As the CEO of IntelliSoft, I’ve had a front-row seat to the incredible shift technology is bringing to healthcare. The transformation we’re seeing isn’t just about adopting new medical software programs; it’s about fundamentally reshaping how care is delivered, managed, and experienced. From hospitals using software to streamline patient management to wearable devices that empower individuals to monitor their own health – technology is making healthcare more connected, efficient, and accessible than ever before.
Today’s healthcare professionals face a rapidly changing environment. Rising patient expectations, growing demand for remote diagnostics, and an explosion of data mean medical organizations must adapt or risk being left behind.
Smartphones, wearables, and apps are no longer optional tools—they are essential components that help doctors, nurses, and administrators work smarter. For patients, these medical office software programs simplify care and make medical support just a few taps away.
At IntelliSoft, we see this evolution as more than just progress; it’s an opportunity to improve lives. We help healthcare providers embrace great medical coding software programs that enhance patient care, reduce administrative bottlenecks, and stay competitive in a dynamic market.
The result? Health services are not only more accessible but also more personal and efficient.
In this article, I’ll walk you through the main types of medical software, a list of medical office software programs, and show you how hospitals and clinics are using them to meet the challenges of modern healthcare.
Whether you’re a provider looking to adopt new systems or just curious about how technology is shaping the future of medicine, you’ll find practical insights that shed light on this exciting transformation.
Table of Contents
Healthcare Goes Digital: Adoption of Medical Software Programs
Healthcare is experiencing a digital revolution, reshaping everything from patient consultations to hospital workflows.
As technology becomes embedded in every step of the care journey, healthcare providers are increasingly adopting medical office software programs to meet rising expectations for efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility. This transformation isn’t just about keeping up with trends —it’s about meeting the demands of modern medicine with tools that make care smarter, faster, and more patient-centric.
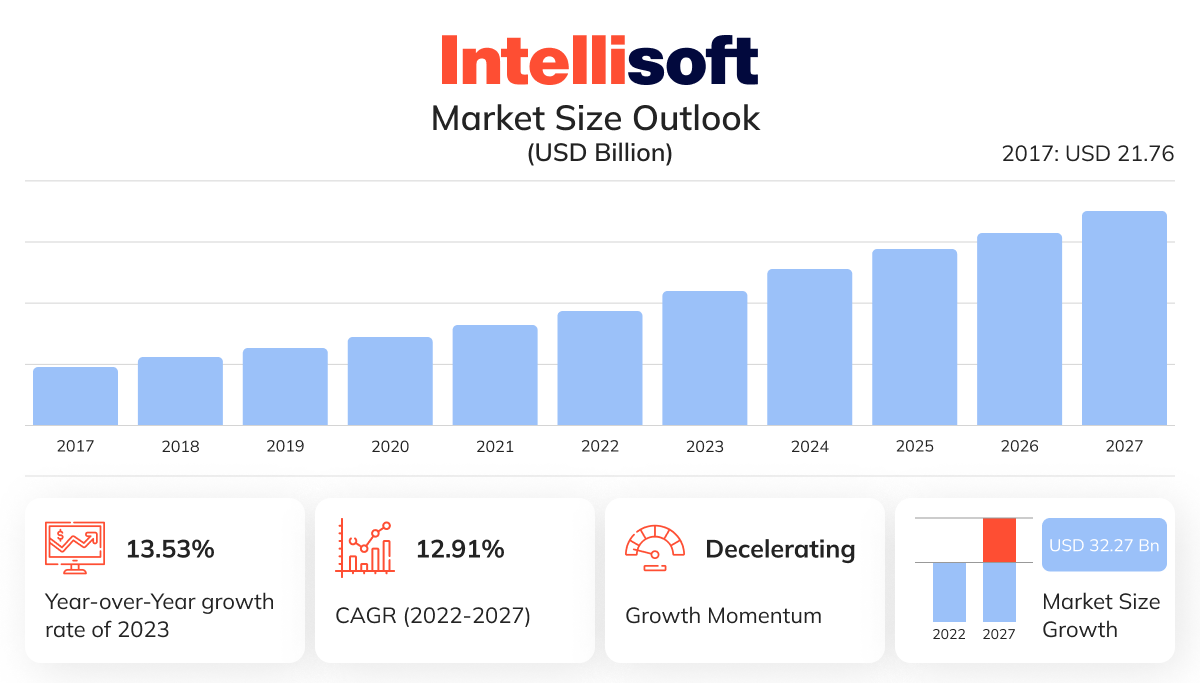
A striking example of this shift is the Electronic Health Records (EHR) market. According to a Technavio report, the market is projected to grow by USD 32.27 billion between 2022 and 2027, with a 12.91% compound annual growth rate (CAGR). This surge reflects more than a preference for digital tools – it’s a response to the need for better care coordination, streamlined processes, and reduced human errors.
Yet EHRs are only one part of the broader digital landscape:
- Telemedicine platforms bridge the gap between doctors and patients, making healthcare accessible from virtually anywhere.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) tools help analyze medical data faster, offering more accurate diagnostics and personalized treatment plans.
- Wearables and Internet of Things (IoT) devices enable continuous health monitoring, empowering patients.
Most Popular Types of Software in Healthcare Industry
As healthcare providers strive to improve patient care, streamline operations, and stay competitive, medical software programs are playing a crucial role in every aspect of medical services. Below is a detailed look at the most popular types of healthcare software, a medical software programs list, how they function, and their real-world applications.
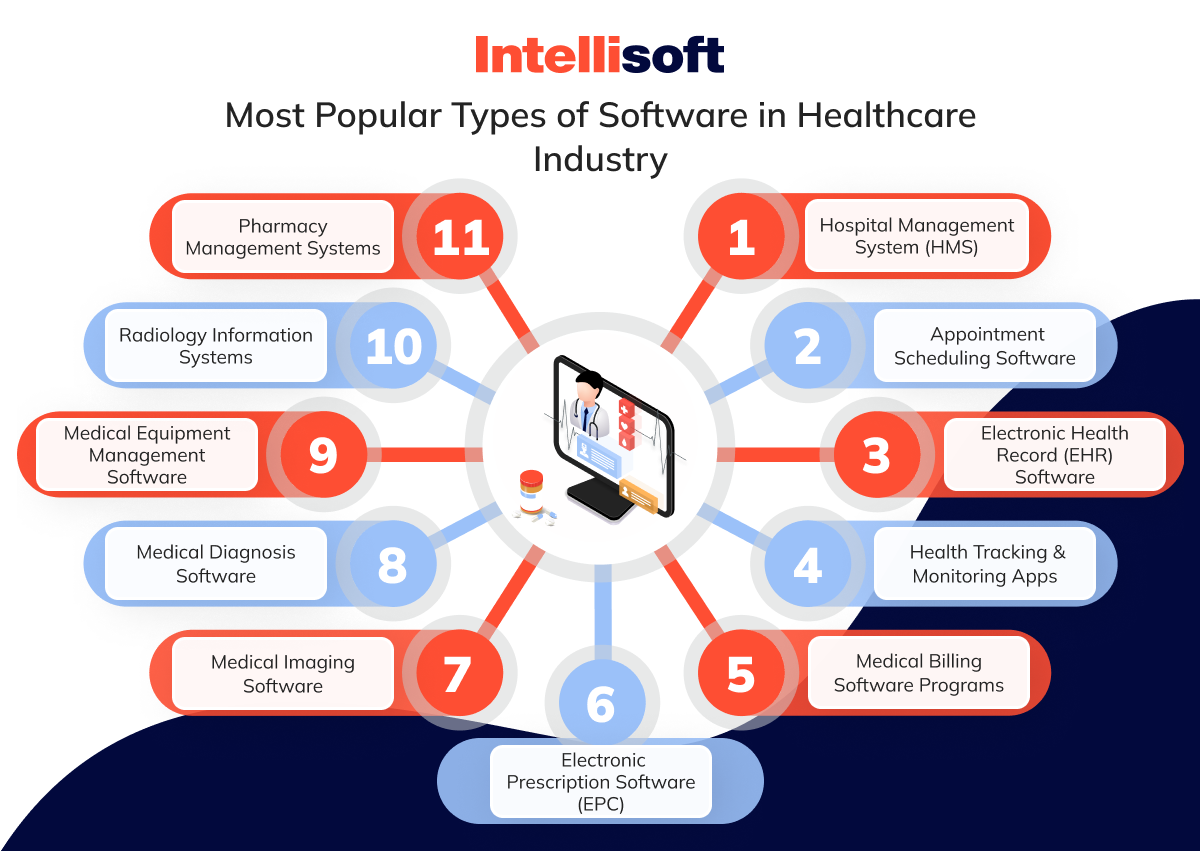
Hospital Management System (HMS)
HMS software serves as the backbone for large healthcare institutions, helping them manage everything from patient records to staff scheduling and inventory. Hospitals rely on these tools to integrate administrative, financial, and clinical functions, creating a unified platform to handle day-to-day operations.
For example, Mediware Hospital Management System allows staff to manage admissions, discharges, and patient history with ease. HMS systems also help track the availability of medical equipment and beds, reducing bottlenecks and ensuring optimal resource allocation.
Appointment Scheduling Software
Gone are the days of long wait times at the doctor’s office. Appointment scheduling software programs for medical offices simplify the process for both patients and healthcare providers by offering online booking portals, automated reminders, and real-time availability updates.
Zocdoc is a great example of medical appointment scheduling software programs – it allows patients to book appointments directly with providers, view wait times, and receive reminder notifications. For clinics, this software reduces no-shows and ensures more efficient scheduling.
Electronic Health Record (EHR) Software
EHR software centralizes a patient’s medical history, including lab results, prescriptions, and treatment plans, making this information easily accessible to healthcare providers. With seamless sharing between doctors, specialists, and hospitals, medical records software programs improve coordination and reduce duplication of tests.
Medical office computer software programs like Epic and Cerner are widely used in hospitals to manage patient data, ensuring physicians always have the latest information at their fingertips. This makes patient care more personalized and reduces the risk of medical errors.
Health Tracking & Monitoring Apps
From chronic disease management to fitness tracking, medical software programs empower patients to take charge of their health. They monitor metrics such as blood pressure, glucose levels, or sleep patterns, providing insights for both patients and healthcare providers.
Apple Health and MyFitnessPal are well-known examples, giving users real-time access to their health data and progress. Some apps integrate with wearable devices like the Apple Watch or Fitbit, allowing continuous monitoring and early detection of potential health issues.
Medical Billing Software Programs
Medical billing software programs simplify the complex process of managing insurance claims, patient payments, and reimbursements. Medical billing and coding software programs reduce administrative errors and ensures providers are compensated accurately and promptly.
Software like Kareo allows healthcare practices to submit claims electronically, check insurance eligibility, and track outstanding payments, all in one platform. This type of software is crucial for maintaining financial health in medical institutions.
Electronic Prescription Software (EPC)
EPC software eliminates the need for handwritten prescriptions, reducing the risk of errors and fraud. It allows doctors to send prescriptions directly to pharmacies, ensuring patients receive their medications quickly.
With platforms like DrFirst, physicians can check drug interactions, recommend alternatives, and monitor prescription history to avoid conflicts, enhancing patient safety. EPC systems also improve adherence to treatment by streamlining the refill process.
Medical Imaging Software
Medical imaging software processes images from MRI, CT scans, and X-rays, allowing radiologists to analyze and share results more efficiently. These tools provide 3D visualizations, image enhancement, and diagnostic tools to detect abnormalities early.
For instance, OsiriX is a popular imaging software used by radiologists for quick access to high-resolution scans, helping physicians make timely and informed decisions.
Medical Diagnosis Software
AI-powered diagnosis software assists healthcare providers by analyzing patient symptoms and suggesting possible conditions. This software helps improve diagnostic accuracy and speeds up treatment planning.
Platforms like Ada Health use AI algorithms to guide patients and doctors toward the right diagnosis by considering a range of symptoms and patient history, acting as a powerful decision-support tool.
Medical Equipment Management Software
Managing medical devices and equipment is critical in hospitals to ensure functionality and compliance. These medical management software programs track maintenance schedules, repairs, and inventory levels to prevent downtime and safety risks.
Medical device maintenance software programs like TMA Systems monitor equipment usage, send alerts for maintenance and ensure everything is in top working order, reducing equipment failures during critical moments.
Radiology Information Systems
RIS software focuses on managing radiology workflows, from scheduling imaging tests to generating reports. It integrates with PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems) to provide access to imaging results and reports in real-time.
Software such as Carestream RIS enhances communication between radiologists, technicians, and referring physicians, ensuring quicker diagnostic results and better patient care.
Pharmacy Management Systems
Pharmacy management software streamlines the entire medication supply chain, from tracking inventory to ensuring compliance with regulations. These systems help prevent medication shortages and reduce errors in dispensing.
A system like PrimeRx helps pharmacies manage prescriptions, monitor stock levels, and automate refills, ensuring patients get their medications without delay. It also integrates with EPC systems to streamline the prescription-to-dispense process.
How to Choose the Best Medical Software Program?
Selecting the right software programs used in medical offices is crucial for healthcare providers, as it directly impacts patient care, operational efficiency, and overall success. With countless solutions available, it’s essential to make an informed decision based on your organization’s specific needs. Below are key factors to consider to ensure the software you choose is the right fit.

Identify Your Needs and Goals
Before diving into medical documentation software programs options, clearly define your objectives. Are you looking to streamline patient scheduling? Improve billing accuracy? Enhance EHR accessibility? Understanding your priorities helps narrow down options and ensures the software aligns with your long-term goals. For example, smaller clinics may focus more on billing automation with the help of a list of medical billing software programs, while larger hospitals might need comprehensive hospital management systems (HMS) for resource tracking and patient management.
Consider Ease of Use and User Interface
Even the most advanced medical practice software programs won’t be effective if it’s difficult to use. A clean, intuitive interface allows healthcare providers to focus on patient care instead of wrestling with technology. Look for solutions that offer easy navigation, minimal learning curves, and mobile-friendly features, especially for on-the-go access in busy environments.
Ensure Compatibility and Integration
Healthcare providers often rely on multiple systems, such as EHR, billing, medical spa software programs, and appointment scheduling software. It’s essential that the new solution integrates smoothly with your existing software to avoid data silos and inefficiencies. For instance, an appointment scheduling tool that syncs with EHR records ensures seamless data sharing, reducing manual input and minimizing errors.
Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Medical software must comply with regulatory frameworks such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the U.S. and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe. Choose software from vendors who are transparent about their compliance measures, ensuring your operations meet legal requirements and protect patient confidentiality.
Security and Data Protection
Healthcare software handles sensitive patient information, making robust security essential. Look for software with encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security updates to protect against data breaches. Additionally, the software should offer role-based access controls to ensure only authorized personnel can view or modify patient data.
Scalability
As your healthcare practice grows, so will your software needs. A scalable solution ensures that you won’t need to switch platforms down the line. Whether you plan to expand to multiple locations or introduce new services like telemedicine, the software should adapt without compromising performance.
Cost and Budget
While it’s tempting to opt for the most feature-rich solution, it’s crucial to balance medical billing software programs cost with functionality. Evaluate whether the software fits your budget, including implementation costs, licensing fees, and ongoing maintenance expenses. Some vendors offer subscription models, while others may charge a one-time fee—choose the pricing structure that aligns with your financial plan.
Customer Support and Training
Even the best software can have technical issues. Reliable customer support ensures you get timely assistance to resolve problems without disrupting operations. Also, ensure that the vendor provides comprehensive training and onboarding for your staff. Well-trained users are more likely to fully leverage the software’s capabilities, improving your return on investment.
Vendor Reputation and Reviews
Research the vendor’s reputation by reading user reviews and industry reports. A company with positive feedback is more likely to offer reliable products and excellent service. Consider asking for recommendations from peers in the healthcare industry who have experience with the software you’re evaluating.
Free Trial or Demo
Many vendors offer free medical coding software programs trials or demos, which give you a hands-on experience with the software. Use this opportunity to test whether the platform meets your requirements and to gather feedback from your staff. Testing free medical billing software programs during the trial period ensures there are no surprises after implementation.
Customization and Flexibility
No two healthcare providers have identical needs. Look for medical coding software programs that offer customizable features, such as custom reporting tools or configurable dashboards, to match your workflows. Flexible software allows your organization to adapt to future changes in policies, technology, or patient needs.
Performance and Speed
In healthcare, delays can have serious consequences. Choose software with high uptime and fast performance, especially for mission-critical systems like EHRs or diagnostic tools. Software that lags or crashes can disrupt operations, cause frustration among staff, and negatively impact patient care.
Related readings:
- Automation in the Industry of Healthcare: Main Benefits for Business
- Medical Imaging Software Development: a Detailed Guide
- Hospital App Development: Innovate, Integrate, and Provide Better Care
- What Technologies Are Driving the Health Protection System?
- HIE Health Information Exchange: A Complete Guide
- AI Chatbots in Healthcare To Maximize Care Quality
Off-the-Shelf vs Custom Healthcare Software Development
Choosing between off-the-shelf and custom-built healthcare software is a critical decision for healthcare providers. Each option has its advantages and challenges, and selecting the right path depends on factors like budget, timeline, and specific organizational needs. Below is a closer look at both options to help you make an informed decision.
Custom Medical Software Development
Custom medical coding encoder software programs are designed specifically to meet the unique needs of your organization, offering unparalleled flexibility and control over functionality and features.
Advantages of Custom Software Development
- Tailored to Specific Needs. Custom solutions are built to address the exact requirements of your practice, ensuring that no unnecessary features clutter the system.
- Integration with Existing Systems. Custom software can seamlessly integrate with your EHR, billing, or appointment systems, creating a unified workflow.
- Scalability. As your organization grows, custom software can evolve with it, ensuring smooth expansion and adaptation to future requirements like new telemedicine services or regulatory updates.
- Improved Security. Custom-built systems can implement advanced security measures tailored to your needs, ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR.
- Competitive Advantage. Offering innovative and personalized patient services, such as AI-powered diagnostics, can set your organization apart from competitors.
Challenges of Custom Software Development
- Longer Development Time. Building software from scratch takes time, which might delay implementation.
- Higher Initial Cost. Custom solutions require significant investment in development and ongoing maintenance.
- Dependency on Developers. Your organization may need to rely on external developers or an in-house IT team for updates, bug fixes, and future upgrades.
Example: A large hospital network that wants an integrated HMS, telehealth platform, and pharmacy management system tailored to its unique workflows may choose custom software to ensure seamless operation.
Off-the-Shelf Healthcare Software
Off-the-shelf medical coding and billing software programs are pre-built and ready to use, making it a popular choice for organizations looking for quick deployment and lower costs.
Advantages of Off-the-Shelf Software
- Faster Deployment. Since it’s already developed, off-the-shelf software can be implemented almost immediately.
- Lower Upfront Cost. Pre-built solutions are generally more affordable than custom development. Many offer subscription models to spread the cost over time.
- Proven Reliability. Off-the-shelf products come with tested functionality and ongoing updates, ensuring that you get a stable, bug-free experience.
- Customer Support and Documentation. Vendors typically provide robust support, user manuals, and training, helping your team adapt quickly.
- Industry-Standard Features. Most pre-built solutions come with standard healthcare functionalities like EHR management, scheduling, and billing, making them suitable for common use cases.
Challenges of Off-the-Shelf Software
- Limited Customization. The software may not meet all your organization’s specific needs, requiring workarounds or additional software.
- Integration Issues. Off-the-shelf solutions may not easily integrate with your existing systems, leading to inefficiencies or duplicated efforts.
- Scalability Constraints. Some pre-built software may struggle to scale with your organization as it grows, leading to future limitations.
- Security Risks. Generic solutions may not have advanced security protocols tailored to your organization’s specific needs, posing potential risks.
Example: A small private clinic with straightforward scheduling and billing needs may opt for Kareo or Athenahealth, off-the-shelf software designed to handle essential healthcare functions without the complexity of custom development.
How Much Does Software Development In the Healthcare Industry Cost
Estimating the cost of healthcare software development is no easy task – there’s no universal price tag. Costs depend on several variables, including the software’s complexity, required features, compliance needs, and the timeline. To offer a better picture, let’s explore the key stages of development, their typical effort, and how they translate into real-world expenses.
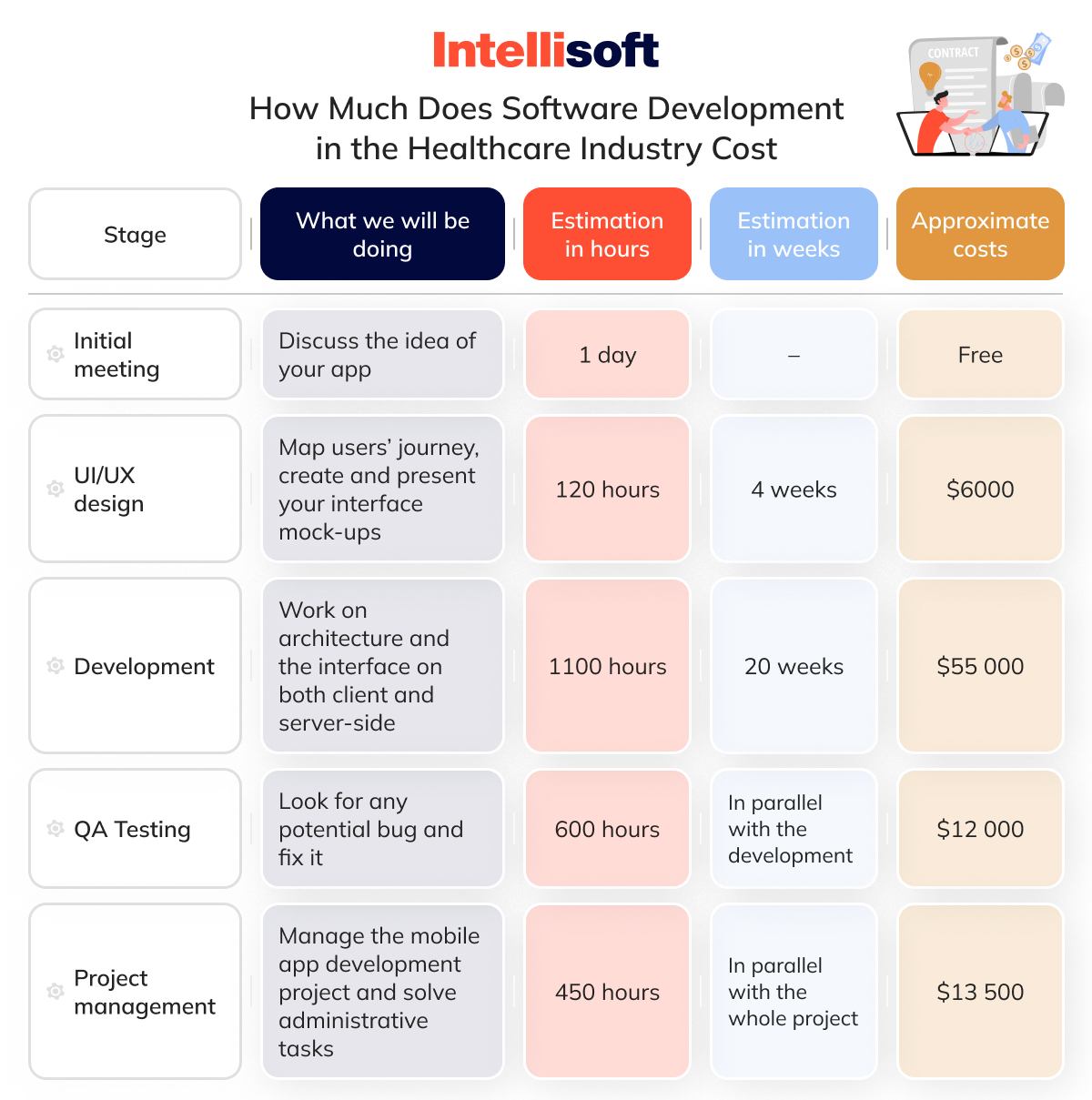
What Influences These Costs?
- Scope and Features. A basic patient app with limited features can cost around $50,000 to $100,000, while a complex hospital management system or telemedicine platform could easily exceed $200,000.
- UI/UX Design Quality. Investing in a smooth, user-friendly interface ensures higher patient and clinician satisfaction, which adds value – but it requires both time and expertise. As reflected in the table, a thorough design process costs around $6,000.
- Development Complexity. Building healthcare software often involves creating both client-facing interfaces and a robust backend. This can take several months, with costs ranging from $55,000 or more, depending on the architecture and technologies used.
- Compliance Requirements. Software that processes patient information must meet regulations like HIPAA or GDPR. Implementing advanced encryption, access controls, and auditing tools increases both time and cost, but ensures legal compliance and data safety.
- Project Management & QA. Managing a project efficiently and running QA testing in parallel avoids delays and costly errors. As shown, project management alone can cost $13,500, while QA services add another $12,000.
SDLC in Healthcare
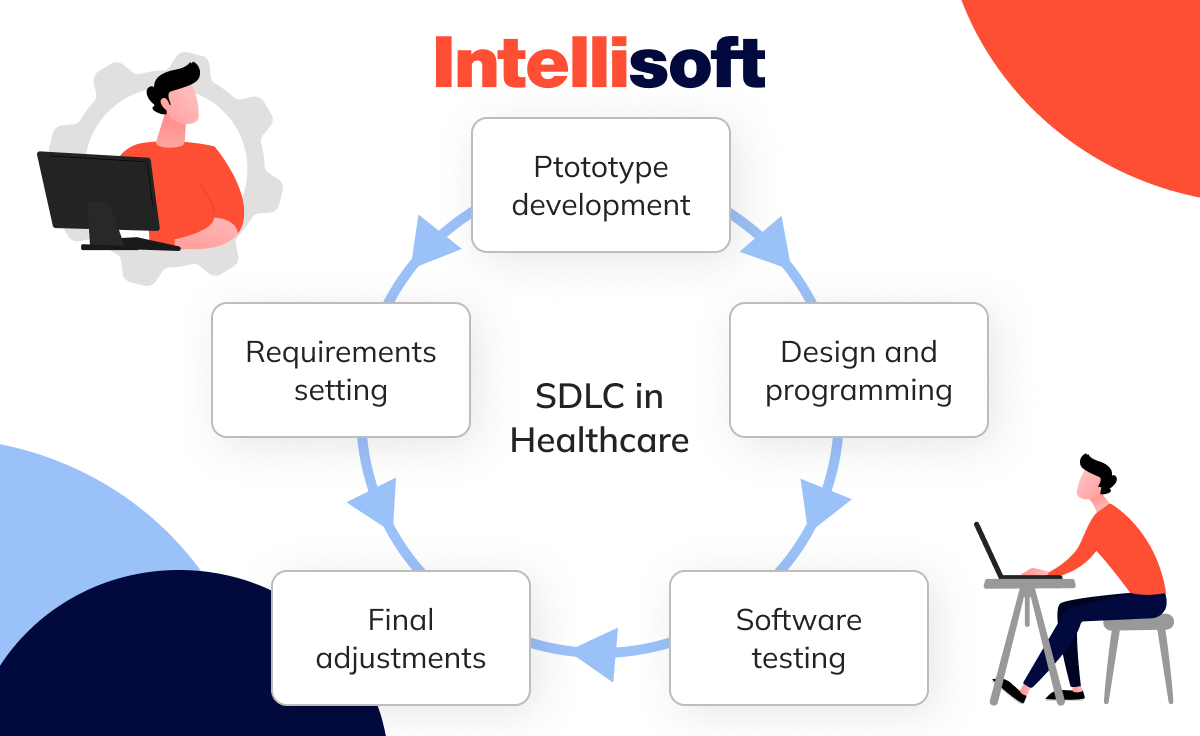
Developing software for the healthcare industry requires a thoughtful and well-structured process to meet the unique demands of medical institutions. The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) ensures that healthcare solutions are safe, reliable, compliant with regulations, and optimized for user needs. Below is an overview of the key phases in the SDLC for healthcare software.
1. Requirements Gathering and Analysis
This stage focuses on identifying the organization’s needs, including the software’s purpose, required features, and compliance requirements (such as HIPAA or GDPR). Developers collaborate with stakeholders – doctors, nurses, hospital administrators, and IT specialists – to collect insights and align the software with healthcare workflows.
Example: A hospital seeking scheduling software programs for medical offices will outline goals like reducing no-shows, integrating with patient records, and sending automated reminders.
2. Prototype Development
A prototype is a preliminary version of the software designed to demonstrate basic functionality. It helps both developers and stakeholders assess the feasibility of the solution and identify potential gaps early on.
Example: A simple, clickable mockup of an Electronic Health Record (EHR) interface allows doctors to review and suggest improvements to the user flow before full development begins.
3. Feedback and Iteration
Gathering feedback from stakeholders – end-users, administrators, or IT staff – is critical. Their input ensures the proposed solution meets operational needs and aligns with expectations. This phase may involve several rounds of revisions to refine the software.
Example: Nurses using an early version of a monitoring app may request additional alerts for critical health indicators, prompting developers to adjust the design accordingly.
4. Design and Development
Once the requirements and prototype are approved, developers work on UI/UX design and backend development. They create user-friendly interfaces while building a solid infrastructure that integrates with existing healthcare systems. This phase ensures both usability and performance.
Example: EHR systems must seamlessly integrate with other hospital software, such as medical billing tools or laboratory systems, ensuring interoperability and smooth data exchange.
5. Software Testing and Quality Assurance (QA)
Testing ensures the software functions properly and is free of bugs, glitches, and security vulnerabilities. Healthcare applications require rigorous QA to ensure patient safety, data security, and compliance with industry regulations. Testing often includes functional testing, performance testing, and security audits.
Example: In a telemedicine app, testers verify that patient-doctor video calls run smoothly and that personal health data is encrypted throughout the interaction.
6. Final Adjustments and Compliance Checks
Before launch, the software undergoes final adjustments to ensure everything is in order. This step involves validating the solution against healthcare standards and regulatory frameworks, ensuring it complies with privacy laws and is ready for deployment in real healthcare settings.
Example: An imaging software platform must comply with FDA and HIPAA regulations before being rolled out to radiologists.
SDLC for Custom Healthcare Software Development
Custom software requires additional steps to meet the specific needs of healthcare providers or niche markets. Below are some additional considerations for a tailored development approach:
1. Identify the Target Audience
In custom projects, understanding the end-users – whether patients, doctors, or administrators – is essential. Knowing their behaviors, preferences, and pain points ensures the software solves real problems.
Example: A health tracking app for elderly patients may focus on large fonts and voice commands for ease of use.
2. Sketch the Architecture
Developers map out the software’s architecture and flow, ensuring it can handle the demands of healthcare institutions. This process ensures all moving parts work together efficiently.
Example: An app for emergency departments needs fast access to critical patient data, which requires robust architecture and minimal loading times.
3. Incorporate Feedback and Iterate
Custom software requires even closer collaboration with stakeholders. Frequent feedback helps tailor the solution to meet both organizational goals and user expectations.
4. Elaborate UI/UX Design
A customized user interface ensures the software is intuitive and accessible for healthcare professionals. Good UI/UX is especially critical in high-pressure environments, like emergency rooms, where every second counts.
5. Protect the Technology with Encryption
In healthcare, data privacy and security are paramount. Developers must implement encryption, two-factor authentication, and other security measures to protect sensitive information.
6. Ensure Compatibility with Existing Systems
Healthcare software must seamlessly integrate into the institution’s existing IT infrastructure. This ensures interoperability between various systems – such as billing software, pharmacy tools, and EHRs – and enables smooth workflows.
Challenges in Developing Medical Computer Software Programs
Developing healthcare software involves unique challenges that require careful planning and execution. Below are key hurdles developers face:
Data Integration
Ensuring seamless communication between different systems (EHRs, billing, and monitoring tools) is crucial for efficiency.
User Adoption
Healthcare professionals need time and training to embrace new technologies, which can slow implementation.
Regulatory Compliance
Meeting standards like HIPAA and GDPR ensures patient data privacy but requires thorough audits and strict practices.
Technology Access
Not all healthcare institutions have access to advanced infrastructure, limiting software adoption in underserved areas.
Cost
Development, maintenance, and upgrades of medical software can be expensive, especially for custom solutions.
Data Security
Protecting sensitive health information requires encryption, multi-factor authentication, and constant security updates.
Data Accuracy
Accurate data input is essential to prevent medical errors and ensure patient safety.
Storage Requirements
Large volumes of data – like medical imaging – require robust cloud solutions or local servers with extensive capacity.
User Experience (UX)
Software must be user-friendly, as healthcare professionals need quick access to information without delays or confusion.
Customization
Every institution has unique needs, making software customization critical but challenging, especially for off-the-shelf solutions.
Medical Software Development: IntelliSoft Experience
When Daintel, a Danish healthcare solutions provider, set out to build a Critical Information System (CIS) in 2005 for Intensive Care Units (ICU) and Anesthesia Departments (AN), the challenges were immense. Handling complex medical data in real time and enhancing patient care across hospitals was no small feat. After the system proved successful in several Danish hospitals, including Odense University Hospital, Daintel sought to expand internationally. That’s where IntelliSoft came in—to accelerate development and smooth the path to new markets.
The Challenge
Daintel’s CIS had to meet several intricate requirements. It needed to:
- Integrate advanced modules for patient administration, electronic prescriptions, fluid balance monitoring, and device data collection.
- Ensure real-time data collection from medical devices, labs, and departments.
- Adapt to new regions by integrating with local Hospital Information Systems (HIS).
- Securely manage high volumes of sensitive patient data, ensuring scalability and data privacy.
In 2016, the CIS was successfully implemented in Landspítali, Iceland’s largest hospital. However, when Cambio Healthcare Systems acquired Daintel in 2019, the planned launch in Sweden added a new layer of complexity, requiring seamless integration with different hospital systems.
IntelliSoft’s Solution
Leveraging 15+ years of healthcare software expertise, IntelliSoft collaborated closely with Daintel to refine the CIS, making it scalable and ready for international deployment. Here’s how IntelliSoft contributed:
- Scalable Architecture. We streamlined the system architecture to efficiently handle real-time data from ICU and anesthesia departments. A centralized server structure and specialized storage server allowed seamless sharing of patient data across departments.
- Advanced Modules. IntelliSoft enhanced critical modules, including the Electronic Observation Module (EOM), which consolidates data from medical devices and labs. This feature provides doctors with a comprehensive, single-screen view of patient health, enabling quicker decisions in emergency scenarios.
- Custom Interfaces. To ensure the CIS worked with various HIS systems across countries, we built custom interfaces, including a Common Context Interface (CCOW). This ensures that patient and user data remains synchronized across multiple applications.
- Improved Security. Given the sensitive nature of healthcare data, IntelliSoft integrated advanced encryption protocols to secure both data transfers and storage. Additionally, we upgraded the authentication system with Keycloak to enable Single Sign-On (SSO) and seamless integration with Windows Active Directory.
- Efficient Development and Deployment. IntelliSoft revamped the development pipeline by rewriting build and deployment processes in PowerShell, making updates faster and more manageable.
The Results
With IntelliSoft’s expertise, Daintel’s CIS evolved into a more robust, scalable solution. Its seamless data integration, enhanced security, and improved decision-making capabilities have made it an indispensable tool for healthcare providers.
The system has now been successfully implemented in Landspítali and is prepared for Swedish market expansion through Cambio Healthcare Systems. Trusted by numerous Danish hospitals, the CIS continues to streamline critical care, improve patient outcomes, and securely manage vast amounts of real-time medical data.
With IntelliSoft’s refinements, the CIS is now poised to transform healthcare operations in even more regions, helping hospitals worldwide deliver better patient care and manage healthcare complexities more efficiently.
How IntelliSoft Can Help With Medical Software Program Development
At IntelliSoft, we understand that developing medical software isn’t just about writing code – it’s about enhancing patient care, improving workflows, and ensuring seamless data management across complex healthcare environments. With over 15 years of expertise in healthcare software development, we’ve partnered with leading healthcare providers to build scalable, secure, and user-friendly solutions.
Whether you need to integrate advanced modules into an existing system, create custom interfaces for interoperability with other hospital platforms, or enhance data security with cutting-edge encryption and authentication protocols, IntelliSoft is ready to assist. From Electronic Health Records (EHRs) to Critical Information Systems (CIS), we specialize in crafting solutions tailored to your institution’s needs.
Our comprehensive approach ensures that each project is meticulously planned, compliant with healthcare regulations, and optimized for performance and scalability. We prioritize seamless user experience and efficient deployment, so your teams can focus on what they do best – providing exceptional care.
Choosing IntelliSoft means working with a team that combines deep technical knowledge with real-world healthcare insights. Let us help you navigate the challenges of software development, from design to deployment, and transform your medical operations with innovative solutions that make a real difference.
Contact us today; with IntelliSoft by your side, you’re not just investing in technology — you’re investing in better healthcare outcomes for patients and smoother operations for your organization.