Why should you consider integrating a fuel management system? The reason is simple: Managing a fleet can be an expensive affair. On average, a truck covers a distance of about 10,000 kilometers per month and consumes around 30 liters of fuel per 100 kilometers (just like the Millennium Falcon uses more fuel than an X-wing fighter). A slight change of just 1 liter per 100 kilometers can lead to significant savings of more than 100 liters on the company’s balance sheet. Besides, fuel costs are one of the most critical expenses involved in fleet management and can account for up to a tremendous 60% of a fleet’s total operating budget.
The major problem lies in the unpredictable nature of petrol prices, which are influenced by numerous external economic and political factors beyond a fleet management company’s control and prediction. However, fleet managers can tackle growing fuel costs using advanced technologies. Advanced commercial solutions enable managers to optimize cost by controlling every transaction and tracking the fuel available per vehicle in real-time. This helps to manage uncertainties and make informed decisions.
By analyzing data gathered by telematics devices, managers can establish fair policies for fuel usage and take their fleet management to a whole new level. Let’s delve into the details and explore the various benefits that monitoring solutions can offer businesses.
Table of Contents
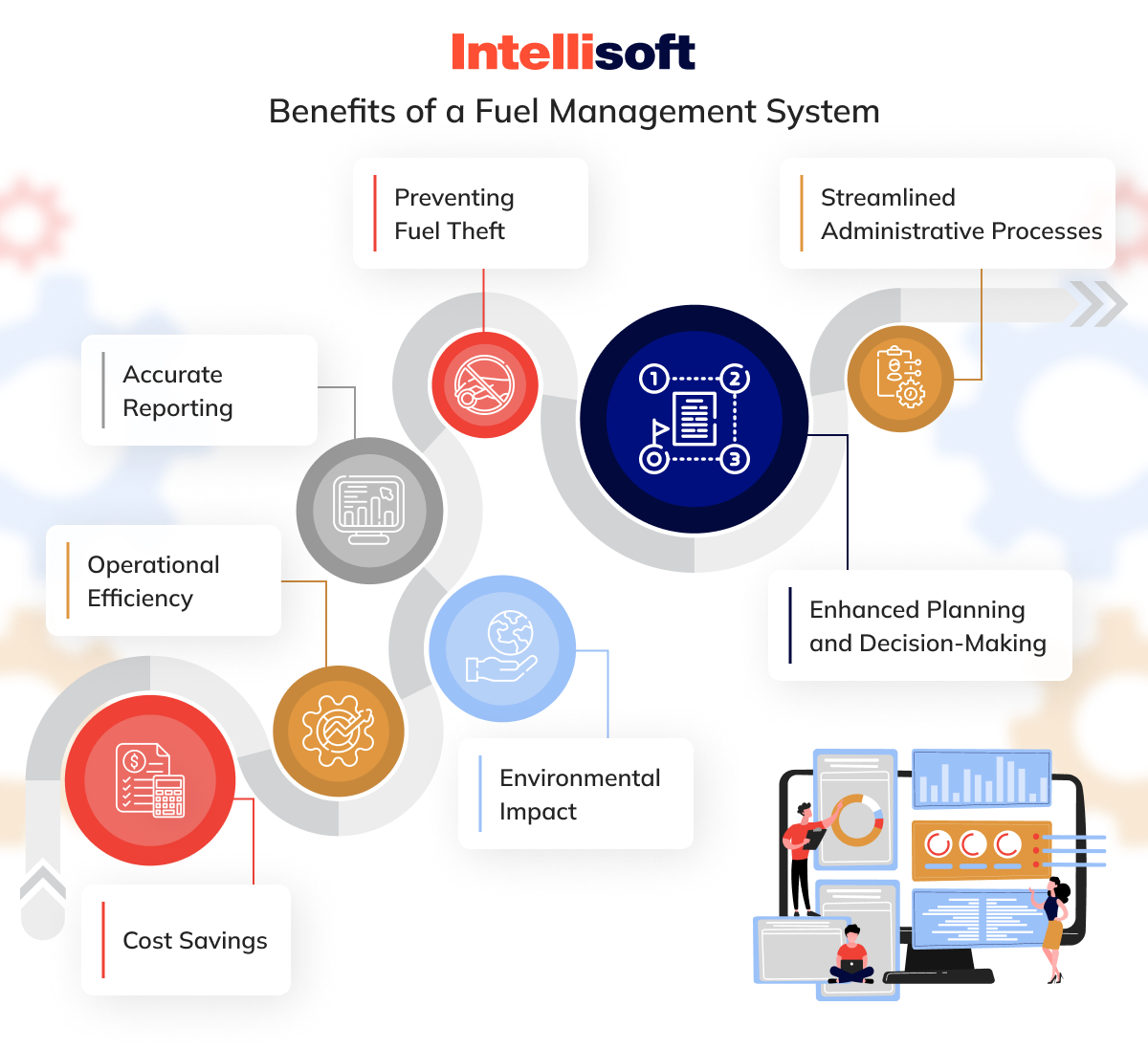
Benefits of a Well-Implemented Fuel Management System
A well-implemented fleet fuel management system offers numerous benefits for businesses involved in fleet operations. These advantages contribute to overall efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability. Here are the key benefits:
Cost Savings
- Fuel Efficiency. Significant reductions are achieved by utilizing real-time fuel consumption monitoring and optimization, leading to substantial cost savings.
- Preventative Maintenance. Early detection of maintenance needs prevents expensive issues, ensuring vehicles run optimally.
Operational Efficiency
- Route Optimization. Integrated solutions offer insights to refine routes, reducing fuel consumption and boosting delivery or service efficiency.
- Real-time Monitoring. Continuous observation facilitates swift decision-making, enhancing fleet management effectiveness.
Environmental Impact
- Emission Control. Fuel management systems contribute to lowering carbon emissions and encouraging eco-friendly driving habits.
Accurate Reporting
- Data Precision. Real-time data collection guarantees accurate reporting on fuel use, expenses, and other vital metrics.
- Regulatory Compliance. These solutions aid in meeting legal requirements by providing precise and transparent data for reporting.
Preventing Fuel Theft
- Enhanced Security. 65% of the companies reported exposure to fraudulent activities, such as drivers using fuel cards for personal purchases or sharing them between drivers. Using sensors and monitoring systems is critical in detecting and preventing theft, thus reducing financial losses.
Enhanced Planning and Decision-Making
- Insightful Data Utilization. Access to detailed data empowers informed decisions for strategic planning and resource distribution.
- Performance Analysis. Key performance indicators (KPIs) offer valuable insights into fleet efficiency and overall health.
Streamlined Administrative Processes
- Process Automation. A fuel tracking system reduces manual labor, freeing up resources for strategic tasks.
- Billing Precision. Automated software enhances the accuracy of billing and reimbursement procedures.
What Are the Main Components of a Fuel Management System?
This system has a comprehensive set of tools that enable the efficient use of fuel in different applications. It comprises critical components monitoring, controlling, and optimizing fuel usage. Depending on the system’s intended purpose and complexity, there may be different components, but here are some of the primary elements of a fuel management system for fleets:
Fuel Monitoring Devices
Fuel level sensors and flow meters are two important tools for monitoring fuel consumption. They are responsible for measuring the fuel in the tanks, and providing real-time information on fuel levels. On the other hand, flow meters are used to calculate the rate at which fuel flows through pipelines or dispensers. Together, these two tools help provide a comprehensive understanding of fuel consumption rates and enable efficient management of fuel usage.
Data Acquisition System
This software gathers information from various sensors and meters for thorough analysis and reporting. It integrates with other elements of the fuel consumption monitoring system.
Fuel Dispensing Equipment
Dispensers facilitate a regulated approach to fuel dispensing, typically incorporating electronic mechanisms to track and record transactions. Nozzles and hoses are vital for transferring fuel from storage units to vehicles or machinery.
Fuel Storage Tanks
This particular design is intended to store and systematically arrange significant amounts of fuel efficiently. It may involve the integration of numerous tanks that can accommodate various fuel types, ensuring the availability of a diverse range for different purposes.
Fuel Management Software
This solution provides a central platform for overseeing all the relevant data, offering a comprehensive range of reporting, analysis, and control capabilities. A fuel tracking system with this solution often includes features such as monitoring transactions, managing inventory, and reporting usage, all of which help streamline the tracking process and ensure maximum efficiency.
Control Systems
Automated systems have been developed to efficiently manage and monitor fuel dispensing, tank levels, and access to fuel stations. These systems facilitate fuel dispensing and ensure that the fuel station is secure by incorporating security measures to prevent unauthorized usage. Such systems are designed to provide convenience, safety, and security to fuel station owners and their customers.
Communication Infrastructure
Network or communication protocols enable data exchange between different software components. They provide a way for these components to communicate seamlessly and effectively. In addition, these protocols enable remote monitoring and management, which allows for greater control and flexibility in managing a network or system.
User Interfaces
This may feature touchscreens, keypads, or other input devices. The fuel management system for fleet can be interacted with through various displays or systems. These systems may include touchscreens, keypads, or other input devices.
Security Measures
Access control systems are used to prevent unauthorized usage of resources. These systems employ a range of authentication methods to ensure that only authorized personnel has an access, such as:
- key cards
- PIN codes
- and biometric verification.
These methods are particularly useful in securing sensitive areas or information, as they provide an additional layer of security beyond traditional lock and key systems.
Reporting and Analytics
The software can generate detailed reports covering a range of pertinent data, including fuel usage and transactions. These reports can provide valuable insights that can help optimize fuel utilization and enhance overall efficiency. By leveraging the information provided, businesses can make informed decisions that result in better performance and cost savings.
Alarm and Alert Systems
The system is designed to detect and report any unusual events or problems that may arise, including, but not limited to, low fuel levels, leakage, or unauthorized access attempts. It will promptly notify the relevant operators or managers of any such anomalies, allowing them to take appropriate action to resolve the issue and prevent potential harm or damage.
Maintenance and Diagnostics
This feature keeps a close eye on the state of your system’s various components, offering detailed and comprehensive diagnostics to help you identify potential problems before they occur. By being proactive about maintenance, you can ensure that your software runs smoothly and efficiently at all times, with minimal downtime and disruption.
How Do Fuel Management Systems Work?
Traditionally, fleet managers manually log fuel usage using pen and paper, which was both tiring and environmentally devastating. Fleet fuel management system software revolutionizes this process, enabling fleet managers to automatically monitor and record fuel data, facilitating informed decision-making to enhance efficiency.
Various solutions come with their own set of features, yet they commonly assist in tracking the fuel consumption of an entire fleet. These systems often leverage vehicle and driver data to boost efficiency, reduce CO2 emissions, and cut costs. This approach establishes consumption goals and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) based on specific metrics such as refueling frequency per vehicle.
Moreover, fleet fuel management systems offer enhanced control over fuel purchasing. The software provides comprehensive information on all transactions, offering insights into the factors influencing and categorizing them accordingly. Besides, it alerts you to the refueling needs of each vehicle. This feature is crucial; for instance, if a particular vehicle requires thrice as many refills as others, the system enables you to identify and address any underlying issues promptly.
Relevant articles:
- What Is a Modern Fleet Information Management System?
- Machine Learning in Logistics Industry: Benefits and Use Cases
- How to Develop Logistics Management System: Timeframe, Tech Stack, and Costs
- Ultimate Warehouse Optimization With Smart Warehouse Technologies
- Uber For Trucks App Development: Essential Features and Costs
What Is the Difference Between SaaS Fuel Management Systems and Custom-Made Ones?
SaaS (Software as a Service) fleet fuel management systems and custom-made (bespoke) systems are two approaches to acquiring and implementing unique software. Here are the key differences between the two:
SaaS Fuel Management Systems
Deployment
SaaS (Software as a Service) solutions are predominantly cloud-based, with the software hosted on the SaaS provider’s servers. Access to the fuel monitoring system is typically via web browsers.
Accessibility
What Is a Fuel Management System? It is a convenient tool, and SaaS systems offer the flexibility to access any location with an internet connection. This makes them ideal for businesses operating across multiple locations or working remotely.
Cost Structure
The pricing for SaaS solutions is usually based on a subscription model. Users pay a regular fee for access, while the provider is responsible for ongoing maintenance and updates.
Implementation Time
SaaS software is known for its quick implementation. Users can start utilizing this solution shortly after subscribing, which speeds up the process significantly.
Scalability
SaaS solutions are highly scalable and can be easily adjusted to accommodate varying numbers of users or expanded feature sets per organizational requirements.
Updates and Maintenance
The SaaS provider handles all aspects of updates, maintenance, and security. This approach significantly reduces the workload of the user’s IT department, ensuring a smoother operational flow.
Custom-Made Fuel Management Systems
Deployment
Customized systems offer the flexibility of on-premises deployment, where the organization hosts and manages the fleet fuel management system software. Alternatively, you can implement a hybrid model that combines on-premises infrastructure with cloud-based elements.
Accessibility
The level of accessibility of these systems varies based on their deployment. On-premises setups might face more access limitations compared to their cloud-based counterparts.
Cost Structure
Custom-developed solutions typically require a significant upfront investment. This includes a fuel management system price, implementation, and subsequent maintenance, which the organization usually bears.
Implementation Time
The time to develop custom software is subject to the intricacy of the desired features and the overall development process, potentially leading to a more extended implementation period.
Scalability
While custom systems offer the potential for tailored scalability, adjusting or expansions might necessitate additional development efforts.
Updates and Maintenance
Managing updates, maintenance, and security predominantly falls on the organization. However, this can vary if the development team has a specific maintenance agreement.

Considerations for Choosing Between SaaS and Custom-Made
Cost Considerations
Due to their lower initial costs, organizations with limited budgets often prefer Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) systems. However, organizations that can invest more upfront may choose custom software. Custom software offers bespoke functionalities tailored to specific needs. In other words, SaaS systems are a cost-effective option for those looking for a basic set of features. On the other hand, custom software is a more comprehensive solution that offers personalized features and tools.
Deployment Speed
Software as a Service (SaaS) solutions are an excellent option for organizations that require quick implementation. These solutions can be deployed quickly and efficiently, which is ideal for organizations that must get up and running as soon as possible. On the other hand, developing and deploying custom solutions can be more time-consuming. This is because custom solutions tend to be more complex and require a higher level of customization to meet the organization’s specific needs.
Flexibility in Design
Custom solutions offer a high level of flexibility, allowing for tailoring numerous features and integration capabilities to specific needs. On the other hand, SaaS solutions may have some limitations regarding customization. However, they benefit from continuous updates that the service provider provides, ensuring that the software remains up-to-date with the latest features and security patches.
Maintenance and Support
SaaS models provide maintenance and support, reducing the workload on IT teams. Custom solutions require internal or external maintenance and support, leading many to choose SaaS for its streamlined and cost-effective approach.
Scalability Features
Software as a Service (SaaS) systems can be easily adjusted to varying numbers of users, making it easy to scale up or down as required. This flexibility allows businesses to adapt quickly to changing demands without extensive development or customization. However, development teams can create custom systems for enterprises with unique requirements to meet their needs precisely. While this approach may require further development, it can provide a tailored solution that suits their needs.
Decision Factors
The decision between opting for a SaaS fuel management system for fleet and a custom-made solution hinges on the organization’s particular needs, budgetary constraints, and the value placed on control and customization.
How To Build a Fuel Management System?
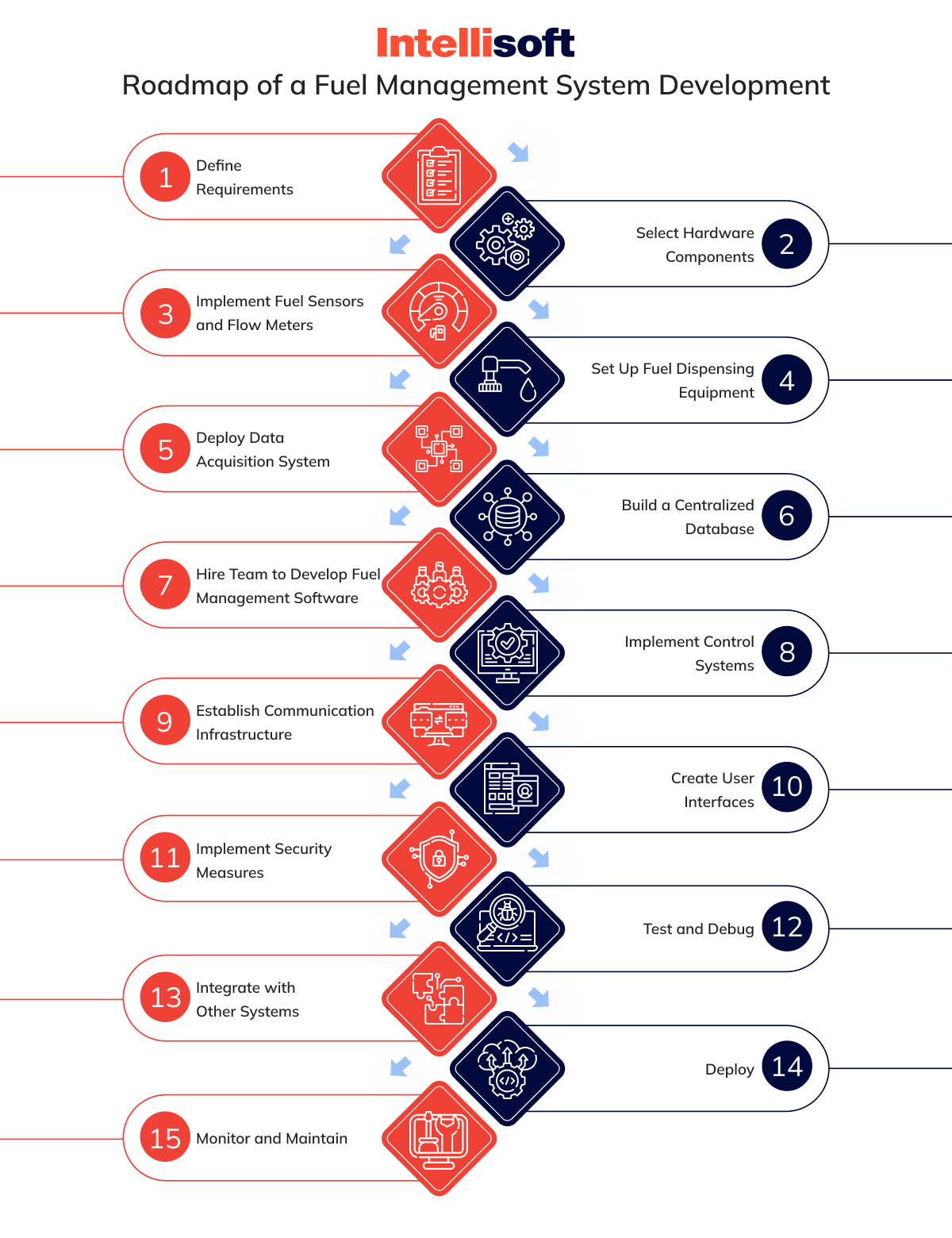
Designing a fleet fuel management system necessitates the integration of various hardware and software components. A fundamental framework for creating a basic solution is outlined below. However, it is essential to note that the system’s intricacy is subject to specific requirements and can vary accordingly.
Define Requirements
When developing fuel management software, it’s important to identify essential features and critical requirements such as the number of fueling stations and fuel types. Also, consider system integration, security measures, and reporting needs. This ensures the software meets organizational needs while providing high functionality and security.
Select Hardware Components
It’s crucial to consider carefully which hardware components to include in your system. You should focus on choosing key components that meet your system’s needs, such as sensors, flow meters, and dispensers. It’s equally vital to ensure that all the selected hardware components are compatible with one another and can work together seamlessly.
Implement Fuel Sensors and Flow Meters
Installing fuel sensors in the storage tanks is recommended to keep track of fuel levels. These sensors can accurately measure the amount of fuel and provide real-time data. Besides. incorporating flow meters into dispensers or pipelines can help measure the fuel flow accurately.
Set Up Fuel Dispensing Equipment
To set up a fuel station, you should install fuel dispensers and equip them with electronic systems that regulate dispensing. Besides, the dispensers should implement user interfaces to enable customers to initiate transactions quickly.
Deploy Data Acquisition System
Establishing a system that can gather information from various sources, such as sensors, meters, and dispensers, is crucial. Once this system is in place, it’s essential to focus on data processing to ensure that the solutions can efficiently process and structure the data for in-depth analysis.
Build a Centralized Database
To improve data management, create a unified database that stores all relevant information centrally. Prioritize security and scalability by implementing robust security features and designing the database for future growth and new data sources.
Hire Team To Develop Fuel Management Software
Forming a specialized team dedicated to creating fuel consumption monitoring software is recommended. The team should focus on data processing, analysis, and visualization. Essential features to consider in the software include capabilities for tracking transactions, managing inventory, generating reports, and conducting analytics.
Implement Control Systems
To manage fuel dispensing safely and efficiently, establish regulatory control systems. Monitor tank levels, regulate access to fuel stations, and manage fuel dispensing. Incorporate robust security protocols with access control measures to ensure system safety and security.
Establish Communication Infrastructure
When developing a system, implementing efficient data transfer protocols is vital to creating effective communication networks between components. Prioritize reliability and security by safeguarding against potential threats or vulnerabilities that could compromise data integrity or confidentiality. This ensures smooth and effective system functionality, resulting in an effective and resilient system.
Create User Interfaces
Creating diverse user interfaces that cater to different platforms, such as web-based dashboards, mobile apps, and desktop applications, is essential. While crafting these interfaces, focusing on usability and information delivery is crucial. This means the interfaces must have a user-friendly design that delivers critical information and functionalities effectively to the users.
Implement Security Measures
Incorporate robust security features like authentication methods to restrict unauthorized access. Implement strong encryption and secure communication protocols to enhance system security. These measures can help protect sensitive information and improve overall security posture.
Test and Debug
It is essential to conduct comprehensive testing to ensure the fuel consumption monitoring system is reliable and accurate. This includes executing extensive tests to detect and rectify any glitches or problems in the system. In addition to this, the system should be validated in various scenarios, such as testing it under multiple conditions, to confirm its dependability and precision.
Integrate with Other Systems
Integrate your software with other critical business systems, such as fleet management or accounting software. This integration allows for improved visibility and control over expenses and ultimately helps to optimize your overall business operations.
Deploy
Implement the finalized version of the fuel monitoring system to make it fully functional and available for practical purposes.
Monitor and Maintain
It is crucial to implement monitoring tools to ensure your system’s smooth and uninterrupted functioning. These tools will allow you to keep track of the system’s health and performance continually, detecting any issues or problems that may arise. Besides, developing a maintenance plan that includes regular updates, patches, and hardware upkeep is paramount. This will help keep your system up-to-date and functioning optimally, reducing the chances of unexpected glitches or malfunctions.
Developing Fuel Management Systems With IntelliSoft
By adopting such a system, you can significantly cut down on your expenses over time by reducing fuel wastage, theft, and misuse. Such a system empowers you with precise, up-to-the-minute information that can skyrocket your business operations to new heights of efficiency and profitability. With accurate data at your fingertips, you can make informed decisions on streamlining your overall business operations.
At IntelliSoft, we represent a comprehensive approach to optimizing fuel usage, enhancing operational efficiency, and ensuring environmental compliance. By carefully implementing each phase – from defining requirements to testing and debugging – we provide a robust, secure, and efficient solution tailored to the specific needs of any organization. With a focus on innovation and user-friendly design, IntelliSoft will stand as a reliable partner in integrating a fleet fuel management system.
If you want to jump in a rocket and lead your business to the stars, please contact us and speak with a specialist.