Welcome to the thrilling world of IoT and cybersecurity, where the only thing multiplying faster than smart devices is the hair-pulling complexity of keeping them safe! Here at IntelliSoft, we’ve seen it all – from smart toasters that almost joined a cybercrime syndicate, to fitness trackers plotting to take over the world (well, almost).
But don’t let smart devices intimidate you! IntelliSoft not only excels in developing custom software solutions, but our experts also know a thing or two about guarding the realm of IoT. In this guide, we’ll arm you with the best practices and considerations for IoT device security concepts. Why listen to us?
When securing your interconnected gadgets and IoT development, we’ve got more tricks up our sleeve than a magician at a tech convention. For example, for one of our biggest clients, when integrating IoT, we utilized OPC Unified Architecture, enabling efficient collection of data. To ensure secure data transmission and keep the client’s IoT network isolated from other sensitive business data, OpenVPN was employed.
So, get ready for a journey into securing your IoT ecosystem.
Table of Contents
Internet of Things (IoT) Devices Explained
The world of IoT devices is a futuristic playground where everyday objects gain superpowers through internet connectivity. Imagine your coffee maker whispering to your alarm clock, “It’s go-time!”. That’s IoT magic at work. These savvy gadgets range from mundane toasters to high-tech industrial sensors, each with a mission: to gather data, take commands, and execute actions seamlessly.
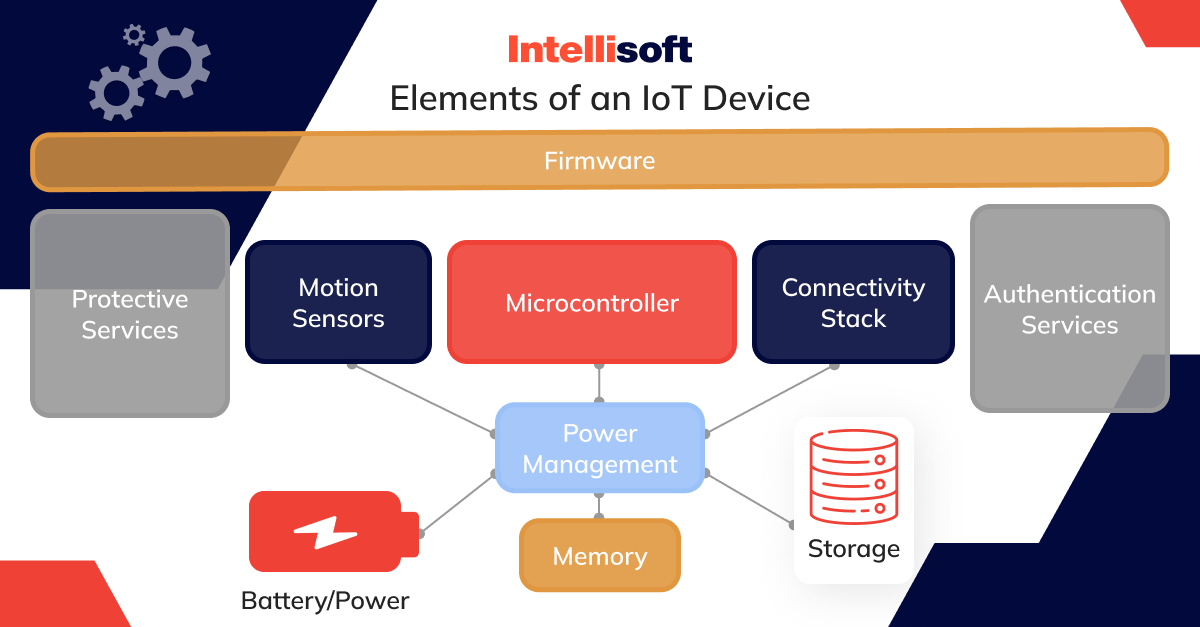
IoT devices, simply put, are the endpoints in a chain of communication that starts with a human or machine and stretches all the way to cloud platforms and data centers. These devices have various essential components that enable them to perform their tasks efficiently.
Firstly, there’s firmware. Think of it as the device’s in-built instruction manual that helps all the other parts work together. It controls the device’s hardware, and while it can be updated, it isn’t usually programmed by the end-user.
Next, we have protective services. This is part of the device’s built-in software that keeps it secure. It stops unauthorized actions and keeps data encrypted – like a digital lock and key. Motion sensors are the device’s senses. They detect movement in various ways, whether it’s a simple shake or precise location tracking via satellites like GPS.
The microcontroller is the device’s brain. It runs the software and processes all the information the device uses and creates. For talking to other devices and connecting to networks, IoT devices have what’s called a connectivity stack. This stack can include various connection types, like Bluetooth, mobile networks, and Wi-Fi.
Some IoT devices also have authentication services, which are like bouncers at a club, checking IDs to make sure everything trying to connect is supposed to be there. Power management is all about efficiency – making sure the device uses power in the best way possible and recharges without a fuss.
Memory in an IoT device is like a short-term to-do list. It holds all the immediate information the device needs to operate at the moment. Lastly, storage is the device’s long-term memory, keeping data safe for when it’s needed later, like locations where the device has been or data from other connected devices.
In essence, each IoT device is a mini-computer designed to perform specified tasks as part of the larger IoT ecosystem. Understanding how these devices work is a crucial first step in keeping them secure.
What is the IoT Ecosystem?
The IoT ecosystem is a complex web of players, each with a critical role in ensuring that IoT and ICS devices function smoothly and securely. At the core of this ecosystem are the software developers. Like composers, they write the intricate code that breathes life into IoT devices, enabling them to carry out their intended functions with precision.
Then we have the hardware engineers, the master builders of the IoT world. They are responsible for crafting the physical components, such as processors and microcontrollers, that serve as the backbone of any IoT device.
Network connectivity is the ecosystem’s circulatory system, comprising service providers, local LANs, and mobile networks, including 4G and 5G. They are tasked with the crucial job of transporting data, ensuring that the devices stay connected in the grand symphony of the IoT network.
A platform in the IoT ecosystem is like the stage where all the action happens. These platforms, often cloud-based, handle the immense volumes of data produced by IoT devices, processing it for further use.
Data analysts and scientists are the ecosystem’s interpreters, making sense of the information. They analyze the data to extract actionable insights that can inform decisions and drive efficiency.
IT workers and managers form the support crew dedicated to the upkeep of the IoT infrastructure. Their responsibilities include managing endpoints and overseeing IoT network traffic throughout the device’s lifecycle.
Cybersecurity and IoT workers and managers are the guardians of the ecosystem. They deploy security controls, manage cyber threats, and establish data protection schemes to keep digital threats at bay.
Lastly, AI and machine learning services are the automated brains that bring a level of self-sufficiency to the IoT ecosystem. They help automate device operations, streamline data collection, and transform data into valuable information.
This interplay of roles and functions is what turns the IoT ecosystem into a coordinated and dynamic network capable of driving innovation and efficiency across various industries.
What Are the Common IoT Threats?
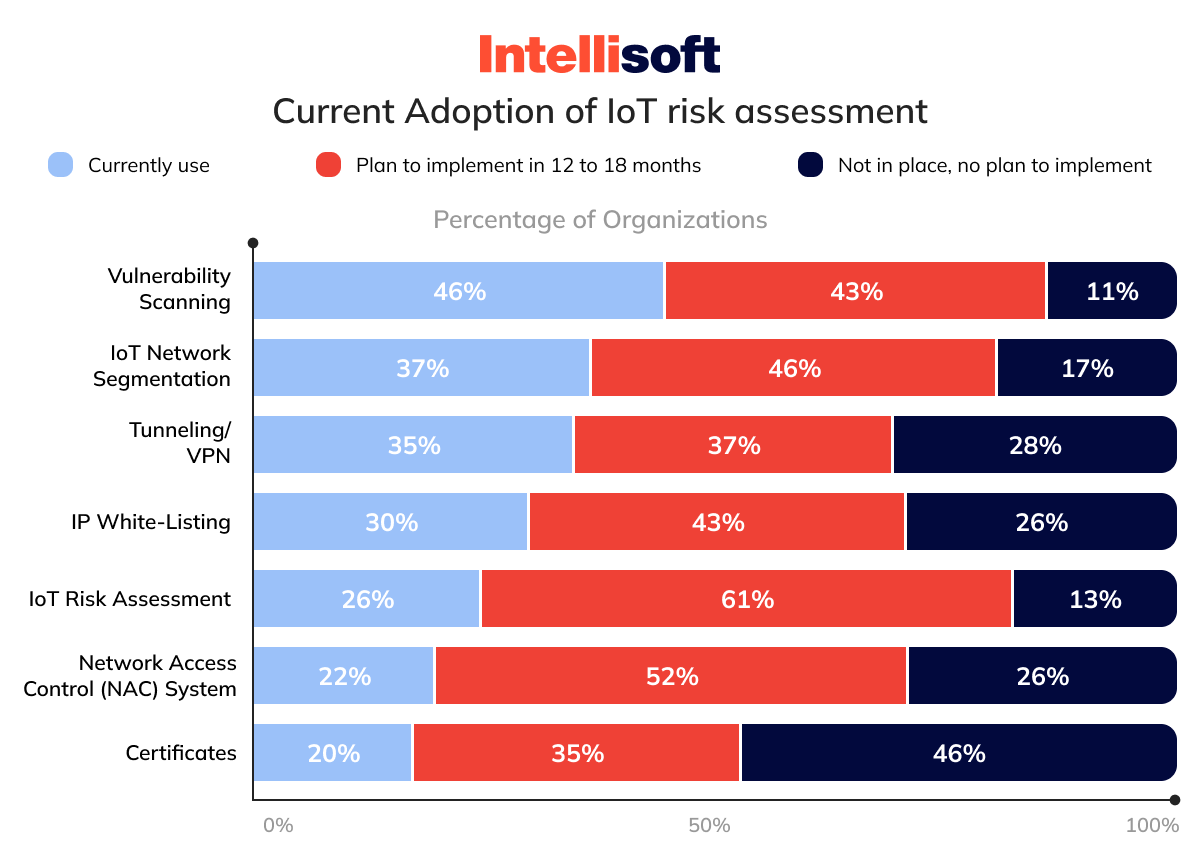
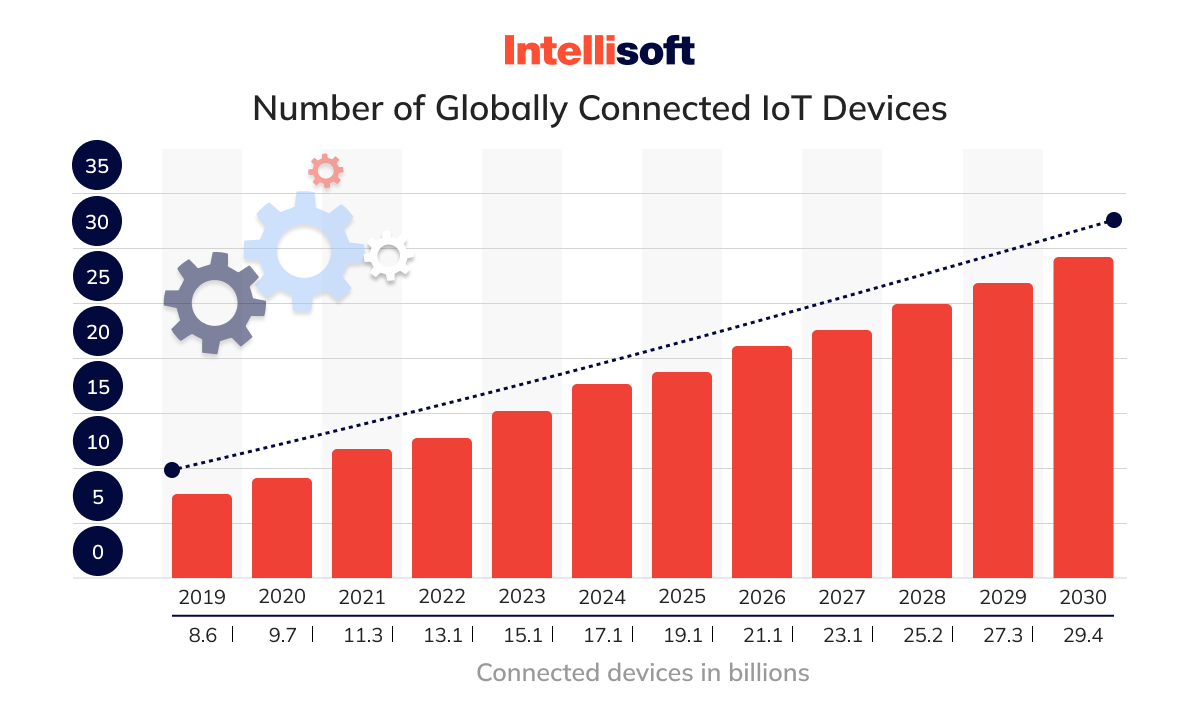
The Internet of Things (IoT) market is growing, with McKinsey forecasting its global value to hit a staggering $12.6 trillion by 2030. As the number of devices skyrockets, each one adds to a growing target for cyber adversaries. Unprotected IoT devices are potential gateways for hackers to access personal and business data stored in the cloud. To safeguard business operations against such invasions, they are employing measures such as vulnerability scanning and network segmentation, among others.
Despite these efforts, common pitfalls remain. A significant concern is the lack of user awareness. Users often remain uninformed about the security capabilities of their devices or how to use them properly. This ignorance is a chink in the armor that hackers are all too willing to exploit. Additionally, improper device updates, or the absence thereof, can leave devices vulnerable to emerging threats.
Another weak link is the absence of efficient and robust security protocols and built-in security patches. In the rush to market, developers may overlook these crucial elements, leading to devices that are insecure by default. Such devices often come with preset configurations, including default passwords that users cannot change, making them low-hanging fruits for cybercriminals.
Further compounding the problem is the issue of non-existent upgrade paths. Certain devices are unable to update their firmware, rendering them perpetually at risk and detrimental to the health of the entire IoT network. Moreover, the practice of loading complete operating systems onto devices that require only a fraction of that computing power can, once compromised, turn these devices into potent tools for attackers.
Security risks of IoT devices can lead to the creation of botnets, a network of enslaved devices under the control of an attacker. These botnets can consist of thousands, even millions of devices and can be leveraged to conduct Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks or spread malware.
Service providers across various domains remain on high alert due to these IoT security concerns. As the Internet of Things (IoT) devices are becoming more and more common in our everyday lives, the risk of them being used to spread malware is on the rise. With the growing quantity of connected IoT devices, it is essential to be aware of the potential security threats associated with them and take adequate measures to safeguard against them. It necessitates a comprehensive and proactive approach to IoT cybersecurity.
How Do IoT Attacks Happen?
The use of IoT in cyber security attacks is a breed apart, primarily because IoT connectivity extends over a vast, often uncharted attack surface. These devices and apps can hoard mountains of sensitive personal, operational, and corporate data, setting the stage for a security challenge that transcends the traditional triad of confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
For cybersecurity and IoT professionals, the stakes are high. Data breaches and cyberattacks are everyday concerns, but the real chill comes from the potential physical harm and operational disruptions that an IoT vulnerability could cause. To counter such threats, these professionals must sharpen their focus on several key areas.
Securing connectivity involves safeguarding the channels through which IoT devices communicate, ensuring that the data in transit cannot be intercepted or tampered with. Device hardening, on the other hand, is about reinforcing the IoT devices themselves, making them impervious to intrusions and manipulations.
Threat monitoring must be a continuous effort, with a watchtower manned 24/7 to spot and respond to any signs of malicious activity. It’s an essential early-warning system in the IoT defense strategy.
Security posture management is the strategic side of IoT device security concepts. It’s about maintaining a robust defense stance, ready to evolve as new threats emerge. It is important to regularly evaluate and improve security measures to anticipate and prevent any potential threats or use of IoT in cyber security attacks from malicious individuals or groups. This approach helps ensure that all systems and data remain protected, and that any vulnerabilities are quickly identified and addressed.
Lastly, securing data on the backend, particularly in the cloud, ensures that even if attackers breach the first lines of defense, the stored data remains out of their reach. This multi-layered approach is crucial, as IoT attacks are not limited by the digital sphere. Their consequences can manifest in the physical world, making the role of IoT cybersecurity professionals critical to both our virtual and tangible well-being.
Related readings:
- IoT Connectivity: A Comparison Guide
- How to Build a Mobile IoT Application: The Only Guide You’ll Need
- How to Hire an IoT Developer: IoT Developer Salary And Job Description
- How to Build an IoT Dashboard: Benefits, Challenges, and Process
- Testing IoT Devices: Why and How to Examine the Internet of Things
Types of Cybersecurity and IoT Threats
In the interconnected web of IoT devices, cybersecurity threats loom large, each with unique implications for personal privacy, corporate integrity, and operational continuity. With the surge in IoT adoption, the types of threats have expanded, reaching into every corner where a smart device resides. Let’s talk about the primary threats that concern IoT security professionals today.
Service Disruption
A service disruption is an orchestrated attack aimed at making an IoT service unavailable. Imagine a smart dam’s controls being hijacked, halting power generation, or a city’s water system being rendered inoperative. The repercussions extend beyond mere inconvenience, potentially creating life-threatening situations or severe economic impacts. Mitigating such threats requires robust security protocols and continuous monitoring to ensure service continuity.
Data Theft
IoT devices often hold the keys to a treasure trove of personal data. Data theft occurs when an unauthorized party gains access to this sensitive information. The implications are far-reaching, with risks of identity theft, financial fraud, and a significant breach of privacy. Protecting this data necessitates stringent access controls, data encryption, and vigilance against phishing and other social engineering tactics.
Data or Service Manipulation
Unlike theft, which steals information, data or service manipulation alters it, potentially causing catastrophic outcomes. An attacker, for instance, could tweak the settings of a medical device, endangering patient lives or disrupting service delivery, leading to economic losses and damaged infrastructure. This threat underscores the need for secure and tamper-proof configurations and rigorous validation processes for any changes to IoT device settings.
Non-compliance
As governments worldwide intensify efforts to safeguard data privacy, non-compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA can have severe consequences. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines, legal challenges, and erosion of customer trust. Ensuring compliance requires a comprehensive understanding of relevant regulations, diligent data management practices, and periodic audits.
The threat landscape for IoT devices is varied and dynamic, demanding a multi-faceted and proactive security approach. As the IoT ecosystem continues to grow, staying informed and prepared is the best defense against these evolving cybersecurity threats.
Examples of IoT Cyber Security Breaches
The exponential increase in IoT devices has, unfortunately, come with a rise in high-profile cybersecurity breaches. These incidents highlight the vulnerabilities inherent in connected devices and the far-reaching consequences of such attacks.
Mirai Botnet Attack
The Mirai botnet attack of 2016 is a notorious example of IoT devices’ susceptibility to cyber threats. A botnet, essentially a network of infected devices, was leveraged to perform massive distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. The Mirai botnet, comprising hundreds of thousands of compromised devices, disrupted services for major websites such as Spotify, Netflix, and PayPal, causing widespread outages.
VPNFilter Malware
In 2018, a sophisticated malware named VPNFilter infected over 500,000 routers across 50 countries. The malware had the capability to not only steal information but also to render routers inoperable. It laid bare the security IoT risks associated with network-connected devices and the importance of securing routers, which often act as gateways to IoT in cyber security ecosystems.
Tesla Model X Hacked
A cybersecurity expert, Lennert Wouters from KU Leuven University in Belgium, exposed a vulnerability in the Tesla Model X’s Bluetooth keyless entry system in 2020. He managed to hack the vehicle within a mere two minutes, allowing him to open the car and even drive away. This event served as a harsh reminder that even the most advanced IoT devices, such as modern vehicles relying on wireless keys, are not immune to IoT security risks.
Verkada Camera Feeds Hacked
In 2021, a security breach at Verkada, a video surveillance startup, resulted in unauthorized access to 150,000 live camera feeds. The compromised cameras were inside sensitive public and private sector locations, including schools, hospitals, and prisons, illustrating the potential privacy and security implications of IoT devices within critical infrastructure.
These examples underscore the critical need for enhanced IoT security solutions. As IoT devices become more and more common in our daily lives and essential services, the potential impact of these breaches grows, making it imperative to prioritize and invest in IoT cybersecurity.
Best Practices for Securing IoT Devices
In an age where our devices are getting smarter by the day, it’s not enough to just “lock the doors” to secure them. You need to build a digital fortress. Here are the best practices for fortifying your IoT devices against the majority of cyber threats.
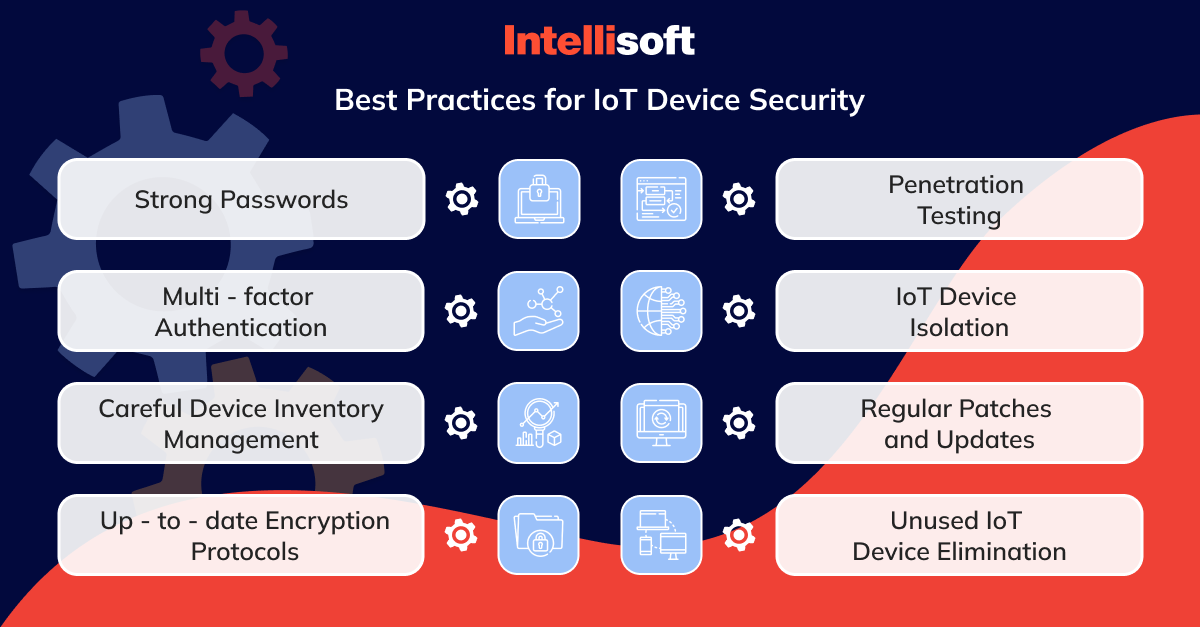
Use Strong Passwords and Multi-factor Authentication
The adage “keep it complicated” applies perfectly to passwords. The default is a no-go zone. Opt for unique, complex passwords that are as hard to crack as a riddle wrapped in a mystery. To add an extra level of protection, use multi-factor authentication (MFA), your digital guard dog that barks only when you tell it to. Remember, if an MFA request wasn’t triggered by you, it’s an impostor knocking.
Carefully Manage Device Inventory
Knowing your digital inventory is half the battle won. Each device is a soldier in your army, and you need to know its strengths and weaknesses. Tools like NinjaOne can ensure that every device on your network is accounted for and monitored. This inventory management enables you to identify and secure any vulnerable point in your IoT ecosystem, making sure no device becomes a weak link.
Use Up-to-date Encryption Protocols
In the world of IoT, encryption is the secret language that keeps eavesdroppers at bay. Make sure your devices speak in codes that only you understand by using the latest encryption protocols. This practice turns sensitive data into gibberish for anyone who doesn’t have the key. It is crucial, especially for data in transit.
Conduct Penetration Testing or Evaluation
Think like a hacker to beat a hacker. Penetration testing involves a simulated cyber attack on your system to identify exploitable vulnerabilities. It’s a proactive approach to identify weaknesses before an actual attack occurs, allowing you to fortify your defenses accordingly. Penetration testing is like a fire drill for your IoT devices. You need to be sure that when an actual fire breaks out, your escape routes are clear, and your sprinklers are working.
Isolate IoT Devices From Critical Systems and Data
Separation is key in IoT device security concepts. By using network segmentation, you can isolate your IoT devices from critical systems. This strategy limits the impact of a potential breach, ensuring that even if one device is compromised, the infection doesn’t spread to your entire network. Practice digital distancing by segregating your IoT devices from the vital organs of your network.
Regularly Patch and Update IoT Devices
Stay updated or stay vulnerable. Regular patches are the vitamins that keep your IoT devices’ immune system strong. Employ an RMM solution to administer these updates automatically, keeping your network’s health in check. It’s a good way of ensuring all devices are up-to-date with the latest security measures, thereby reducing the risk of vulnerabilities being exploited.
Eliminate Unused IoT Devices
An unused IoT device is like an unlocked door in an abandoned house. It invites trouble. It’s highly unlikely you’ll be thinking about securing or patching a device that you don’t need. If a device is no longer in use, cut the cord. It will decrease the amount of potential entry points for attackers, tightening your network’s overall security. It’s better to be safe than sorry.
Securing IoT devices is not a one-off task but a continuous process. You can use these practices as a blueprint for a more secure IoT environment.
Cloud Security in IoT
In the sprawling world of IoT, where devices are constantly buzzing with data, cloud security stands as a beacon of protection. You need to safeguard data and ensure the entire operational fabric of IoT remains intact and invulnerable. Let’s discuss the essential practices for cloud security in IoT.
Follow a Secure Software Development Methodology
The journey to secure software begins at the drawing board. It’s crucial to embed security into every phase of the development lifecycle. A methodology like the Microsoft Security Development Lifecycle offers a roadmap, guiding teams from conception through deployment, ensuring each step is fortified against vulnerabilities. This approach isn’t just about fixing bugs; it’s about architecting a system that’s secure by design.
Choose Open-Source Software with Care
Open-source software is like a double-edged sword. It accelerates development but can expose you to IoT security risks if not chosen wisely. The vibrancy of the community behind an open-source project is a litmus test of its security robustness. Active communities mean regular updates and quick responses to vulnerabilities. On the flip side, obscure projects might lack support, leaving gaping holes when it comes to security in IoT.
Integrate with Care
The junctures where libraries and APIs meet are often fertile ground for security flaws. Even unused functionalities, accessible through API layers, can become backdoors for threats. Rigorous scrutiny of all interfaces during integration is non-negotiable. This practice seals potential breaches, ensuring airtight security in IoT at every connection point.
Protect Cloud Credentials
Cloud credentials are the keys to your IoT kingdom, and they need to be guarded zealously. Regular password changes and avoiding use on public systems are basic yet vital practices. An exposed credential can turn into a highway for attackers straight into your IoT system.
Define Access Controls for Your IoT Hub
Precision in access control is vital. For IoT Hub, it’s about understanding and defining who gets access and to what extent. Tools such as Microsoft Entra ID or shared access signatures (SAS) offer mechanisms to fine-tune these permissions, ensuring that each component has just the right level of access, no more, no less.
Define Access Controls for Your IoT Central Application
Similarly, IoT Central applications demand their own set of access protocols. The goal is to tailor access rights, aligning them perfectly with the required functionalities. This level of detailed control prevents over-privileged access, a common pitfall in IoT device security concepts.
Define Access Controls for Backend Services
When it comes to backend services consuming IoT data, the mantra remains the same – precise control. Understanding how these services interact with your IoT Hub or IoT Central and configuring the appropriate permissions is essential. This step ensures that the flow of data to and from these services is under strict surveillance, leaving no room for unauthorized access.
Monitor Your IoT Solution from the Cloud
Visibility is key in cloud security. Utilizing IoT Hub metrics in Azure Monitor or monitoring IoT Central application health offers a panoramic view of your IoT solution’s health. This monitoring is like having a 24/7 surveillance system that alerts you the moment something goes wrong.
Set Up Diagnostics
Operational intelligence is a crucial ally. By logging events and funneling these diagnostics to Azure Monitor, you gain insights into the operational aspects of your solution. This practice can be compared to having a health check-up for your IoT ecosystem, ensuring it runs smoothly and any anomalies are caught and addressed promptly.
Securing the cloud aspect of IoT is a multi-faceted endeavor. It requires a harmonious blend of careful planning, vigilant monitoring, and meticulous control over access and integration. By adhering to these best practices, you can create a safe cloud environment for your IoT devices.
Typical Internet of Things (IoT) Security Issues and Solutions
If you want to battle potential IoT issues effectively, it’s crucial to understand the security landscape. Let’s discuss some common IoT security issues and solutions.
Password Security Flaws
Passwords are the first line of defense, yet they are often the weakest link. Hard-coded and default passwords can be easily exploited, as evidenced by the Mirai malware attack we mentioned earlier. This malware hijacked devices by using common usernames and passwords, culminating in a massive botnet and a 1Tbps DDoS attack that crippled major internet services.
The antidote to password vulnerabilities is straightforward yet vital. Change default passwords immediately upon receiving new devices. Use strong, unique passwords and consider limiting logins to a single IP address to reduce unauthorized access risks.
Inconsistent Updates and Faulty Update Mechanisms
IoT devices, often designed for user-friendliness and connectivity, can become vulnerable over time. The Satori IoT worm, similar to Mirai but with targeted exploits for specific vulnerabilities, exemplifies this issue.
Ensure regular scanning of third-party software and hardware included in your IoT environment. Utilize secure and encrypted channels for updates and verify the integrity of these updates before deployment. This proactive approach can significantly mitigate IoT security risks associated with outdated software.
Insecure Interfaces
IoT devices process and communicate vast amounts of data, making their interfaces potential weak points. Inadequate device authentication, authorization, and encryption can lead to data breaches and compromised devices.
Implement strict device authentication and authorization procedures. Utilize X.509 standard certificates for each IoT device to ensure secure identification and verification. In case of suspicious activity, the ability to disconnect a device can be crucial in preventing further damage.
Inadequate Data Security
Insecure communications and data storage are prevalent issues. The attack on a casino in 2017, where a fish tank thermometer was used to access sensitive data, underscores this vulnerability.
Employ strong data encryption for both stored and in-transit data. Explore machine learning solutions where data processing occurs at the edge and only analytics are sent to the cloud, significantly reducing security challenges.
Inadequate IoT Device Management
As we discussed earlier, there are many vulnerabilities in IoT and cybersecurity, including the use of unauthorized devices, legacy operating systems, and compliance violations. This mismanagement poses serious security IoT risks.
You can appoint a dedicated Operation Technology (OT) Manager to oversee network management. Regularly update or replace legacy devices and segment the network to manage it effectively. Periodic security checks on all IoT devices and networks are essential for maintaining security integrity.
The Internet of Things Skill Gap
The rapid advancement of IoT technology has created a significant skills gap. This gap presents a challenge in effectively managing and securing IoT environments. As a solution, you can invest in retraining and upskilling programs for employees, focusing on emerging IoT technologies. Recruitment strategies should be forward-looking, anticipating future needs.
Building a pipeline of cyber security in IoT devices of professionals equipped to handle IoT challenges is critical for long-term success.
All of these factors are essential in protecting your IoT network. As IoT continues to integrate into our daily lives, staying vigilant and proactive in managing these IoT security issues and solutions becomes more crucial than ever.
Best IoT Cyber Security Tools
In the ever-evolving landscape of IoT, the right tools can guarantee the security of your network. Let’s explore some of the best tools for cyber security in IoT devices that are instrumental in fortifying IoT ecosystems.
M2MLabs Mainspring
M2MLabs Mainspring stands out as a robust framework primarily designed for developing IoT applications. It excels in device management, data modeling, and communication. What makes M2MLabs Mainspring a go-to tool is its focus on flexibility and scalability, which are essential for managing the diverse and growing range of IoT devices. Its ability to model complex device structures and efficient communication protocols makes it a formidable tool for securing IoT ecosystems.
Flutter Wireless
Flutter Wireless is a standout tool in the IoT sphere, tailored for hobbyists, students, and engineers. This Arduino-based platform features a fast ARM processor, long-range wireless communication with over a half-mile range, and built-in battery charging, making it ideal for diverse applications like robotics, sensor networks, and consumer electronics. Its unique capability for boards to communicate directly without a router, coupled with robust 256-bit AES encryption, ensures secure and efficient operations. Simple yet powerful, Flutter is designed to facilitate a wide range of electronics projects, offering both versatility and enhanced security in the IoT landscape.
Eclipse IoT Project
The Eclipse IoT is an umbrella project that comprises several services and frameworks designed for IoT. This project brings together a community of developers and industry stakeholders to collaborate on open-source software for IoT. The tools under the Eclipse IoT project umbrella provide a wide range of functionalities, from device management to data analysis and more, making it a comprehensive solution for IoT security needs.
Moddable
Moddable is an innovative platform designed to transform how embedded software is created. It brings JavaScript, a language that powers web applications, to low-cost hardware used in consumer and industrial IoT products. The Moddable SDK supports a range of features such as IoT networking and cybersecurity, sensors, touch displays, security, audio, and data storage. This platform enables faster, more secure product development, leveraging the flexibility of JavaScript for embedded devices. It’s ideal for enterprises looking to quickly market IoT products that are easy to use, reliable, and secure.
Node-RED
Node-RED is a programming tool that allows you to connect hardware devices, APIs, and online services in innovative ways. It provides a user-friendly, browser-based editor that makes it easy to create connections between different nodes using the extensive node palette. This tool can be deployed to its runtime in a single click. Security in Node-RED is multi-faceted, offering both authentication and encryption capabilities to safeguard communications and data flow within IoT networks.
Each of these tools brings unique strengths to the table, from robust application development to comprehensive device management and secure data handling. Incorporating them into your IoT strategy can significantly improve the security and effectiveness of your IoT operations, ensuring your network is resilient against the myriad of threats in the digital world.
Client Testimonials

Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of IoT device security concepts requires a comprehensive understanding of the threats, tools, and best practices, from tackling password security flaws and ensuring consistent updates to employing robust tools that play a critical role in safeguarding IoT ecosystems.
We understand that conquering the wild waves of security risks of IoT, dodging cyber sharks, and navigating through the sea of information may feel like you’re on a digital Columbus-level expedition. In this ocean of IoT, staying afloat with robust security is essential.
If you’re looking for a savvy, reliable crew to help chart this course, look no further than IntelliSoft. We’re the navigators with the invaluable experience you need for your IoT journey – crafting brilliant solutions that are absolutely secure. Contact IntelliSoft, and let’s set sail towards a safe, innovative IoT future!