange data between systems, applications, and software solutions. The standards of HL7 are meant to minimize administrative issues and rather focus on the quality of healthcare delivery.
HL7 has helped healthcare practitioners establish clear and easy communication between various applications they use, including apps for billing and keeping patient information.
HL7 V2
HL7 V2 (Healthcare Level Seven Version 2) allows seamless communication between various systems in a healthcare organization. According to the official HL7 website, 95% of US healthcare organizations use V2.x, and more than 35 countries have such implementations.
Let’s take a look at V2 technical characteristics:
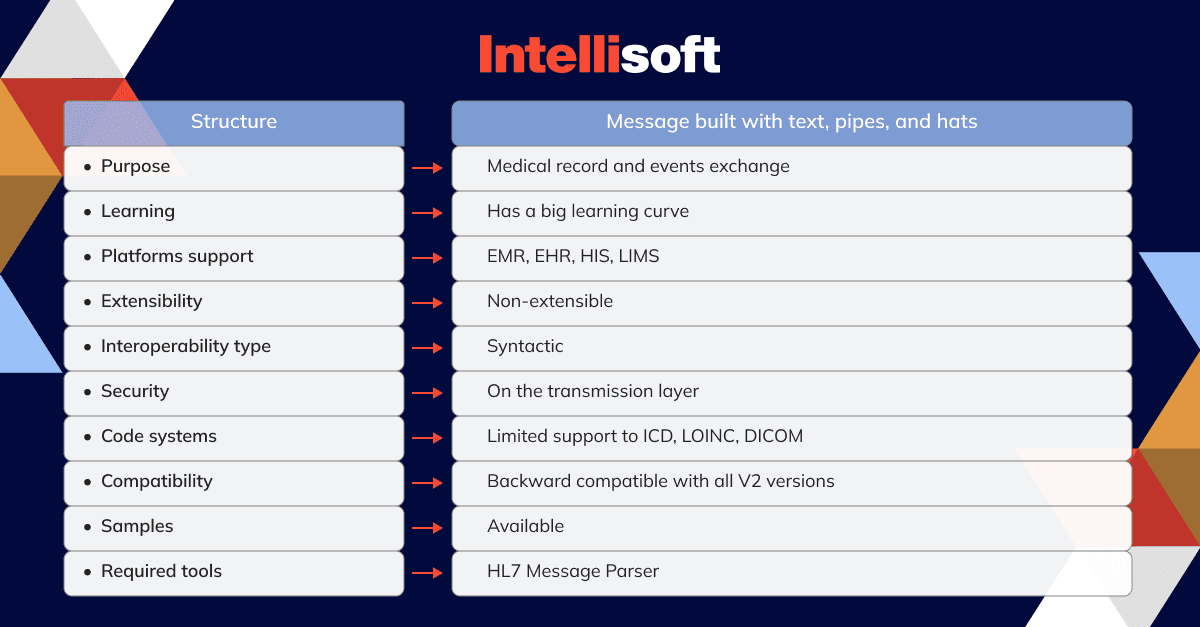
When to use HL7 V2?
V2 is used to transfer data between systems. The types of data can include observation results, medical prescriptions, financial transactions, measurable results, and so on. It is a great option for communication between systems that have no option of storing data in databases. The reasoning for it lies in the type of V2 message, which includes the following segments:
- The Message Header (MSH): a mandatory segment that includes data about the sender and the recipient.
- The Patient Identification (PID): includes demographic data of a specific patient (name, date of birth, location). This segment is also mandatory.
- Patient Visit (PV1): includes information about patient visit details, such as time, visit ID, caregiver, and servicing facility.
- The Observation Request (OBR): allows the identification of the observation ordered for Observation Result message generation.
- The Observation Result (OBX): an optional segment that includes data about the observation result.
- Clinical Trial Identification (CTI): links the result to a clinical trial. This is also an optional segment that contains information about the clinical trial identification information and phase of the study.
This messaging type works for transmitting data between systems in one organization, and it’s impossible to scale it across multiple organizations.
HL7 V3
After the success of V2, the requirements for data transmission continued to grow, so there was a desperate need for a more comprehensive messaging standard. That’s when V3 was introduced. It is based on a common Reference Information Model (RIM) – a universal reference model for all data that needs representation in the healthcare sector.
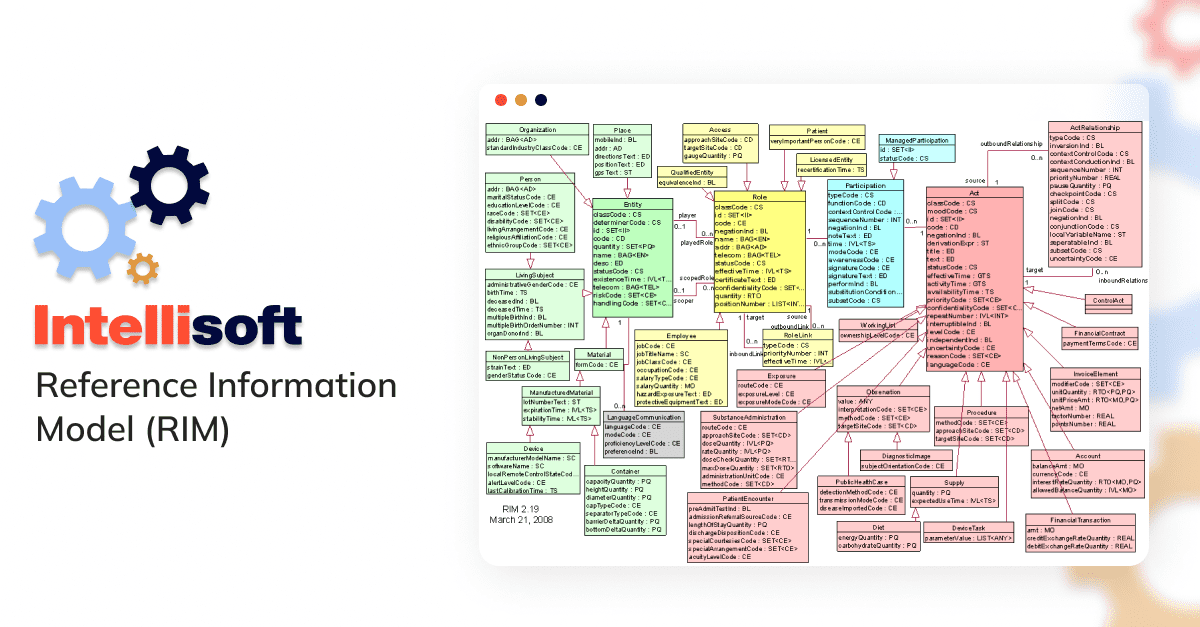
All users of HL7 V3 need to implement RIM, making the implementation process rather complicated and more expensive.
Let’s consider the technical characteristics of HL7 V3:
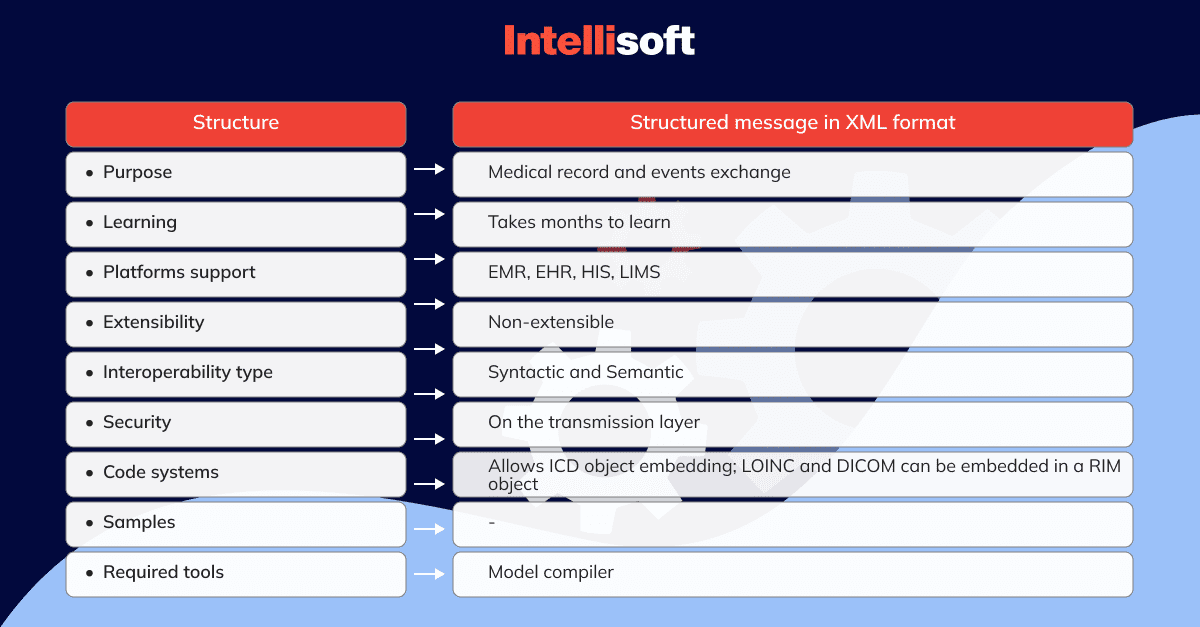
When to use HL7 V3?
If your data exchange requirements can not be met by V2, then it’s time to switch to V3. It covers the same use cases as the previous version and even more, yet it makes V3 an extremely complex and costly option.
HL7 CDA
The Clinical Document Architecture (CDA) is a tool for establishing a uniform structure and communication format for clinical records. It facilitates the seamless exchange of vital patient information among different entities engaged in healthcare delivery. Typically employed for inter-organizational data sharing, this documentation system ensures the efficient transfer of crucial medical data between relevant stakeholders.
CDA defines the following characteristics for all clinical documents:
- Persistence
- Stewardship
- Potential for authentication
- Context
- Wholeness
- Human readability
Here are the technical characteristics of CDA:
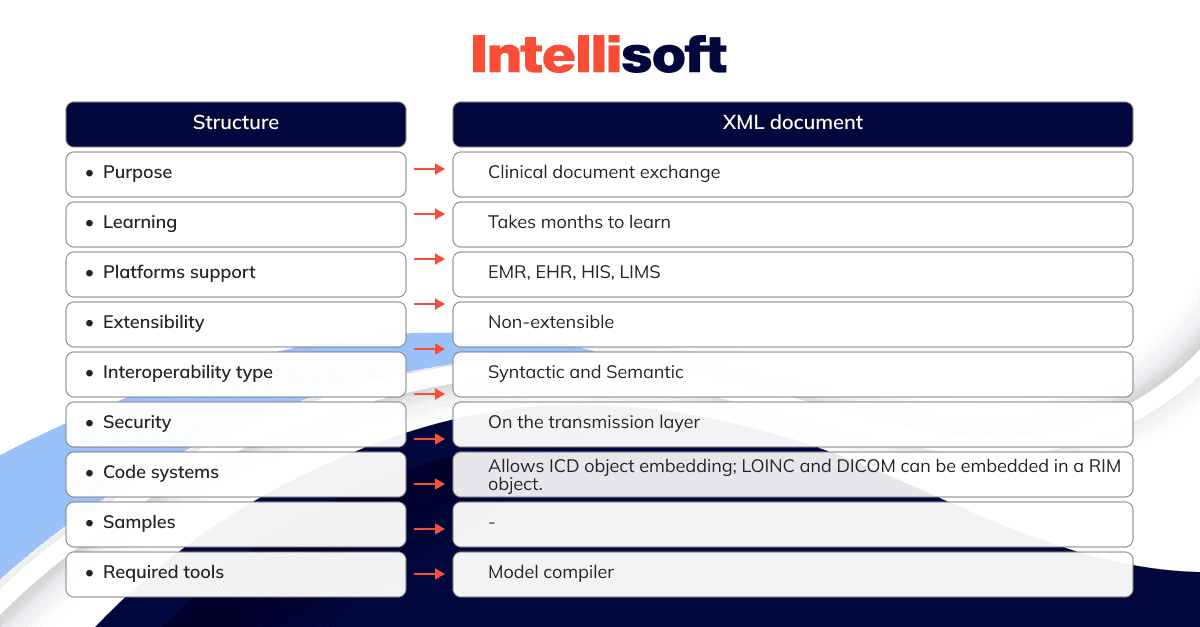
When to use CDA?
CDA is used to exchange patient data. Typically, CDA text includes sounds, text, images, and other types of content. CDAs are used in clinics, hospitals, and other types of healthcare organizations. A CDA document can be any of the following: a referral, discharge summary, clinical summary, physical examination, prescription, diagnostic report, and so on.
What is FHIR?
FHIR was introduced by HL7 as a part of a new variant of health data standards included in V2, V3, and CDA. The goal was to make the development of IT solutions that address interoperability challenges faster and simpler.
FHIR supports the RESTful API approach. REST is an exchange standard that defines operations like create, read, update, delete, and more. Thus, REST APIs make the process of data migration between servers simpler, improving the standard’s scalability.
The main benefit of FIHR is that it is based on all the previous models, including their best features, yet fixing their issues. It is not limited to supporting current markings and types of documentation. On the contrary, it is super versatile when it comes to information processing. Moreover, its previous version could not provide full interoperability.
What are FHIR Resources?
FHIR resources are small units of exchange that define behavior and meaning, have a specific location and identity, are the smallest unit of transaction, and provide meaningful data for healthcare practitioners.
It is possible to extend and adapt resources to provide more manageable solutions if your organization requires more customization and optionality.
Let’s take a look at resources examples:
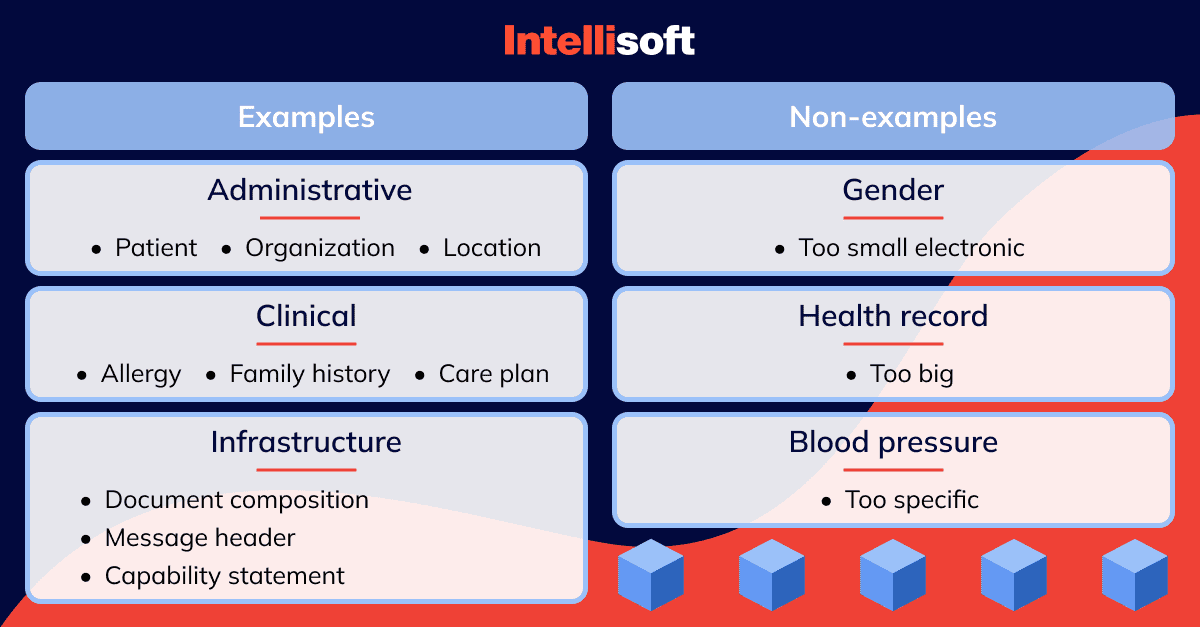
Why adopt FHIR?
The reasons for adopting FHIR are innumerable: it simplifies implementation, facilitates information sharing, and helps support mobile apps. Moreover, it is super beneficial for all parties: patients, payers, and providers.
This standard makes the process of decision-making faster and easier by allowing clinicians to exchange patient data among teams. It is also possible to grant patient access to their health data via user-friendly apps that operate on smartphones, wearable devices, and tablets.
When to use FHIR?
It can cover all the most common use cases in healthcare. It can be used to exchange lab test results, scans, clinical letters, and other documents essential for patient treatment.
It is commonly used for health data exchange, EHR (electronic health record) integration, in mobile health apps, clinical decision support, research and population health management.
Related readings:
- The Internet of Things (IoT) in Health Care
- How Artificial Intelligence innovate the healthcare industry
- The Quality Management System (QMS) for medical device startups
- A Step-by-Step Guide to Developing HIPAA-compliant Medical Apps
- What Technologies Are Driving the Health Protection System?
Core HL7 and FHIR protocols
Both HL7 and FHIR standards transmit data between systems based on the rules set by their protocols. The main protocols include:
OSI Layer 7 Protocol
This protocol provides application services for network software based on HTTP, SMTP, and other level 7 protocols. It keeps the content and format of the data exchanged and doesn’t have any connection with the type of transmission between the apps.
Event-Driven Protocol
An event-driven protocol is used when there’s a healthcare event that requires the exchange of information between systems/applications. These events can include when a patient is admitted to a facility or when a doctor issues a prescription to the pharmacy. An app then captures this event and exchanges data with other systems that might need it.
Application to Application Protocol
This protocol’s goal is to ensure communication between two independent apps that aren’t client-server-type applications. The role of each application does not matter; what matters the most is the type of message they share.
Standard Protocol
For the two applications to exchange information, they need to be connected by a non-standard link. That’s what standard protocol does: it facilitates link-building and helps prevent data exchange problems when connecting to a third-party system.
Exchange Protocol
Exchange protocol defines how applications will transfer their data to one another. In this case, data processing and storage do not matter. The database structure should match HL7 message definitions, but this is also not mandatory.
FHIR and HL7 Similarities
Both standards belong to the family of standards created by Health Level Seven International. Thus, there’s no real winner when choosing between the two because both standards will help you with the same interoperability tasks.
Yes, FHIR is the latest version of standards, relying on the best features of its predecessors. Moreover, it fixes bugs and issues that couldn’t be fixed by V2, V3, and CDA. Overall, it is a more modern version, but it doesn’t mean that previous ones should be overlooked. In fact, they still have a lot of similarities, so let’s go through them.
Built around reusable “chunks” of code
All standards developed by Health Level Seven International provide developers with resources to achieve interoperability in healthcare systems. Thus, all developers have reusable parts of code that allow them to build systems faster.
Forward/backward compatibility
Both standards are backward/forward compatible. Backward compatibility is when readers with a new schema can extract data from an older schema without any issues. Forward compatibility is when a reader with an older schema extract data from a newer schema. Being forward/backward compatible allows HL7 and FHIR to use interfaces and data from different versions, reducing investment in hardware and software for the company.
Extensibility mechanism
Both allow you to extend existing systems by adding new features or modifying current ones. A lot of healthcare systems require constant changes, so this mechanism is a must for them.
HL7 vs FHIR: Main differences
As we have already discussed, FHIR and HL7 have some similarities, but due to the different underlying development technologies, they are more distinct than similar. FHIR relies on RESTful web services and open web technologies such as JSON and RDF data formats. The majority of developers are familiar with these technologies, making the development process faster.
Now, let’s go through the main differences between the two.
Architecture
FHIR uses RESTful APIs, allowing it to handle large amounts of data from various interfaces without any bottlenecks. On the contrary, HL7 is based on messages, fields, and records.
Extensibility
Medical data and technologies are constantly changing and evolving, making it essential to add new features to information standards to meet growing requirements. With FHIR, it is possible to use new features and extensions because it is interoperable. HL7, on the contrary, is not interoperable.
Security
HL7 secures patient data through transport layer security. FHIR does it through the transport layer security and SSL, and it also has an authorization protocol for secure data exchange between healthcare professionals and patients.
Platforms
Unfortunately, HL7 was not created taking into account modern technological solutions, so its platforms are limited to HIS, EMR, and EHR. FHIR, however, it supports both these platforms and mobile apps and wearable IoT-enabled devices.
Use cases
Since FHIR is more advanced than HL7, its use is not limited to EHR and EMR. It allows for the free flow of information across all partners and sources. For example, FHIR can be used on wearable devices and mobile health apps, and Apple Watch is a great example. It collects data about blood pressure and heart rate, and it can be shared with a doctor for effective health monitoring. HL7, on the contrary, is only used to exchange data among health organizations.
Reliability
FHIR is considered to be more reliable since it has specific resources that handle specific data. HL7’s reliability is impacted by its multiple option columns.
Human readability
With FHIR, all the data shared is human-readable. V2 does not support human-readable versions of the shared data.
Accessibility
FHIR is free to use for developers since they don’t need a login. Moreover, there are no exchange protocol restrictions. RESTful APIs also make it easier to use FHIR than HL7.
HL7 vs FHIR: A Comparison Table
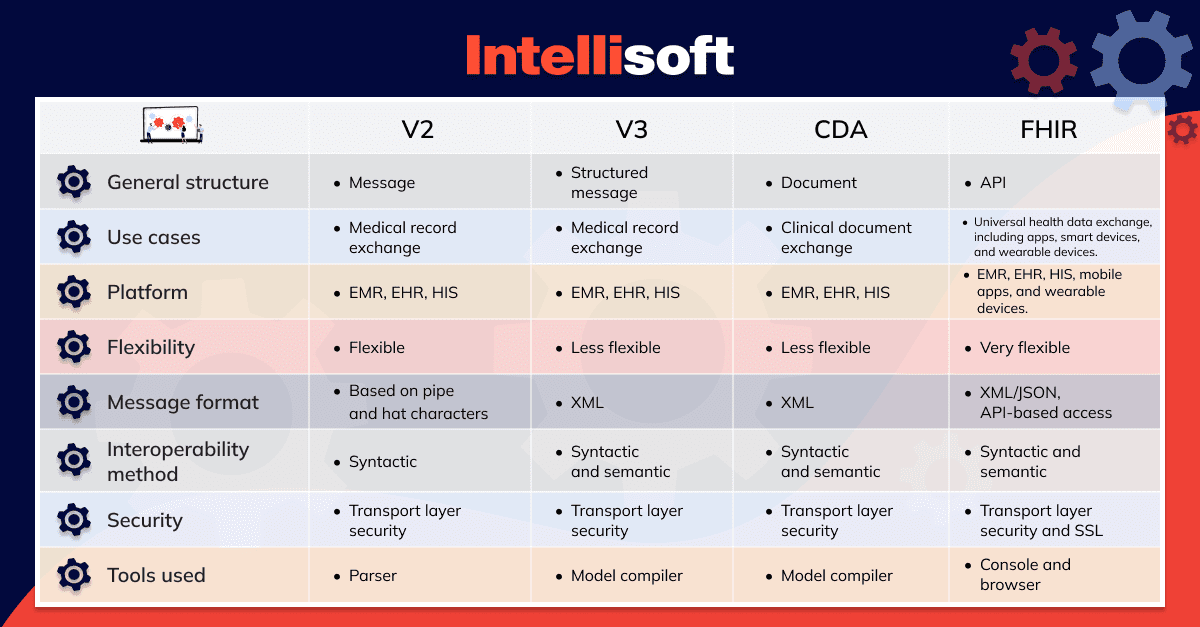
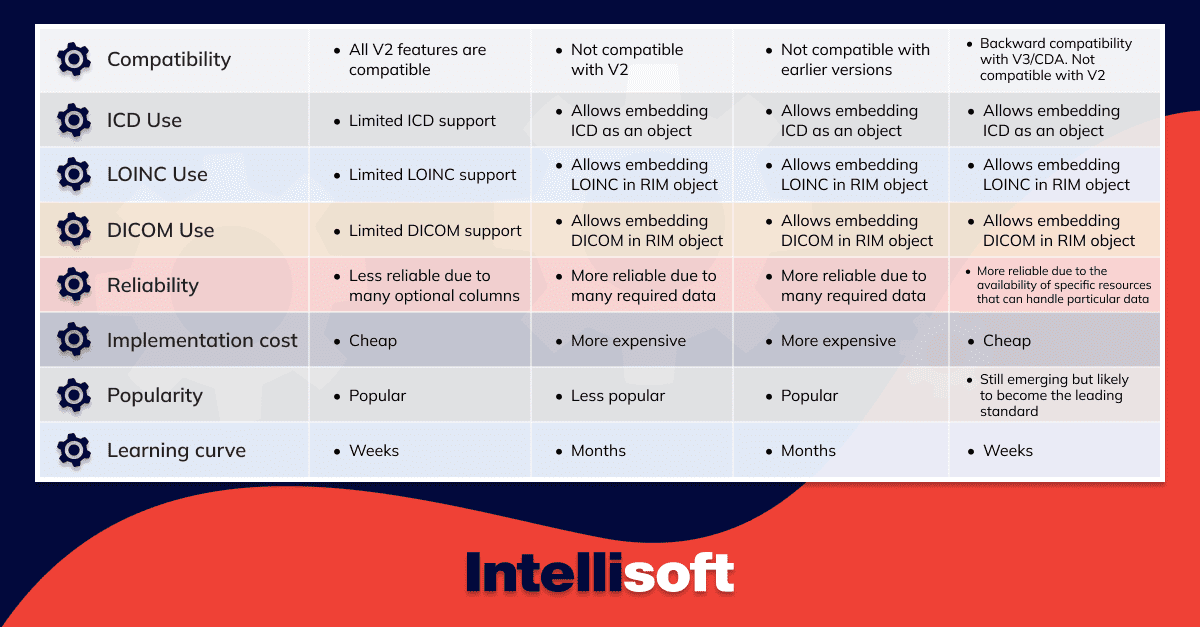
Which One Should You Select?
Choosing between FHIR and HL7 is not a win-or-lose situation. The choice here depends on your existing system and your requirements. Since FHIR is the most recent version, and it includes major improvements of V2 and V3, it makes FHIR a preferable option for many healthcare institutions. Let’s look at the advantages of FHIR.
Advantages of FHIR include:
- More tools for flexible development: FHIR allows developers to create a system that meets any client’s needs. Moreover, RESTful API makes FHIR compatible with mobile apps, which is essential for quick and easy data exchange. FHIR also supports all data formats used in standardization.
- Free access: It doesn’t matter what resources you need to implement FHIR; they are all available for free, making the implementation low-cost.
- Easy implementation: FHIR is not as complex as its previous versions. It covers more areas, so it’s easier to achieve interoperability, and most developers know how to use JSON and RDF data formats.
- Increased security: FHIR is super secure, so you don’t have to worry that patient data will leak anywhere and get into the wrong hands. Moreover, with FHIR, both patients and administrators have control over the data, and it is available to them through a mobile app.
Conclusion
At first sight, it might seem that HL7 and FHIR are almost the same. Indeed, they are just different versions of the same standard. However, keeping up with the developing technologies and new information-sharing requirements in healthcare is the key to ensuring effective operations and patient care.
In this respect, it is a better choice to stick to the latest version – FHIR. It is easy to implement and has more tools for flexible and secure development. If the choice seems too complex for you or you need a trusted partner to help you develop an action plan, look no further; just contact us.