Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) offers a lifeline for businesses when disaster strikes. It ensures that both physical and virtual servers are replicated and hosted, ready to switch over seamlessly if your primary systems fail. By adopting cloud based disaster recovery, you not only minimize downtime but also speed up recovery, making sure your business bounces back faster than ever.
In recent years, DRaaS has surged in popularity. As companies grow increasingly conscious of data security, many are turning to third-party providers for their disaster recovery (DR) planning. In fact, the DRaaS market was valued at $11.5 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow by 22% in 2024, according to a report by Global Market Insights.
This post delves into cloud disaster recovery: how it operates, its advantages and challenges, and how to plan effectively for disasters within cloud computing. At IntelliSoft, we’ve assisted numerous businesses in adapting and securing their operations with our cloud services. Let us be your guide on this journey to unshakeable business resilience. So, fasten your seatbelts and prepare for an in-depth exploration of cloud-based DRaaS—it could be the game-changer your business is looking for!
Table of Contents
What is Disaster Data Recovery?
Your company’s data is priceless and irreplaceable. What would you do in an emergency situation? How can you protect the integrity of your data and preserve its safety even amidst the chaos? Disaster Data Recovery is a carefully designed protocol to retrieve and reinstate lost, compromised, or damaged data following an unpredictable disaster. It is the safety protocol your company needs to safeguard its data from the unexpected quakes of the digital world.

Disaster Recovery in the Cloud
Digital disasters always come without warning. To keep things from descending into chaos, you need a well-defined set of policies and procedures. This is where cloud disaster recovery shines. It’s a strategy, a master plan designed to protect organizations from the cataclysmic effects of data loss after a disruptive event.
With cloud computing, disaster recovery transforms into a less daunting and more manageable task. Think of it as having an ace up your sleeve, a reliable fallback when the odds aren’t in your favor. Cloud based disaster recovery can be orchestrated through strategies like implementing a sturdy backup mechanism or even deploying multiple servers across various geographical zones. This approach minimizes the potential damage that could arise from a single cataclysmic event.
Importance of Disaster Recovery
In the modern world, businesses and organizations heavily rely on digital data and IT systems. This data might include critical information such as customer details, financial records, project data, and operational processes, among others. IT systems, on the other hand, may host business applications, communication systems, and other essential tools for day-to-day business activities.
Disaster recovery isn’t merely a data recovery mechanism – it is your business’s lifeline when navigating data loss and service disruptions. The cornerstone of a good cloud based disaster recovery plan hinges on two parameters: recovery time objective (RTO) and recovery point objective (RPO).
RTO sets the clock ticking—it defines how long you can afford to be in the dark after a disaster, similar to how long a power outage can last before causing significant disruptions. RPO, on the other hand, sets the coordinates for your time-traveling data recovery mission. It defines how much data you can afford to lose between backups, determining how far back in time you need to journey to recover the lost data.
Here are some of the reasons why disaster recovery is essential:
- Business Continuity
In case of a disaster, your primary goal is to keep the business running or to resume operations as quickly as possible. The longer a business is offline, the more severe the financial and reputational damage. - Data Protection
With the rising trends in digital transformation, data has become one of the most valuable assets for businesses. A disaster recovery plan ensures that this critical information is protected and can be restored in case of any unfortunate event. - Customer Trust
Downtime can erode customer trust in your ability to provide services or products. In contrast, a robust disaster recovery plan can strengthen their trust, knowing that your company is prepared for any incidents. - Regulatory Compliance
Certain industries are required by law to have disaster recovery plans in place to protect sensitive data (like healthcare or financial services). - Cost Savings
While setting up a disaster recovery plan requires an investment, the cost of not having one can be significantly higher when a disaster strikes, due to lost business, recovery costs, and potential regulatory fines.
Types of Disasters You Need to Be Ready For
Different types of natural disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods, are uncontrollable forces of nature that can wreak havoc on your physical infrastructure. But disasters aren’t always Mother Nature flexing her muscles. Power failures, as mundane as they sound, can be an Achilles’ heel, causing substantial disruptions. Similarly, hardware failures can leave your business in the lurch.
We also have human error. When it comes to your business data, these errors or accidents can have far-reaching repercussions. And last but not least, cyber-attacks and insider threats. People armed with malicious intent can compromise your data and disrupt your operations.
By now, you’re probably realizing that having a robust disaster recovery plan isn’t just an optional extra—it’s essential. Having a carefully designed disaster recovery plan is crucial for addressing unexpected events that could potentially harm your company’s IT infrastructure. It ensures a methodical response to mitigate the impact of such incidents.
Disaster Recovery Strategies in Cloud Computing
The significance of cloud based disaster recovery strategies is unparalleled in the realm of data management. By balancing preventive, corrective, and detective measures, these strategies become key to ensuring business continuity. So, let’s break down these three major components.
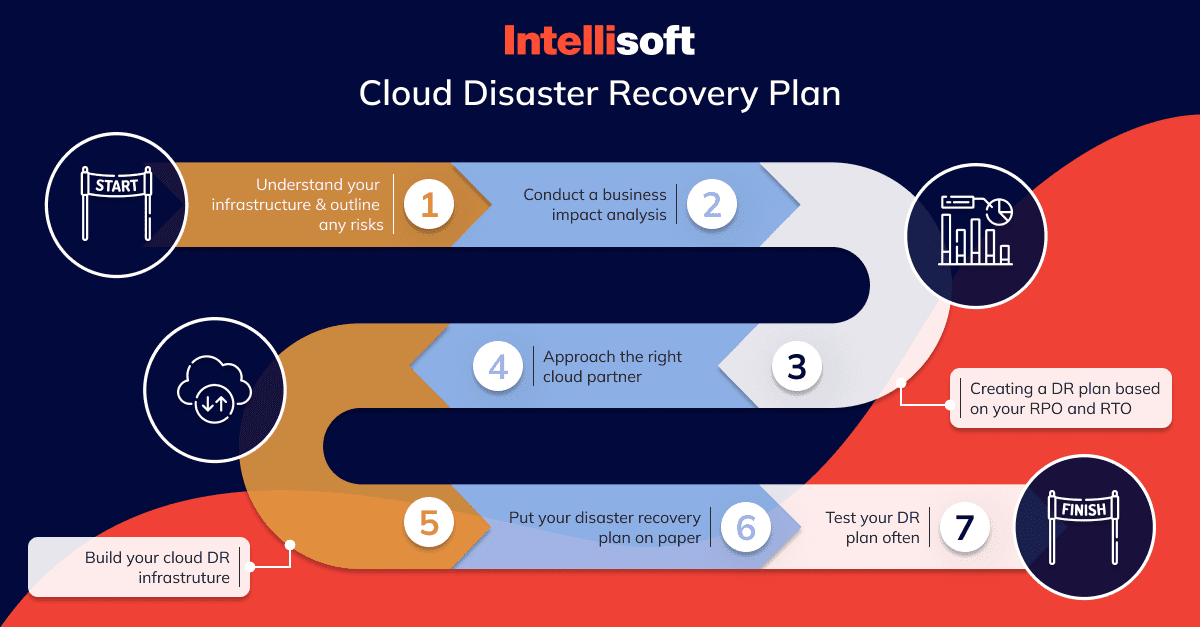
Preventive Measures
Preventive measures serve as the first line of defense in any disaster recovery plan. They incorporate actions and systems put in place to halt disasters from happening in the first place. Within the cloud computing environment, preventive measures often involve regular system checks, which allow for early detection of potential system malfunctions and can mitigate risks before they escalate into full-blown disasters.
Moreover, building and maintaining robust firewalls, alongside effective antivirus software, provide an additional shield against cyber threats. These technologies operate as gatekeepers, controlling access and protecting the system from unauthorized intrusion.
Corrective Measures
Despite the robustness of preventive measures, there may be instances when unexpected disasters breach these initial defenses. This is when corrective measures are crucial. These measures focus on restoring systems after a disaster has occurred, minimizing downtime and business disruption.
A crucial corrective action is the implementation of an effective backup system. Having a solid backup strategy ensures that, even in the event of data loss, a recent copy of that data is available and ready to be restored, minimizing the overall impact on business operations.
Detective Measures
Detective measures focus on identifying and monitoring system vulnerabilities that may lead to potential disasters. Through constant system analysis, these measures facilitate the early detection of abnormal activities or potential security threats.
Within the scope of cloud computing, detective measures could include continuous network monitoring, regular penetration testing to expose potential security weaknesses, and the deployment of intrusion detection systems. These systems are capable of alerting the system administrators of any unauthorized access attempts, allowing them to take prompt action.
Together, these preventive, corrective, and detective measures form a comprehensive disaster recovery strategy. They work in synergy to maintain system integrity and to ensure that your business can weather any storm, providing the peace of mind that comes with knowing your data and operations are well-protected.
Related readings:
- What is Cloud Computing? Understanding the Basics, Services and Benefits
- SaaS Security Tips and Checklists: Best Practices To Protect Your SaaS Application
- Implementing Offline Data Synchronization in Logistics Applications
- What Are the Security Risks of Cloud Computing? Threats & Solutions
- Become a Master of Tech Due Diligence: a Comprehensive Guide
Role of Cloud Providers in Disaster Recovery
In our data-driven world, where information is as valuable as gold, protecting it from unforeseen events is of paramount importance. The role of cloud providers in disaster recovery has grown significantly, with automated cloud based disaster recovery solutions playing an integral part in the backup and recovery process.
Automated cloud based disaster recovery services are absolutely necessary for safeguarding your data. These services capture snapshots of your data at regular intervals and store them securely in the cloud. In the event of a disaster, your organization can quickly access these backups and restore the system to its previous state. The beauty of automated cloud backup lies in its simplicity, efficiency, and the freedom it provides from the manual task of data backup.
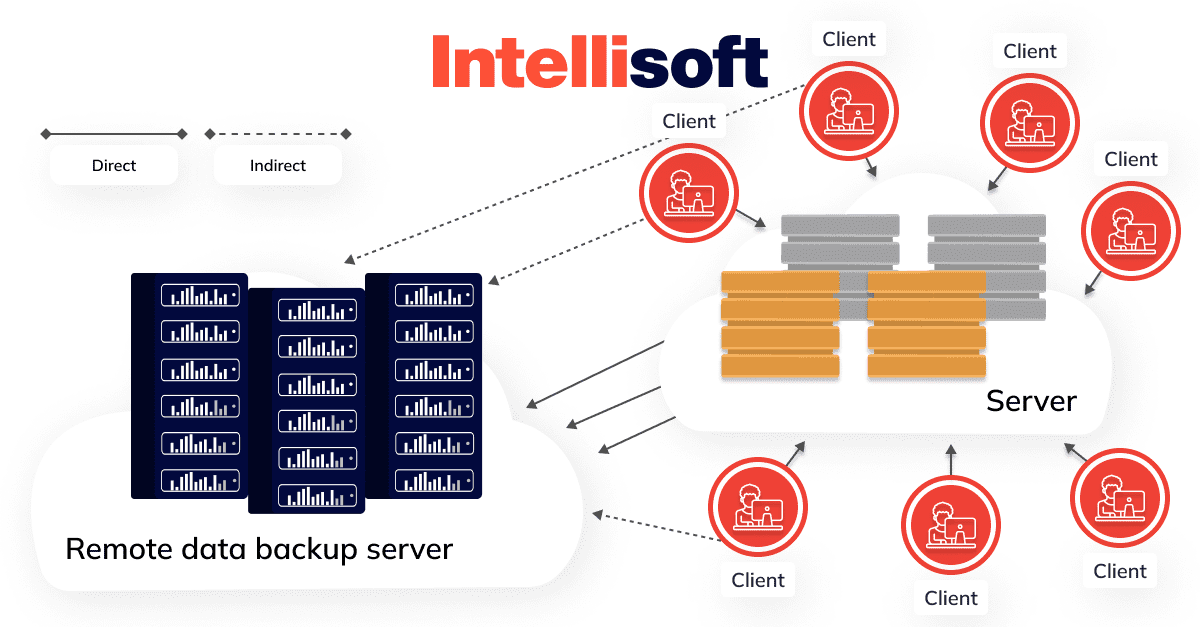
Gearing Up for a Crisis: What is Disaster Recovery as a Service?
But what if we could take this a step further? Enter Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS), an innovative form of cloud-based disaster recovery that is transforming how businesses approach data protection.
DRaaS essentially involves the replication and hosting of physical or virtual servers by a third-party provider to facilitate failover in the event of a disaster. It’s like having a doppelgänger of your entire IT infrastructure safely tucked away at a third-party site, ready to step in and take over operations at a moment’s notice should a disaster occur.
DRaaS allows an organization to back up not just its data, but its complete IT infrastructure in a third-party cloud computing environment. This gives you the double advantage of not just preserving your data, but also ensuring that essential cloud based disaster recovery services provided to you remain available during and after a disaster.
One of the standout advantages of DRaaS is that it reduces the capital expenditure involved in disaster recovery. The organization doesn’t have to own all of the resources or handle all of the management for disaster recovery. It’s all taken care of by the cloud provider. You get to leverage the infrastructure and expertise of the provider at a fraction of the cost it would take to set up a similar disaster recovery operation in-house.
DRaaS represents a giant leap forward in disaster recovery. It brings robust, affordable, and efficient disaster recovery within the reach of even small and medium enterprises. The question, therefore, is not whether your organization can afford to invest in DraaS, but whether it can afford not to.
Behind the Scenes: How Does DRaaS Work?
While the benefits of DRaaS sound compelling, it’s also crucial to understand how this service works behind the scenes. At its core, DRaaS operates by replicating and hosting servers in a third-party vendor’s facilities, creating a secondary infrastructure that’s ready to spring into action when needed.
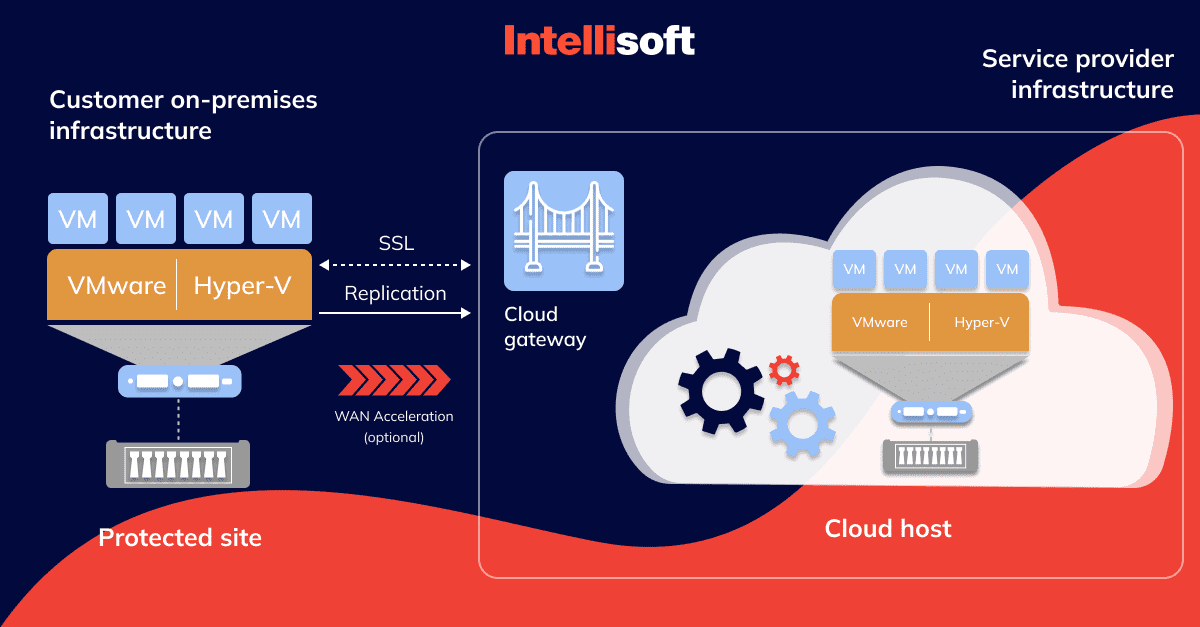
Here’s the simplified step-by-step process:
Step 1. Replication
The initial phase involves the replication of your servers and data. This is done either by duplicating the data in real time, or by taking regular snapshots of your data and servers.
Step 2. Storage
The replicated data and servers are then stored securely in the third-party provider’s cloud infrastructure. This cloud storage is typically distributed across multiple geographically separate locations, ensuring that a disaster in one location doesn’t affect the replicated data.
Step 3. Activation
In the event of a disaster, the DRaaS provider springs into action. The system automatically, or manually, depending on the specifics of your service, switches over to the replicated servers, effectively creating a ‘failover.’
Step 4. Restoration
Once the disaster has been resolved and the primary servers are back online, the system ‘fails back,’ transferring the operations from the DRaaS provider’s servers back to the primary servers. The changes made during the disaster period are synchronized to ensure data continuity.
Step 5. Continuous Monitoring
Throughout this process, the DRaaS provider is continuously monitoring the system, checking for any signs of potential disasters and ensuring that the replication is up-to-date.
What Is Failover/Failback?
Failover and failback are vital strategies in the world of Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS), equipping third-party vendors with the tools they need to keep their clients’ operations running smoothly, no matter the crisis. Failover kicks in when the main system crumbles—be it from a power outage, cyberattack, or other disruptions. This process seamlessly shifts IT operations to a backup system, ensuring continuity.
Failback is the next step, where everything switches back to the original system once it’s back up and running perfectly. In the DRaaS framework, this might mean that a vendor switches a client’s operations from their primary data center to a secondary, fully-equipped site in the blink of an eye. Done right, these transitions are so smooth that users might not notice they’ve moved to a backup system, maintaining uninterrupted service and peace of mind.
Diverse DRaaS Plans Tailored for You
Like most cloud-based services, DRaaS providers typically offer several plans to cater to a variety of business needs. While the specifics can vary between providers, two of the most common models are the traditional subscription model and the pay-per-use model.
Subscription Model
Under the traditional subscription model, businesses pay a fixed monthly or annual fee for a pre-agreed package of services. This package usually includes a certain amount of storage, processing power, and bandwidth. The benefit of this model is that businesses can accurately budget for cloud-based disaster recovery service cost and have guaranteed access to the resources they need.
Pay-Per-Use Model
On the other hand, the pay-per-use model operates on a more flexible basis. Instead of a flat fee, businesses pay for the actual resources used during the disaster recovery period. This model can be more cost effective for businesses that have lower disaster risk or those that require significant resources only in rare disaster situations.
Choosing between these models, or perhaps a hybrid of the two, will depend on your organization’s specific needs, budget, and risk profile. Regardless of the model you choose, the important thing is that with DRaaS you can ensure business continuity and data protection, giving you peace of mind in our increasingly unpredictable digital landscape.
Weighing the Benefits: Advantages of DRaaS
Understanding the nuts and bolts of DRaaS is one thing, but the real question is, how can it truly benefit your organization? As it turns out, DRaaS packs a significant punch when it comes to advantages, especially when compared to traditional disaster recovery methods. Let’s look into some of the key benefits your organization could gain by implementing DRaaS.
Substantial Cost Savings
Possibly, one of the most significant advantages of DRaaS is the potential for considerable cost savings. Traditionally, organizations had to provision and maintain their own off-site disaster recovery environment. This scenario involved significant capital expenditure on infrastructure such as servers, storage, and networking equipment, not to mention the costs associated with securing and maintaining a physical site.
With DRaaS, these high upfront costs are essentially eliminated. DRaaS operates on a subscription model where the costs are spread over time, and you only pay for what you use. This means you can transform a large capital expenditure into a much more manageable operational expense.
Furthermore, because the DRaaS provider is responsible for maintaining the infrastructure, you can save on ongoing costs such as electricity, cooling, and maintenance. These savings can then be reinvested back into your core business, driving growth and innovation.
Time-Efficient and Streamlined Disaster Recovery
Another major advantage of DRaaS is the efficiency it brings to disaster recovery. Traditionally, implementing and testing a disaster recovery plan requires a considerable amount of time and resources. It involves researching best practices, designing a suitable plan, procuring and configuring the necessary infrastructure, and then conducting extensive testing to ensure the plan works as expected.
With DRaaS, much of this process is streamlined. The DRaaS provider has the expertise and resources to implement and manage the disaster recovery plan effectively. They handle the replication, storage, failover, and failback, freeing your IT workforce to focus on strategic tasks that add value to your organization. In a sense, it’s like having an expert team of disaster recovery specialists at your fingertips.
Additionally, because DRaaS providers are specialized in disaster recovery, they have likely invested in automation and efficiencies that most individual organizations could not afford to develop on their own. This means that the cloud based disaster recovery solution can often implement and test a disaster recovery plan more quickly and effectively than an organization could do internally.
The advantages of DRaaS are manifold. Not only does it offer potential cost savings and efficiency gains, but it also provides peace of mind, knowing that your organization’s critical data and applications are protected in the event of an accident. So, isn’t it time to consider DRaaS for your organization? With the ever-increasing reliance on digital infrastructure and the prevalence of cyber threats and natural disasters, a robust and efficient disaster recovery plan is not just an option—it’s a necessity.
What are Examples of Cloud Disasters?
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way we store and manage data, but it’s not without its risks. Even giants like AWS and Google can fall victim to unexpected disasters. Here are two notable incidents that underline the importance of robust disaster recovery plans:
2017 Amazon Outage
In 2017, a seemingly minor attempt to debug a billing issue by an Amazon employee took a dramatic turn. The employee accidentally shut down more servers than intended, triggering a cascading series of failures across multiple server subsystems. This domino effect led to a significant outage, locking thousands of users out of Amazon’s services for several hours. This incident serves as a stark reminder of the risks associated with relying solely on public clouds for disaster recovery.
2016 AWS Cloud Crash in Sydney
Fast forward to 2016, AWS’s Sydney operations faced a daunting challenge when a severe weather event knocked out power at a local utility provider. The outage lasted nearly ten hours and disrupted several Elastic Block Store volumes and Elastic Compute Cloud instances. This not only caused downtime for AWS but also impacted numerous large companies that depended on these services for critical operations.
Future of Cloud Based Disaster Recovery
As we have looked closer at the landscape of DRaaS and its crucial role in cloud computing, it is apparent that it has already transformed the way businesses manage their disaster recovery strategy. But the wheel of innovation never stops turning, and the future holds intriguing possibilities that may further revolutionize the disaster recovery domain. Two major developments that are likely to make a significant impact are the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and Artificial Intelligence (AI) into the disaster recovery process.
Backup Using IoT Devices
The Internet of Things (IoT) is no longer a fanciful concept from science fiction. It’s here, and it’s changing the way we live and work. With billions of IoT devices worldwide, from smart refrigerators to industrial sensors, the volume of data being generated is staggering. This data is not just useful for the immediate purpose it serves, but also provides a wealth of information that could be invaluable if a disaster strikes.
Future cloud-based disaster recovery for SMBs in cloud computing will likely involve using IoT devices for backups. These devices could capture real-time data from various points in a network, enabling businesses to have up-to-the-minute backups. This could significantly reduce the recovery point objective (RPO), ensuring minimal data loss in the event of a disaster.
Additionally, IoT devices could also play a role in disaster prediction and prevention. For instance, sensors could monitor the condition of hardware and predict potential failures, or environmental sensors could detect conditions such as heat or moisture that could lead to a disaster.
Using AI as a Part of Disaster Recovery
While IoT devices can provide extensive data, it’s the application of AI that can truly leverage this data for effective disaster recovery. AI possesses the capacity to swiftly and precisely examine vast quantities of data, identifying trends and making predictions that would be impossible for humans.
In the context of disaster recovery, AI could be used to analyze data from IoT devices and other sources to predict potential disasters before they happen. This would allow businesses to take preventive measures and minimize damage.
AI could also improve the efficiency of the disaster recovery process. For example, machine learning algorithms could be used to optimize backup schedules based on historical data, ensuring the most important data is always backed up first. AI could also automate the recovery process, reducing the recovery time objective (RTO) and minimizing disruption to services.
Moreover, AI could enhance the testing of disaster recovery plans. Through simulation and predictive analytics, AI could provide a detailed assessment of a plan’s effectiveness and suggest improvements, ensuring the plan is as robust and effective as possible.
The future of cloud based disaster recovery looks exciting. With the integration of IoT devices and AI, you can look forward to more efficient, effective, and proactive disaster recovery strategies. This will not only ensure better protection of crucial data but also contribute to your business continuity and resilience in an increasingly digital and connected world. Buckle up for the future because when it comes to disaster recovery, it promises to be a game-changer.
Making a Decision: Is DRaaS the Right Fit for You?
There’s an age-old saying in business, “One size doesn’t fit all.” This truth permeates every aspect of your operations, and it’s no different when it comes to selecting a disaster recovery solution. DRaaS, despite its numerous advantages, may not be the best fit for every organization. But the beauty of the digital age is in its flexibility and adaptability. So, let’s take a look into what kind of organization would benefit from DRaaS and examine the different models that cloud based disaster recovery service providers offer.
If your business handles large volumes of data, maintains a round-the-clock operational schedule, and views extended downtime as a business nightmare, then DRaaS could be your knight in shining armor. It’s like a sturdy safety net, poised to catch you when an unexpected disaster might otherwise cause a fall into the abyss of data loss.
However, the decision to embrace cloud-based disaster recovery services doesn’t end with a simple ‘yes’ or ‘no.’ It involves a deeper dive into the models that providers offer. Not all DRaaS solutions are created equal, and the one you choose should align with your business’s unique needs and capacities.
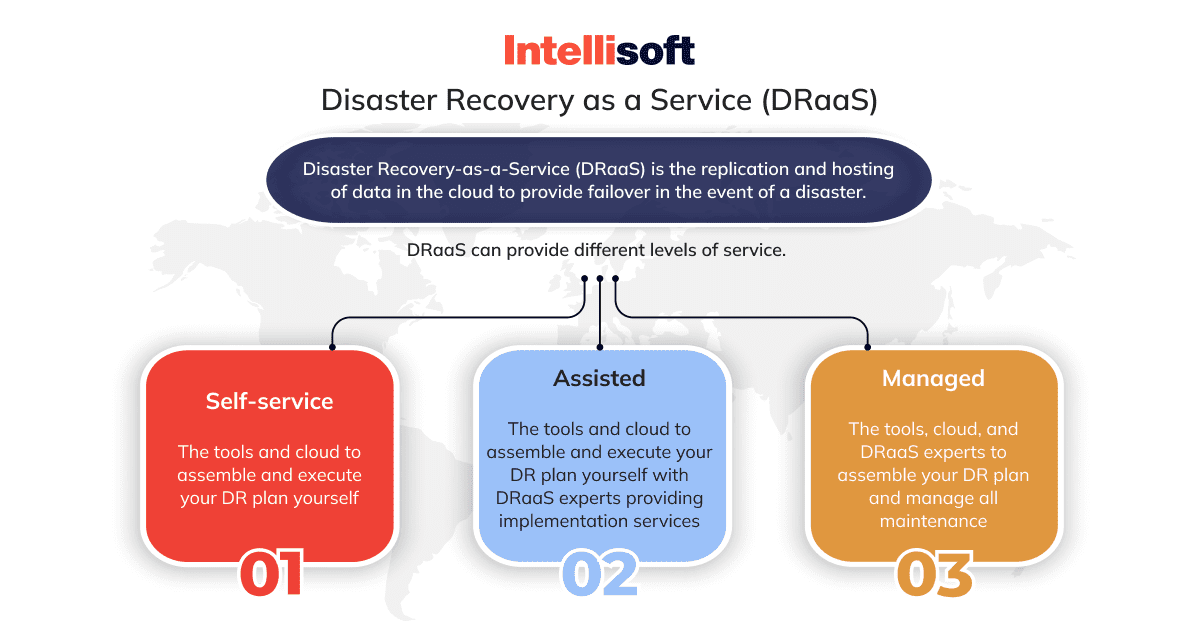
Managed DRaaS
Think of Managed DRaaS as a full-service restaurant. You sit back and enjoy your meal while the restaurant takes care of everything from cooking to cleaning. In the context of disaster recovery, this means that a third-party cloud based disaster recovery service provider takes on full responsibility for your disaster recovery strategy. From planning and implementing to testing and monitoring, they’ve got it all covered. This model is ideal if you lack the in-house expertise or resources to manage disaster recovery or if you prefer to focus on your core business areas.
Assisted DRaaS
Assisted DRaaS, on the other hand, is like a buffet service. You have a range of options, and you get to choose what you want. This model offers a blend of provider management and self-management. If you have unique or custom applications that could be tricky for a third-party provider to handle, you maintain responsibility for those aspects of your disaster recovery plan. It’s the best of both worlds, offering you support where you need it, and control where you want it.
Self-service DRaaS
Finally, we have Self-service DRaaS, which, much like its name suggests, is a DIY model. Here, you’re responsible for planning, testing, and managing your disaster recovery strategy. You can benefit from disaster recovery in virtualized cloud-based environments, often provided by the DRaaS provider. This model is a good fit if you have a robust in-house IT team and want to maintain full control over your disaster recovery process.
As you ponder these options, remember that the key to making the right decision is a thorough understanding of your business’s unique needs and resources. Consider factors such as the volume of your data, the nature of your applications, your in-house IT capabilities and, most importantly, the potential impact of downtime on your operations. When it comes to choosing DRaaS, making an informed decision can mean the difference between a small setback and a complete stop to your business operations.
Conclusion
Disaster recovery planning in cloud computing is essential for every organization, making the often-daunting tasks of data backup and recovery more flexible, scalable, and efficient. By tailoring recovery strategies to their specific needs, with Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs) in mind, businesses can craft near-bulletproof plans for handling cloud disasters.
Small and mid-sized companies are increasingly adopting Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) for its cost-effectiveness and operational efficiency. On the other hand, larger corporations often opt for cloud-based disaster recovery solutions that integrate both hybrid cloud environments and, sometimes, traditional on-premises data centers. This blended approach ensures comprehensive disaster recovery and continuous business operations.
The shift towards cloud solutions as the preferred alternative for IT service delivery continues to gain momentum. Cloud-based disaster recovery strategies enable organizations to safeguard their data and applications economically. The benefits are numerous: lower costs, scalability, flexible contractual terms, and notably enhanced business resiliency.
At IntelliSoft, we see ourselves as more than just cloud based disaster recovery service providers—we are your partners in success. Our managed IT services and support are designed to keep your business both resilient and agile, ready to recover swiftly from any disaster. We provide powerful, all-encompassing disaster recovery solutions, so you can concentrate on your core business activities.
Remember, in the competitive business arena, the show must go on, regardless of the challenges. With IntelliSoft steering your disaster recovery planning, you can be confident that your business will not only survive but also thrive in any circumstances. Feel free to reach out to us anytime; let us be your trusted guide in the dynamic world of digital resilience.