Have you noticed how some manufacturers seem to accelerate their operations while others struggle to keep up? According to McKinsey, digital transformation in manufacturing can increase throughput by 10% to 30%, improve the cost of quality by 10% to 20%, and cut machine downtime in half. Yet, despite these clear advantages, a PwC study found that only a third of manufacturers have moved beyond the planning stages of digital transformation.
What’s holding them back? Often, it’s a lack of knowledge – knowing where to begin, which digital manufacturing solutions are right, or how to make the transition seamless. This article breaks down the barriers, offering clear insights into the benefits of digital transformation, real-world examples, and the latest trends. Whether you’re exploring new ways to improve or ready to scale up, this guide will help you take practical steps toward success.
With 15 years of experience, IntelliSoft has been guiding companies through these critical changes, ensuring they stay ahead of the curve. Let’s unlock what digital transformation can do for your business.
Table of Contents
Why Manufacturers Need Digital Transformation
The drivers of digital transformation in manufacturing are massive, but the journey to realizing its full impact is often more complex than expected. IDC forecasts that by 2027, global spending on DX will exceed $3.4 trillion, with discrete manufacturing taking the lead. Manufacturers are clearly recognizing the importance of digital solutions, with a Forrester Consulting study showing that over 90% of industry leaders consider DX crucial for their future success.
However, the reality behind these bold moves is more nuanced. While companies are eagerly embracing digital tools and AI, the results don’t always match the expectations. Harvard Business Review found that despite 89% of large organizations worldwide being involved in digital and AI transformations, they have only captured 31% of the anticipated revenue lift and just 25% of the expected cost savings.
So why the gap? It’s not for lack of effort or intention. The problem lies in how these digital strategies are implemented. Manufacturers are often missing the mark in execution – investing in technology but failing to fully integrate it into their workflows, processes, and culture. This leaves significant opportunities on the table, with many companies wondering why their digital transformations aren’t delivering the promised results.
The key to closing this gap isn’t just technology, but understanding how to effectively translate these tools into real-world value – making sure that every step of the digital journey is aligned with clear goals and practical execution. As we dive deeper, we’ll explore digital transformation examples in manufacturing and how manufacturers can turn those investments into actual gains, ensuring that the promises of DX are fully realized.
What is Digital Transformation in Manufacturing?
Digital transformation in manufacturing goes beyond simply upgrading technology – it’s about rethinking and reinventing every aspect of the production process.
What are the key technologies and trends enabling digital transformation in manufacturing? It involves integrating digital technologies like AI, IoT, automation, and data analytics into manufacturing operations to drive greater efficiency, improve product quality, and enhance decision-making. This transformation reshapes how manufacturers design, produce, and deliver products, making their operations smarter, faster, and more agile.
The potential impact is huge. By embracing digital transformation in the manufacturing industry, manufacturers can streamline production, reduce downtime, minimize waste, and better respond to market demands. It’s not just about adopting new technologies – it’s about embedding them into the fabric of your business to unlock unprecedented levels of performance and innovation.
Understanding the Three Stages of Digital Transformation
While the benefits of digital transformation are clear, getting there requires navigating through three essential stages:
Planning and Strategy Development
This is where it all begins. Manufacturers need to identify their goals, understand which technologies are best suited for their operations, and build a roadmap for digital integration. This stage often involves aligning teams, working with an executive master in manufacturing automation and digital transformation, securing leadership buy-in, and setting KPIs to measure success. Surprisingly, this is where many companies get stuck – analysis paralysis or vague strategies often lead to slow progress, keeping them from moving beyond the drawing board.
Implementation and Adoption
Once the strategy is in place, it’s time to implement. This stage involves deploying new technologies – whether it’s smart machines, connected systems, or AI-driven analytics—and training employees to embrace these tools. Here, many manufacturers face resistance to change or stumble with system integration, leading to partial adoption or operational disruptions. The key is effective change management and ensuring the workforce is ready to leverage these new systems to their fullest potential.
Optimization and Scaling
The final stage is about refining and scaling. After successful implementation, manufacturers must continually optimize their operations to extract the full value from their digital tools. This means monitoring performance, gathering data insights, and making adjustments to improve efficiency, cost savings, and product quality. At this stage, the focus shifts from technology deployment to continuous improvement, ensuring the business remains competitive and innovative in a rapidly evolving landscape.
Related Readings:
- Key Trends Shaping Digital Transformation You Shouldn’t Miss
- App Development Costs Breakdown: How to Estimate Expenses for Your Next App Project
- Migrating Legacy Systems: Essential Stages and Tips from Pros
- Enterprise Applications Development / Enterprise App Development Trends
- Why Does Your Tech Start-up Need a Business Plan and How to Create One?
Top 6 Benefits of Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
Digital transformation offers manufacturers a unique opportunity to completely revamp their operations, driving efficiency, reducing costs, and positioning themselves for long-term success. By adopting smart technologies like IoT, AI, and data analytics, companies can not only keep up with the competition, but also lead the way in innovation. Below, we explore the top six benefits of digital transformation in manufacturing industry, providing real-world examples of how these changes can impact your business.
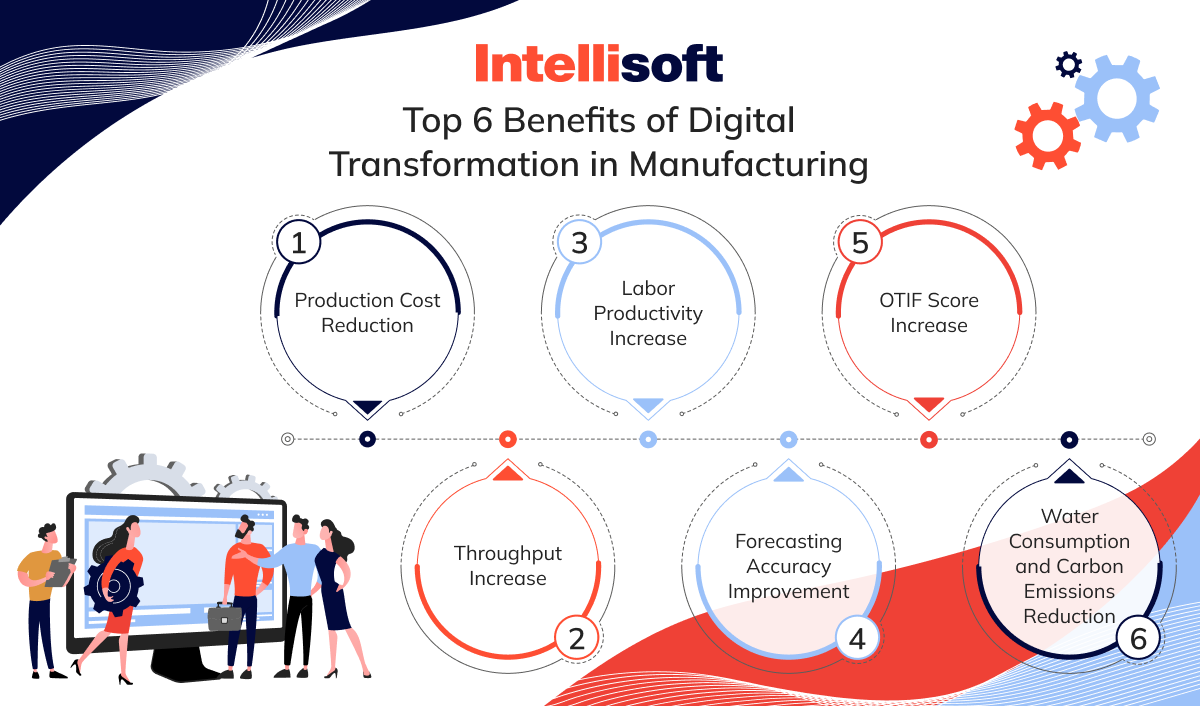
Production Cost Reduction
One of the most immediate and tangible benefits of digital transformation of business processes in manufacturing is the reduction in production costs. By integrating automation, AI-powered predictive maintenance, and real-time analytics, manufacturers can streamline their operations, cut down on waste, and optimize resource use.
For example, a major automotive manufacturer adopted AI-driven quality control systems that significantly reduced the number of defective products, saving millions in rework and scrap costs. Additionally, predictive maintenance allowed them to reduce downtime by scheduling repairs only when necessary, minimizing unnecessary expenses.
Throughput Increase
Increasing throughput is another major advantage of digital transformation in industrial manufacturing. By optimizing machine performance, automating repetitive tasks, and using real-time data analytics to make faster, better decisions, manufacturers can significantly boost production rates.
Take Siemens as an example. By leveraging digital twins – virtual models that simulate production processes – they were able to identify bottlenecks and make precise adjustments to their machinery, resulting in an increase in throughput without the need for additional resources.
Labor Productivity Increase
Digital transformation in manufacturing 2024 doesn’t just replace manual labor with machines – it enhances the productivity of the human workforce. By automating routine tasks, employees can focus on more value-driven activities, increasing overall labor efficiency.
For instance, a textile manufacturer implemented robotic process automation (RPA) to handle routine data entry and inventory management. This allowed their skilled workers to shift their focus to process optimization and innovation, ultimately improving overall productivity.
Forecasting Accuracy Improvement
Accurate forecasting is essential for staying competitive in a fast-paced manufacturing environment, and digital transformation in smart manufacturing can dramatically improve this aspect of business. By using AI and machine learning algorithms, manufacturers can predict demand more accurately, optimize inventory levels, and reduce excess stock.
A consumer electronics company, for example, utilized AI-driven demand forecasting to align production with market trends. This resulted in a reduction in excess inventory and improved delivery timelines by anticipating product demand more precisely.
OTIF Score Increase
On-Time, In-Full (OTIF) delivery scores are critical metrics in manufacturing, and digital transformation helps ensure that products are delivered on schedule and meet customer expectations. With the use of IoT sensors, advanced scheduling software, and real-time supply chain tracking, manufacturers can enhance the reliability of their delivery performance.
A food and beverage company implemented IoT-enabled logistics tracking, allowing them to monitor shipments in real-time and optimize delivery routes. As a result, their OTIF score improved, boosting customer satisfaction and reducing penalties for late or incomplete deliveries.
Water Consumption and Carbon Emissions Reduction
Sustainability is becoming an increasingly important focus in manufacturing, and digital transformation can play a key role in reducing environmental impact. By using data analytics and IoT to monitor resource consumption, manufacturers can minimize water usage, energy consumption, and carbon emissions.
For example, a chemical manufacturer adopted IoT-enabled monitoring systems that tracked their water consumption in real time. By adjusting their processes based on this data, they were able to reduce water usage and lower their carbon emissions, contributing to both environmental goals and cost savings.
Key Technologies That Drive Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
Digital transformation in manufacturing industry is fueled by a blend of cutting-edge technologies, each playing a crucial role in reshaping how products are made, monitored, and delivered.
From smarter machines to real-time data analytics, these technologies don’t just optimize operations – these digital transformation trends in manufacturing redefine the manufacturing experience, making it more efficient, sustainable, and innovative.
What are the key technologies that enable digital transformation in manufacturing?
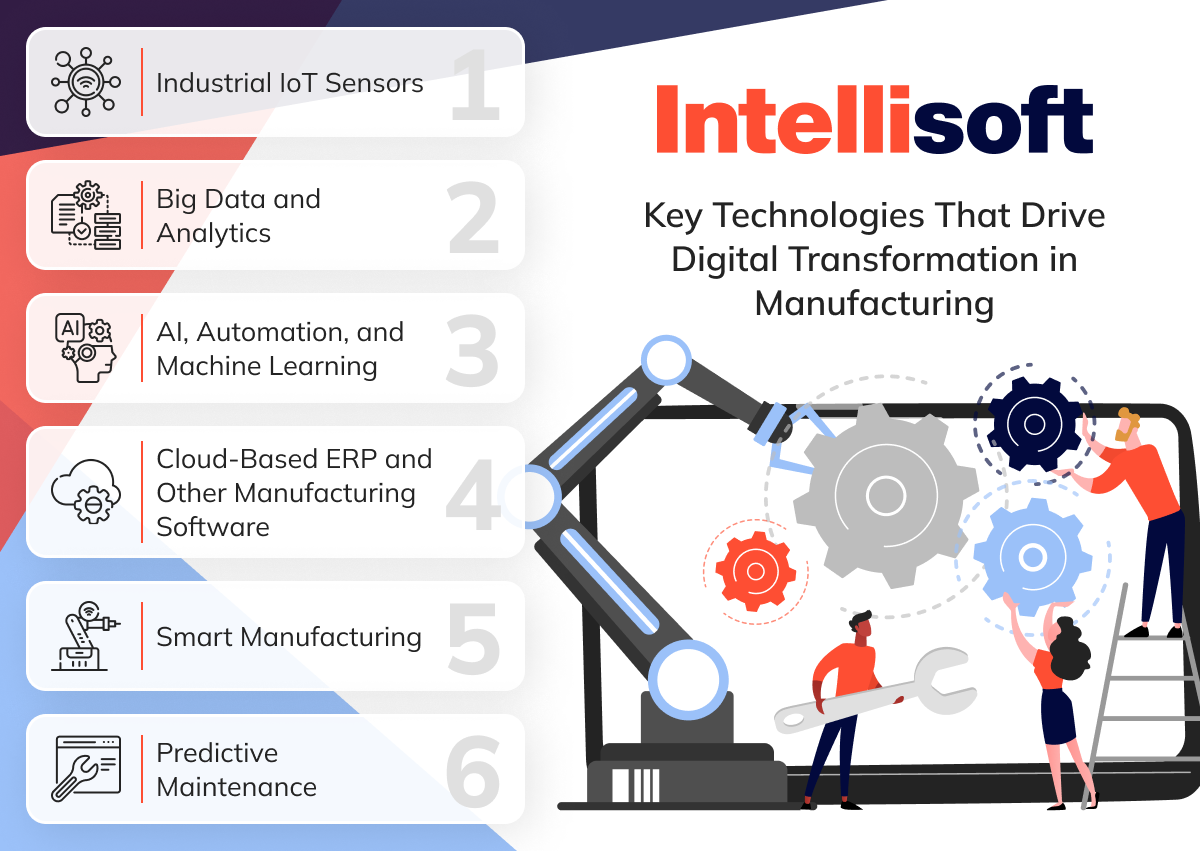
Industrial IoT Sensors
Imagine a factory where every machine, conveyor belt, and even the environment is connected, sending real-time data on performance, wear, and conditions. That’s the power of Industrial IoT (Internet of Things) sensors. These tiny devices collect and transmit data on everything from temperature and vibration levels to machine health, enabling operators to make informed decisions instantly.
For example, an aerospace manufacturer equipped their machines with IoT sensors that monitor temperature and pressure during production. By analyzing this data, they were able to catch potential defects early, drastically reducing rework and improving product quality.
Big Data and Analytics
Big data and analytics turn the flood of information collected from IoT sensors into actionable insights. Instead of just having raw data, manufacturers can use advanced analytics to detect trends, optimize processes, and forecast future needs. This technology allows businesses to move from reactive to proactive decision-making.
A global electronics manufacturer, for instance, leveraged big data analytics to analyze customer demand trends and production rates. This not only helped them streamline their supply chain but also enabled more precise inventory management, reducing both waste and shortages.
AI, Automation, and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI), automation, and machine learning are revolutionizing the speed and accuracy of manufacturing processes. AI can predict machine failures; automation can handle repetitive tasks with precision, and machine learning algorithms can continually improve efficiency over time by learning from data.
A well-known car manufacturer implemented AI-powered robots on their assembly line. These robots can quickly adapt to new tasks and detect inefficiencies in real-time, allowing the factory to improve production speed without sacrificing quality. Meanwhile, AI algorithms used in digital transformation in automotive manufacturing forecast maintenance needs, preventing unexpected breakdowns.
Cloud-Based ERP and Other Manufacturing Software
Cloud-based enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and other manufacturing software are the backbone of digital transformation. These platforms centralize data from all parts of the factory – from inventory and finance to human resources – into one easily accessible cloud environment, making it easier for teams to collaborate and make data-driven decisions.
A footwear manufacturer used a cloud-based ERP to connect their global factories and supply chain operations. This allowed them to track every aspect of production in real-time, drastically cutting lead times and enabling quicker responses to market changes.
Smart Manufacturing
Smart manufacturing is where all these technologies come together. This level of integration allows for smarter decision-making, faster production, and highly customizable products. With smart manufacturing, factories can adapt to changing conditions on the fly, improving everything from production quality to customer satisfaction.
Take the example of a luxury watchmaker who implemented smart manufacturing to personalize their products. Customers can now design their watches online, and the factory automatically adjusts to produce one-of-a-kind items without sacrificing efficiency or speed.
Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance is one of the most impactful technologies in manufacturing, helping companies avoid costly downtime by predicting when a machine will fail before it happens.
For example, a packaging company used predictive maintenance to monitor its conveyor systems. By receiving early warnings about potential failures, they were able to schedule maintenance during off-hours, avoiding major production halts and saving the company millions in lost revenue.
Succesful Examples of Manufacturing Digital Transformation
Digital transformation in pharma manufacturing and other industries isn’t just a theoretical strategy – it’s being put into action by some of the world’s most innovative companies. Below are six digital transformation in manufacturing examples that demonstrate how leveraging technologies like IoT, AI, and digital twins can lead to dramatic improvements in efficiency, cost savings, and customer satisfaction. Let’s take a close look at each digital transformation in manufacturing case study..
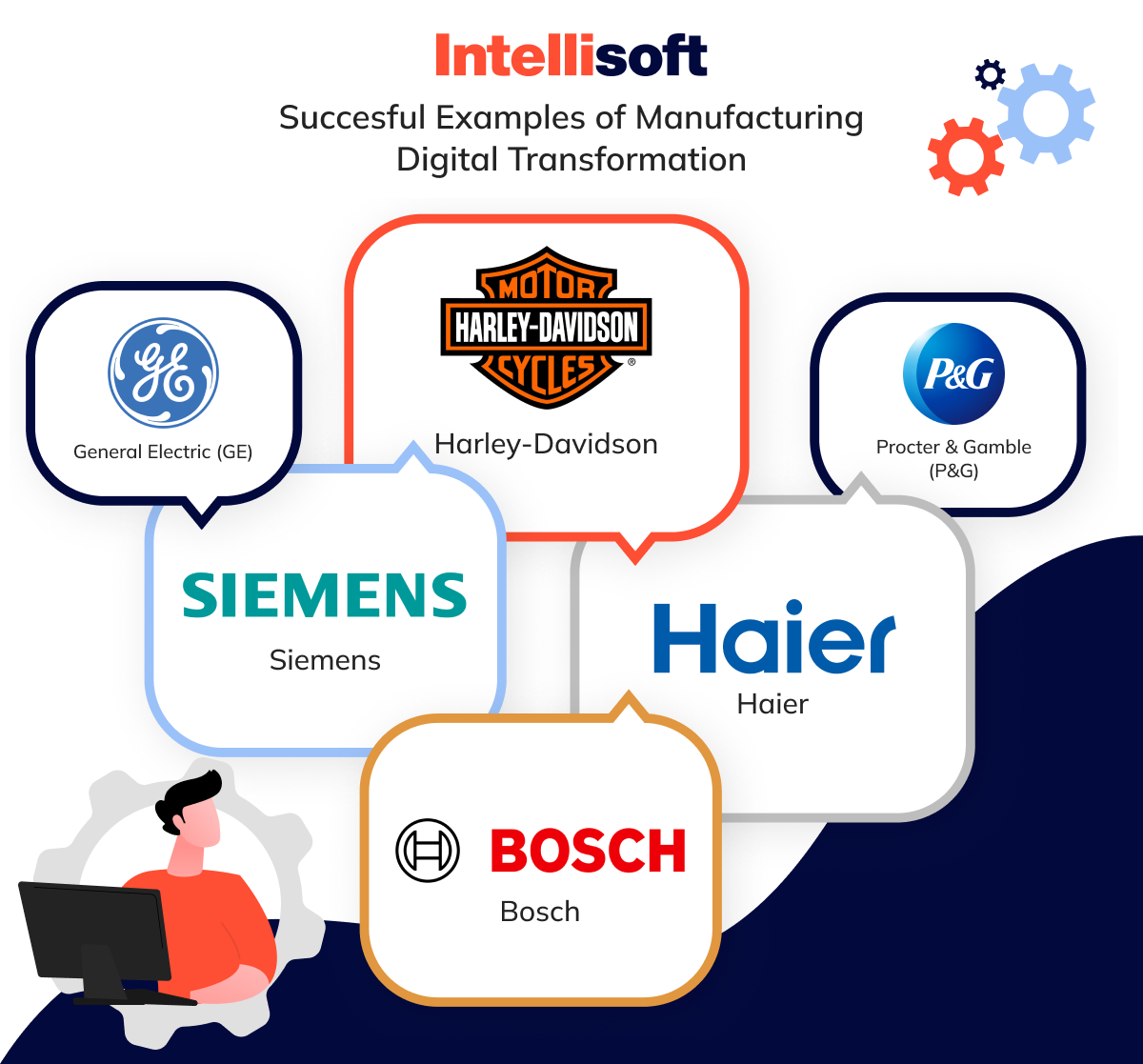
General Electric (GE)
GE pioneered the use of its Predix platform, a cloud-based Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) solution that connects industrial machines to the cloud. This allows for real-time data collection, analytics, and predictive maintenance across its manufacturing facilities.
With Predix, GE improved operational efficiency and reduced unplanned downtime by 10-20%. Additionally, the platform helped GE lower maintenance costs by 15-20% across various sectors like aviation and energy, allowing the company to run smarter, more agile operations.
Siemens
Siemens is at the forefront of digital manufacturing with its investment in digital twin technology and the MindSphere platform. By using digital twins – virtual replicas of physical machines – Siemens simulates and tests production processes before implementing them on the factory floor.
This innovative approach cut product development time by 30%, allowing Siemens to bring products to market faster while maintaining high-quality standards. The enhanced flexibility in production also led to significant cost savings and a more agile manufacturing process.
Bosch
Bosch adopted its “Bosch Industry 4.0” strategy, incorporating automation, data analytics, and machine learning across its manufacturing operations. Additionally, Bosch rolled out predictive maintenance systems, allowing its machines to signal when they need servicing, well before failure.
Bosch saw a 25% boost in productivity and managed to reduce energy consumption by 30%. Furthermore, predictive maintenance contributed to less machine downtime and lower maintenance expenses, helping Bosch run more sustainably while increasing output.
Harley-Davidson
Harley-Davidson revamped its York, Pennsylvania, manufacturing facility by implementing a flexible, data-driven production system. Using real-time analytics, robotics, and digital supply chain management, the company achieved impressive efficiency gains.
Harley-Davidson reduced its production cycle from 21 days to just 6 hours, marking a remarkable 200% increase in production throughput. This agile system also enabled Harley-Davidson to offer mass customization, allowing customers to personalize their motorcycles like never before.
Haier
Haier, a leading Chinese home appliance maker, turned its factories into smart production hubs using IoT and AI. By introducing the COSMOPlat platform, Haier created a fully connected manufacturing ecosystem that links suppliers, production lines, and consumers in real time.
Haier cut its production costs by 20% and halved lead times, drastically improving speed-to-market. Moreover, Haier’s transformation empowered them to offer mass customization, enabling customers to design their products while keeping production efficient and scalable.
Procter & Gamble (P&G)
P&G took a data-driven approach to manufacturing, using advanced analytics and automation to optimize its global production processes. By implementing digital twins and predictive analytics, P&G enhanced both product quality and supply chain efficiency.
P&G’s transformation resulted in a 20% rise in production efficiency and a 30% reduction in energy usage, while also cutting down waste. These improvements helped P&G not only reduce costs, but also speed up their time-to-market, ensuring they remain competitive in the fast-moving consumer goods sector.
Digital Transformation Challenges in the Manufacturing Industry
While the potential rewards of digital transformation in manufacturing are immense, the path to achieving it is often fraught with obstacles. From financial limitations to resistance within the organization, manufacturers face several challenges of digital transformation in manufacturing that can slow or even derail their digitization efforts. What is the top challenge for digital transformation and IoT adoption in industrial manufacturing?
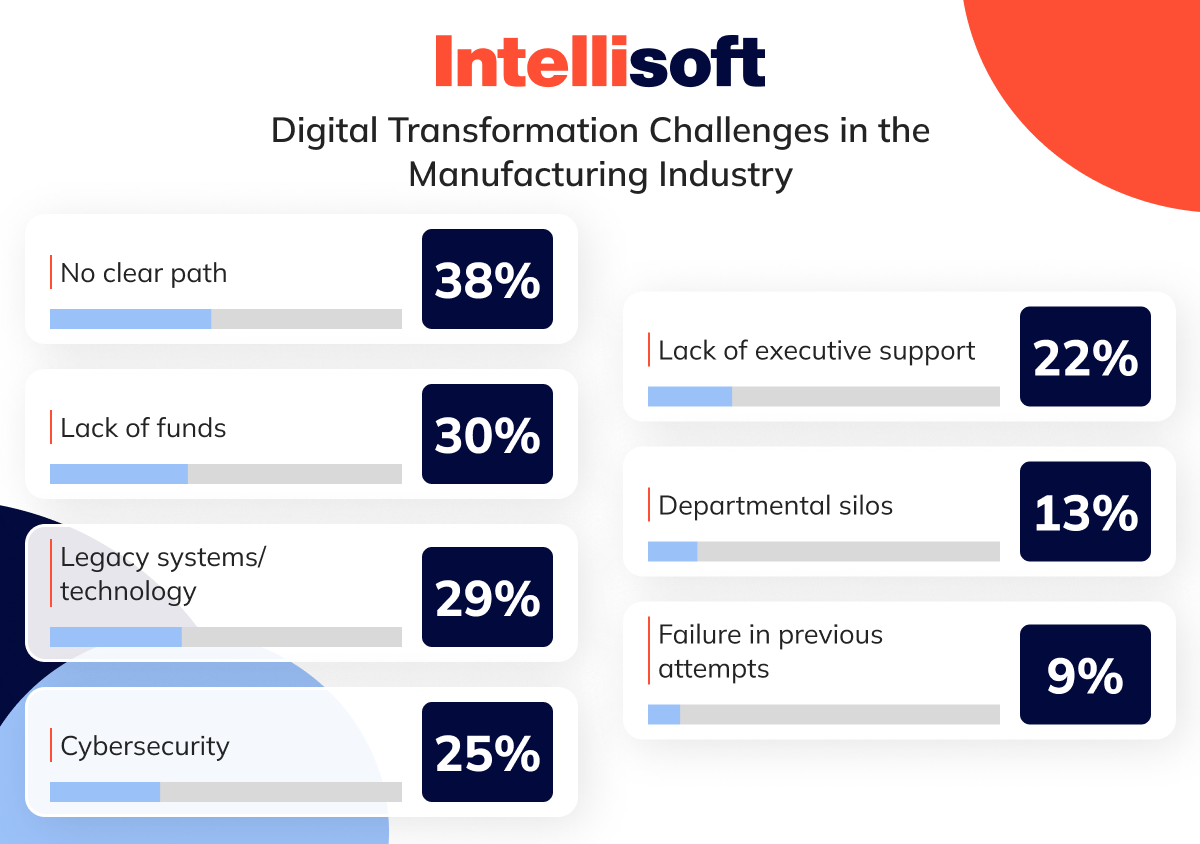
No Clear Path
Many manufacturers start their digital transformation journey without a clear roadmap and face challenges with digital transformation in manufacturing. Without knowing exactly which technologies to adopt or how to integrate them into existing workflows, manufacturers often struggle to make meaningful progress.
For instance, a small automotive parts supplier may invest in IoT sensors but without a broader strategy for data integration or predictive maintenance, they might not see the full potential of the technology.
Lack of Funds
Digitization can be expensive. From implementing advanced technologies to training staff, the cost of digital transformation can be a significant barrier, especially for small and medium-sized manufacturers. The challenge is not just in acquiring the latest technology but also in ensuring long-term ROI, which can be hard to measure in the early stages.
A family-owned furniture manufacturer might be hesitant to invest in automation, fearing that the initial costs won’t be offset by future gains, especially if they’re operating on thin margins.
Legacy Systems/Technology
Many manufacturers still rely on outdated machinery and software that are incompatible with modern digital solutions. These legacy systems can be difficult and costly to replace, creating a significant roadblock to digital transformation. Integrating new technologies with outdated systems often requires custom solutions, further complicating the process.
A textile manufacturer might still be using decades-old machines that can’t easily be connected to cloud-based platforms, forcing them to choose between expensive upgrades or operating in a hybrid environment.
Cybersecurity
As manufacturing processes become more connected through IoT devices, cloud computing, and AI, cybersecurity risks grow exponentially. Manufacturers, especially those new to digital solutions, may underestimate the vulnerability of their systems to cyberattacks.
For example, a precision engineering company could face the risk of cyberattacks on their connected machines, threatening both their production capabilities and customer data.
Lack of Executive Support
Without buy-in from top leadership, digital transformation initiatives can easily stall. If company executives aren’t fully committed to the process, it’s difficult to secure the necessary resources, manage change, or align departments.
In one case, a large industrial equipment manufacturer experienced friction when middle management pushed for digital tools, but the executives, accustomed to traditional methods, resisted full-scale adoption.
Departmental Silos
Manufacturing companies often have rigid departmental structures, making collaboration difficult. These silos can stifle communication and lead to fragmented digital transformation efforts. If IT, production, and management teams aren’t aligned, implementing new technologies can become a disjointed process that doesn’t maximize the potential benefits.
For instance, an electronics manufacturer could struggle to digitize their operations if the production floor and the IT department aren’t sharing data and insights, leaving gaps in their strategy.
Failure in Previous Attempts
The fear of repeating past failures can paralyze organizations. Manufacturers that have tried and failed at digitization in the past might hesitate to try again, even when the technology has improved or new opportunities arise. This fear can be compounded by financial losses or negative employee experiences during previous attempts.
A chemical manufacturer that unsuccessfully rolled out a cloud-based inventory management system might resist trying a similar solution, even though the technology has significantly evolved.
Lack of Understanding of the Digital Transformation Process Leads to Outsourcing
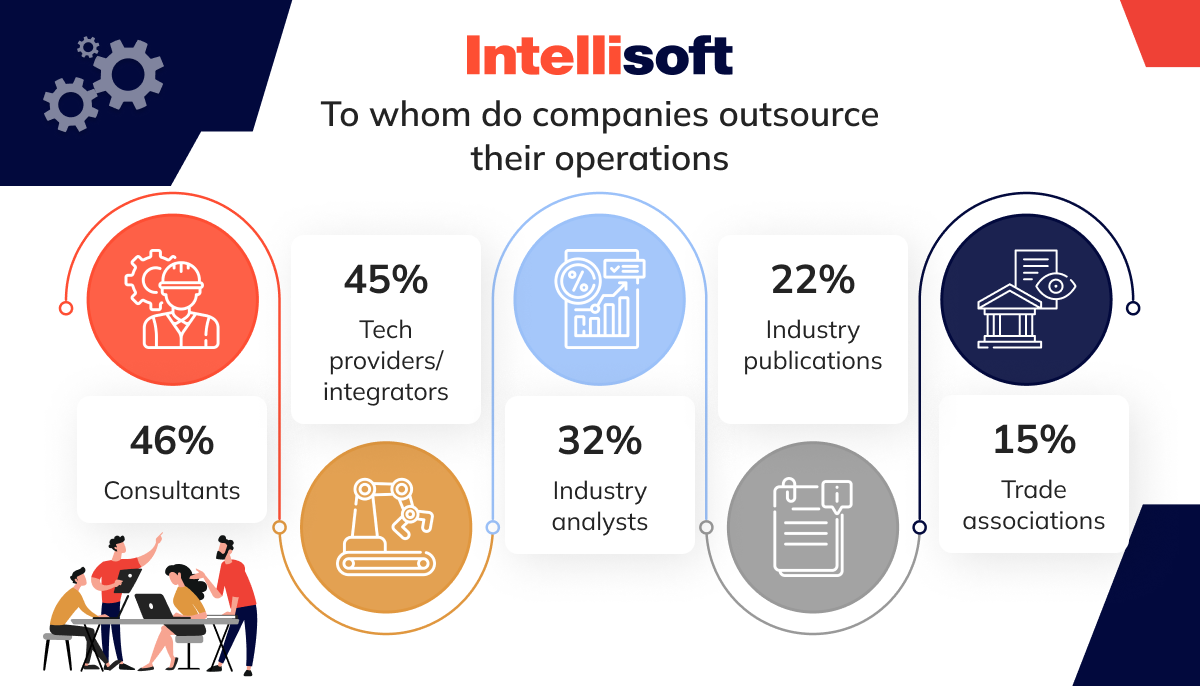
Digital transformation can feel like a daunting puzzle for manufacturers, especially when they aren’t sure where to begin. With so many new technologies – AI, IoT, automation – it’s easy to feel lost or overwhelmed. Many companies find themselves stuck at the starting line, unsure which tools they need or how to bring them all together. That’s where outsourcing becomes a lifeline.
Instead of trying to figure it all out internally, manufacturers often turn to external experts. These partners offer the specialized knowledge that companies may lack in-house. Whether it’s implementing cloud systems or navigating AI, outsourcing allows manufacturers to lean on those who’ve already mastered the game.
Outsourcing doesn’t just save time – it reduces the risk of costly mistakes, accelerates time-to-market, and bridges skill gaps without blowing the budget on hiring or training. For companies without the luxury of an internal digital team, this approach ensures the transition is smoother and faster.
In a world where falling behind in tech can mean losing out, outsourcing is the way many manufacturers turn confusion into opportunity.
Digital Transformation in Manufacturing: In-House vs Outsourcing
When embarking on a digital transformation journey, manufacturers often face a critical decision: Should they handle the transformation in-house or outsource the process? Both approaches have their benefits and challenges, so it’s essential to weigh them carefully.
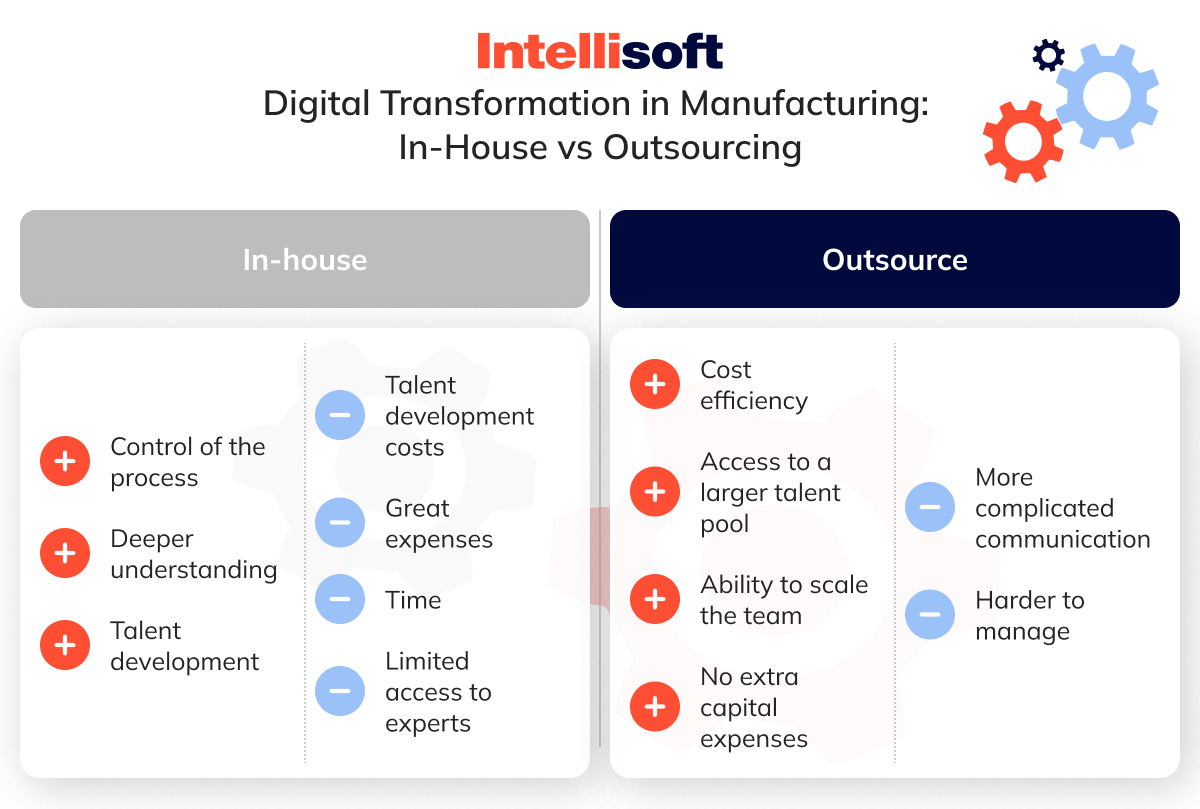
In-House for Digital Transformation: Pros and Cons
Handling digital transformation in-house allows manufacturers to maintain control over the entire process and build a deeper understanding of their own systems. However, it comes with significant costs and time demands.
Pros
- Control of the Process. Managing the transformation internally gives you complete oversight of every step, from selecting tools to setting implementation timelines.
- Deeper Understanding. Since your team knows your business inside and out, they can tailor the transformation to your specific needs, ensuring smoother integration with existing systems.
- Talent Development. Investing in your team’s digital skills can pay off long-term, fostering an environment where innovation thrives.
Cons
- Talent Development Costs. Training employees on new technologies or hiring experts can be expensive, both in time and resources.
- Great Expenses. Building the necessary infrastructure in-house requires a hefty budget, from hardware and software to hiring specialized staff.
- Time-Consuming. Internal transformations often take longer due to the need for skill development, system integrations, and inevitable trial-and-error phases.
- Limited Access to Experts. Finding and retaining top digital talent can be difficult, especially if your company is located outside major tech hubs.
Outsourcing Digital Transformation in Manufacturing: Pros and Cons
Outsourcing offers manufacturers an efficient way to jump-start their digital transformation efforts by tapping into external expertise.
Pros
- Cost Efficiency. Outsourcing can significantly reduce costs compared to in-house efforts, as you won’t need to hire full-time staff or invest in additional infrastructure.
- Access to a Larger Talent Pool. External partners bring specialized skills that might be scarce within your organization, ensuring you benefit from cutting-edge solutions.
- Ability to Scale the Team. Outsourcing allows you to scale up or down quickly based on your project’s needs without long-term hiring commitments.
- No Extra Capital Expenses. With an outsourced team, you avoid the large capital outlays required for software, equipment, or new hires.
Cons
- More Complicated Communication. Collaborating with external partners can lead to communication gaps, especially if they’re working across different time zones.
- Harder to Manage. Managing an outsourced team requires strong oversight and alignment on expectations, which can sometimes lead to misunderstandings or project delays.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Adopt Digital Transformation in Manufacturing Using an IT Outsourcing Agency
Digital transformation in manufacturing can feel overwhelming, but with the right strategy and a trusted IT outsourcing partner, the process becomes much more manageable. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate this journey and unlock the full potential of your digital transformation.
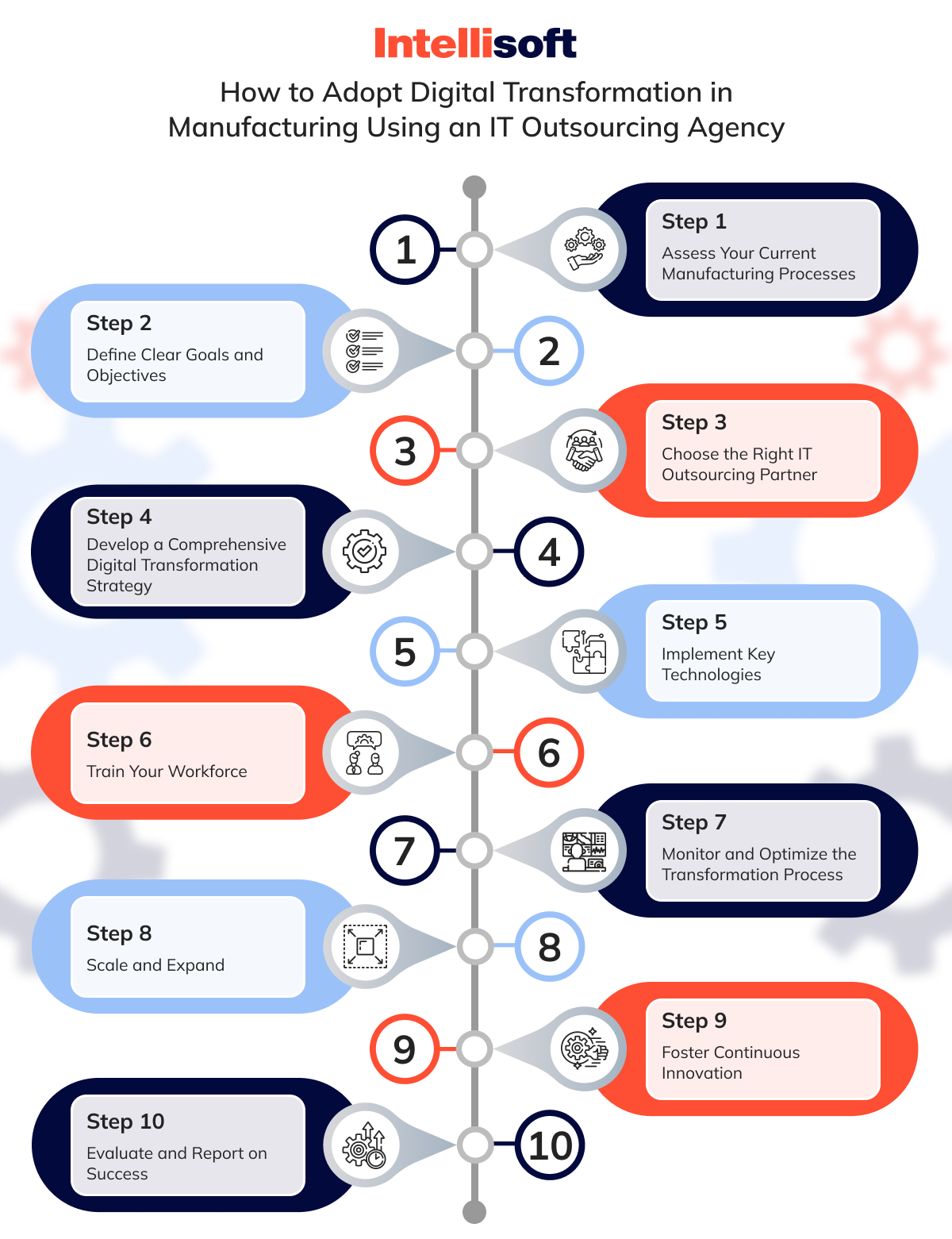
Step 1: Assess Your Current Manufacturing Processes
Before diving into digital transformation, take a close look at your existing manufacturing operations. Identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas where technology could drive improvements. Understanding where you are now sets the foundation for where you need to go.
Step 2: Define Clear Goals and Objectives
What do you want to achieve through digital transformation? Whether it’s improving production efficiency, reducing costs, or enhancing product quality, clearly define your goals.
Step 3: Choose the Right IT Outsourcing Partner
Selecting the right outsourcing agency is crucial to your transformation’s success. Look for a partner with deep expertise in both IT and manufacturing technologies. Their experience will ensure you get tailored solutions that fit your specific industry needs.
Step 4: Develop a Comprehensive Digital Transformation Strategy
Work closely with your IT partner to create a detailed roadmap for your digital transformation. This strategy should include technology choices, timelines, budget forecasts, and milestones to keep the project on track. A well-thought-out strategy prevents costly mistakes and ensures smooth execution.
Step 5: Implement Key Technologies
With the strategy in place, begin implementing the technologies that will drive your transformation. This could include industrial IoT, AI, automation, and cloud-based software. Your IT partner will handle the technical side while you oversee how these technologies integrate into your operations.
Step 6: Train Your Workforce
Technology alone isn’t enough – your employees need the skills to use it. Organize comprehensive training sessions to help your team understand and embrace new systems. A digitally capable workforce is essential for long-term success.
Step 7: Monitor and Optimize the Transformation Process
Once new technologies are live, closely monitor their impact on your operations. Track performance metrics, identify areas for improvement, and make adjustments where necessary.
Step 8: Scale and Expand
As your transformation efforts prove successful, consider scaling up. Expand the use of new technologies across other areas of your business to achieve even greater efficiencies and cost savings. With the groundwork in place, scaling becomes much easier.
Step 9: Foster Continuous Innovation
Digital transformation isn’t a one-time event. Encourage a culture of continuous innovation within your organization. Regularly explore new tools, processes, and technologies that can further enhance your manufacturing operations.
Step 10: Evaluate and Report on Success
Finally, evaluate the results of your digital transformation efforts. Measure performance against the goals you set in Step 2 and report on key wins, challenges, and areas for future improvement. Sharing these results with stakeholders will solidify your success and guide future initiatives.
Digital Transformation Tech Stack
The right tech stack is crucial for manufacturers looking to succeed in their digital transformation. Here’s a breakdown of the essential technologies and platforms that drive this change.
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) Platforms
IIoT platforms connect machines, sensors, and devices across manufacturing floors, enabling real-time data collection and analysis.
Example: Siemens MindSphere helps manufacturers monitor assets and optimize processes through connected systems.
Cloud Computing Platforms
Cloud platforms offer scalable infrastructure for storing and processing large amounts of data.
Example: Microsoft Azure provides flexible cloud solutions tailored to manufacturing needs, from production to supply chain management.
Data Analytics and Big Data Tools
These tools turn raw data into actionable insights, helping manufacturers optimize operations.
Example: IBM Watson Analytics offers predictive analytics for enhanced decision-making across production lines.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Frameworks
AI and ML frameworks automate complex tasks, improve predictive maintenance, and enhance product quality.
Example: Google TensorFlow is used to develop AI models that help manufacturers optimize production efficiency.
Digital Twin Technology
Digital twins create virtual replicas of physical systems, allowing manufacturers to test and optimize processes without disrupting operations.
Example: Dassault Systèmes’ 3DEXPERIENCE platform enables simulation and real-time monitoring of manufacturing systems.
Edge Computing Platforms
Edge computing reduces latency by processing data near the source, improving real-time decision-making.
Example: HPE Edgeline offers edge computing solutions to increase speed and efficiency on the factory floor.
Cybersecurity Tools
With increasing connectivity, robust cybersecurity tools are essential for protecting sensitive data and systems.
Example: Palo Alto Networks provides comprehensive security solutions to safeguard manufacturing networks from cyber threats.
MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems)
MES platforms track and manage the production process from raw materials to finished goods.
Example: Siemens SIMATIC IT offers real-time production monitoring, ensuring seamless manufacturing operations.
Conclusion
Digital transformation in manufacturing is no longer a luxury – it’s essential for survival. Yet, many businesses remain stuck, overwhelmed by outdated systems, high upfront costs, or uncertainty about which technology to adopt. These roadblocks can lead to missed opportunities and stunted growth, leaving manufacturers behind as the industry evolves.
But it doesn’t have to be that way. By leveraging the right tools, a clear strategy, and expert support, manufacturers can turn these challenges into opportunities for innovation and efficiency. Imagine a future where your factory floor is fully connected, predictive maintenance eliminates downtime, and real-time data helps you make informed decisions that drive profitability.
If navigating this journey seems daunting, you don’t have to do it alone. At IntelliSoft, we’ve been guiding companies through successful digital transformations for over 15 years. Let’s turn your manufacturing challenges into strengths – reach out to us today, and let’s shape the future of your business together.