Competency mapping is the strategic process of identifying, assessing, and developing the skills and abilities required for successful job performance. It’s more than just creating a list of job duties; it’s about uncovering the underlying competencies that drive exceptional results. You can make informed decisions about talent development, recruitment, and succession planning by gaining a clear picture of your team’s strengths, weaknesses, and potential.
At Intellisoft, with over 15 years of experience in talent management solutions, we understand the complexities of competency mapping. We can help you navigate this process, from defining core competencies to implementing a sustainable strategy. Let’s explore how competency mapping can transform your organization together.
Table of Contents
What is Competency Mapping Meaning?
What is competency mapping? Competency mapping in HRM is a strategic human capital management process that goes beyond traditional job descriptions to identify, define, and measure the skills, knowledge, behaviors, and attitudes required for successful job performance.
Unlike skills, specific abilities that can be learned through training, competencies are broader attributes that encompass knowledge, skills, and behaviors. They represent the “how” of job performance rather than just the “what”.
For example, a software developer may possess the skill of coding in Python, but their problem-solving competence enables them to apply that skill effectively to complex challenges.
By mapping competency, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of their workforce, identify skill gaps, and make data-driven decisions about talent management.
This holistic view of employee capabilities empowers organizations to optimize talent allocation, enhance performance management, improve succession planning, strengthen recruitment, and foster employee development.
Competency mapping in HR and other fields is a powerful tool for building a high-performing workforce and achieving organizational goals.
Types of Mapping Competencies
Competencies can be categorized into several types, each representing different aspects of an employee’s capabilities. Understanding these categories is crucial for building comprehensive competency mapping in recruitment process.
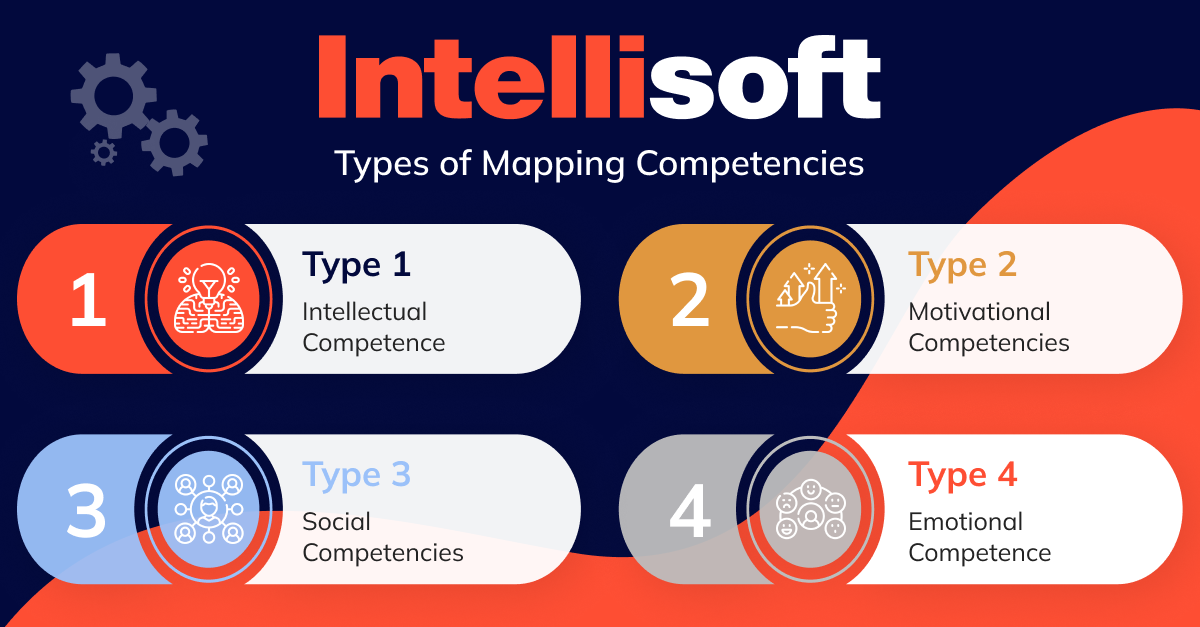
Type 1: Intellectual Competence
Intellectual competencies encompass an individual’s cognitive abilities, problem-solving skills, and knowledge base. These are often acquired through education, training, and experience. Examples of intellectual competencies include:
- Problem-solving. The capacity to identify problems, generate solutions, and implement effective strategies.
- Decision-making. The skill of making informed choices based on available information and analysis.
- Learning agility. The ability to acquire new knowledge and skills quickly and effectively.
- Creativity. The capacity to generate innovative ideas and approaches.
- Technical expertise. Proficiency in specific subject matter or skills relevant to the role.
Type 2: Motivational Competencies
Motivational competencies underpin an individual’s drive, ambition, and goal orientation. These intrinsic factors significantly influence employee engagement and commitment. Key motivational competencies include:
- Achievement orientation. A strong desire to excel and surpass goals.
- Initiative. The propensity to take proactive steps and seize opportunities.
- Competitiveness. A drive to outperform others or achieve superior results.
- Perseverance. The ability to persist in the face of challenges and setbacks.
- Work ethic. A strong sense of responsibility and commitment to one’s role.
Type 3: Social Competencies
Social competencies focus on an individual’s ability to interact effectively with others. Key social competencies include:
- Communication skills. The ability to articulate ideas clearly and effectively, both verbally and non-verbally.
- Teamwork. The capacity to collaborate with colleagues to achieve shared objectives.
- Leadership. The ability to influence and inspire others.
- Interpersonal skills. The capacity to build and maintain positive relationships.
- Conflict resolution. The skill of managing disagreements and finding mutually beneficial solutions.
- Customer focus. A strong orientation towards meeting customer needs and expectations.
Type 4: Emotional Competence
Emotional competencies encompass the ability to understand and manage one’s own emotions as well as the emotions of others. These skills are vital for fostering strong interpersonal relationships and effective leadership. Examples include:
- Self-Awareness. Recognizing and understanding one’s own emotions, strengths, weaknesses, and motivations.
- Self-Regulation. The capability to control one’s emotions and impulses.
- Social Awareness. Comprehending the emotions, perspectives, and needs of others.
- Relationship Management. The skill to build and maintain positive relationships with others.
- Empathy. The ability to understand and share the feelings of others.
By competency mapping & assessment of these different types of competencies, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of their employees’ capabilities and develop targeted development plans.
Why Is It Important?
It’s impossible to imagine the tech industry standing still; it is constantly changing and shapeshifting, demanding businesses to be adaptive and flexible. New technologies, a growing number of experts in the market, and the need to constantly learn and grow demand business owners to change their strategies if they want to remain competitive.
This is where competency mapping and assessment come in handy. It allows businesses to take stock of their current employees and implement changes required for more effectiveness and competitiveness. As the job roles in the sector evolve, so should the organizations’ approaches.
Employee competency mapping clearly defines the skills, knowledge, and behaviors required for success, providing a roadmap for talent development and optimization.
Moreover, among the objectives of competency mapping of competence mapping is that is it essential for driving innovation.
Related Readings:
- What Is Nearshore Outsourcing in Software Development?
- Everything You Need to Know About Team Extension and Dedicated Team Models
- Five Things To Look For In An Ideal IT Offshoring Destination
- Cost to Hire Talent: Staff Augmentation vs In-House Recruitment
- Vendor Selection Process: Essential Criteria for CTOs’ Strategic Choices
How Skill Mapping Impacts Competency Mapping
Skill mapping and the process of competency mapping are distinct yet interconnected processes that contribute significantly to an organization’s talent management strategy. While skill mapping focuses on identifying and assessing specific abilities within a workforce, a competency mapping model adopts a broader perspective, encompassing knowledge, skills, attitudes, and behaviors essential for successful job performance.
Skill mapping serves as a crucial building block for competence mapping. By meticulously identifying and evaluating the skills required for various roles, organizations can:
- Uncover skill gaps. Compare the necessary skills with the existing skill set of employees to identify areas for improvement.
- Inform competence development. Utilize skill data to define the specific behaviors and knowledge associated with each competency.
- Enhance talent management. Identify high-potential individuals, create tailored development plans, and optimize workforce allocation.
By considering not only skills but also knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors, organizations can:
- Develop well-rounded employees. Identify opportunities to cultivate employees beyond their technical proficiencies.
- Align performance with goals. Ensure employee competencies align with organizational objectives.
- Foster a desired culture. Promote a workplace culture that embodies specific behaviors and attitudes.
Key Attributes and Competencies of Engineering Teams
Engineering teams require a unique blend of technical proficiency, soft skills, and problem-solving abilities to drive innovation and deliver high-quality products.
Core Competencies for Engineering Teams
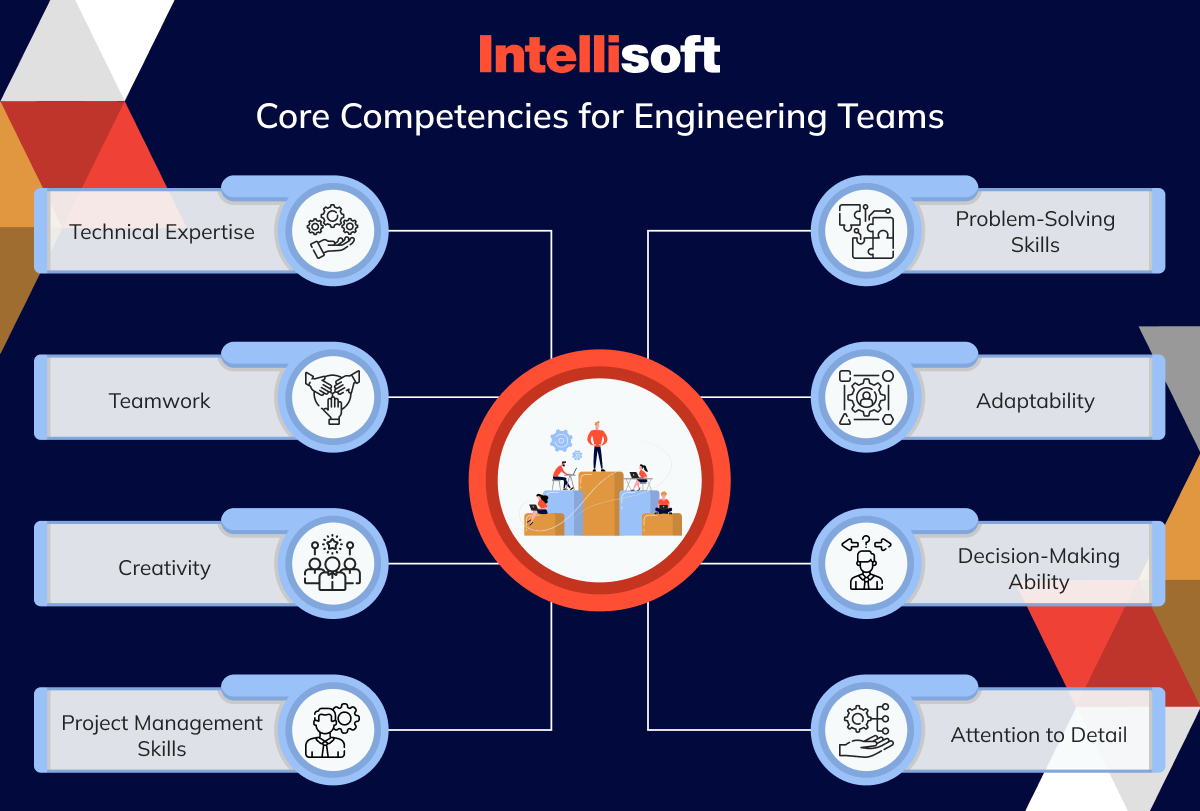
- Technical Expertise. A solid grasp of programming languages, tools, and frameworks is essential.
- Problem-Solving Skills. The capability to dissect complex problems, break them into manageable parts, and devise effective solutions is crucial for overcoming obstacles.
- Teamwork. Strong communication and collaboration skills are vital for maintaining a productive and cohesive work environment.
- Adaptability. The ability to embrace change, learn new technologies, and adjust to evolving project requirements is indispensable in a fast-paced industry.
- Creativity. Innovation is fueled by creativity, enabling teams to explore new ideas and develop unique solutions.
- Decision-Making Ability. Making informed decisions based on available data and expertise is critical for achieving project success.
- Project Management Skills. Effective organization, planning, and execution of tasks are key to ensuring timely delivery and quality outcomes.
- Attention to Detail. Precision in code development and testing helps prevent errors and ensures product reliability.
Steps To Create a Competency Map
A well-structured competence framework is essential for aligning an organization’s talent strategy with its strategic objectives. Competency mapping in performance management guides talent development, performance management, and succession planning by outlining the specific skills, knowledge, and behaviors required for success.
Competency mapping is possible through approaches like:
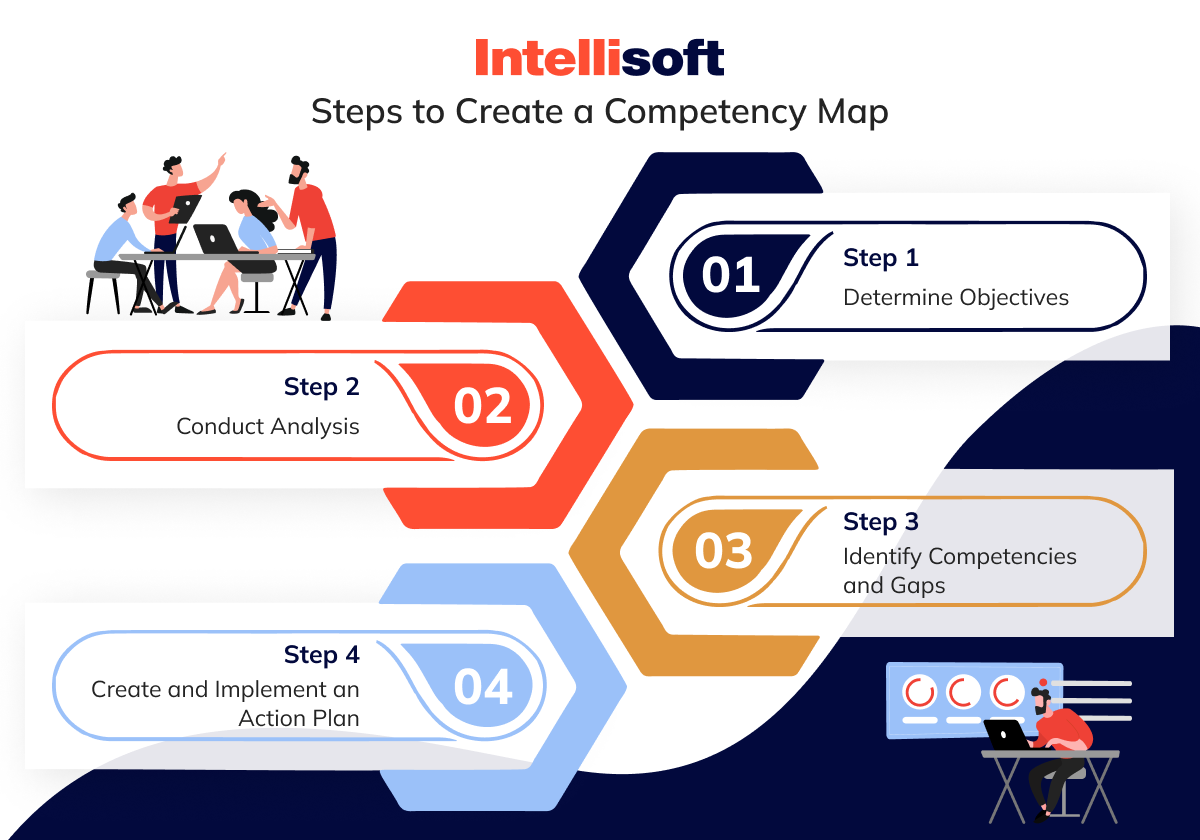
Step 1. Determine Objectives
The foundation of a successful competence map lies in clearly defined objectives. Consider the following questions:
Who will benefit from the competence map? Identify the primary stakeholders, such as managers, employees, or HR professionals.
How will the competence map be used? Determine how the map will be integrated into daily operations, such as performance reviews, talent development, or succession planning.
By clearly articulating your objectives, you’ll ensure that the competence mapping process remains focused and aligned with the organization’s strategic goals.
Step 2. Conduct Analysis
There’s also a need for competency mapping analysis. A thorough analysis is crucial for building a comprehensive competence map.
Key Analysis Areas:
Job Analysis
- Identify core responsibilities and tasks for each role.
- Determine the knowledge, skills, and abilities (KSAs) required for successful job performance.
- Create job descriptions that accurately reflect role expectations.
Skill Assessment
- Identify strengths, weaknesses, and potential gaps in employee capabilities.
Performance Analysis
- Examine performance data to identify patterns, trends, and areas for improvement.
- Determine the competencies that contribute to high performance.
Organizational Analysis
- Assess the organization’s strategic goals, values, and culture.
- Identify the competencies needed to achieve organizational success.
Step 3. Identify Competencies and Gaps
The foundation for effective talent management lies in accurately identifying the competencies crucial for organizational success. This step involves translating the data collected during the analysis phase into actionable insights. Begin by defining the core competencies required for various roles within the organization.
Next, structure them into a hierarchical framework. This framework often takes the form of a pyramid or matrix, visually representing the relationship between different competence levels. Differentiating between core, essential, and desirable competencies provides a clear understanding of the relative importance of each competency.
To bridge the gap between the ideal and the current state of the workforce, organizations must compare the identified competencies against the existing capabilities of employees. This analysis will reveal areas where development opportunities exist.
Step 4. Create and Implement an Action Plan
To ensure the action plan’s effectiveness, integrate competencies into performance management systems. This alignment supports employee development in line with organizational goals and offers a structure for ongoing performance evaluation.
Continuous monitoring and evaluation are crucial for gauging the competence framework’s impact. By tracking the growth of employee competencies and assessing the action plan’s overall effectiveness, organizations can make necessary adjustments to enhance their talent management strategy.
A well-implemented competence framework enables organizations to cultivate a high-performing workforce that drives business success.
Competency Mapping Tools and Frameworks
Effectively implementing a competence mapping process often requires the support of specialized tools and frameworks. These resources can streamline the process, provide valuable data insights, and ensure alignment with industry standards.
Tools
A variety of tools can assist organizations in their competency-mapping efforts.
- Traditional Methods. While more basic, tools like skills matrices and project retrospective feedback mechanisms can provide foundational data for competence mapping. These methods often rely on manual data collection and analysis.
- Competency Mapping Software. Modern software solutions offer automated features to streamline the process.
Skills Base
This competency mapping tool focuses on competence and skills management, providing a centralized repository for employee skills data. It offers features such as skill assessments, gap analysis, and development planning. By automating data collection and analysis, Skills Base empowers organizations to identify skill gaps, measure skill proficiency, and track the impact of development initiatives.
TalentGuard
TalentGuard incorporates competence mapping as a core functionality for talent management and succession planning. The tool helps organizations align employee competencies with strategic goals, assess talent pools, and build high-potential pipelines. By providing a comprehensive view of the workforce, TalentGuard supports data-driven decision-making and talent optimization.
iMocha
Primarily known for pre-employment assessments, iMocha also offers competence mapping capabilities. Leveraging AI-powered technology, the platform analyzes employee performance data to identify strengths, weaknesses, and development areas. By providing actionable insights, iMocha helps organizations tailor development plans to individual employee needs.
HRSG
As a comprehensive HR solution, HRSG offers a suite of modules including competence mapping, performance management, and talent development. By integrating these functions, HRSG provides a holistic view of the employee lifecycle, enabling organizations to align talent strategies with business objectives.
Frameworks
Effectively implementing a competence mapping process often requires the support of specialized tools and frameworks. These resources can streamline the process, provide valuable data insights, and ensure alignment with industry standards.
The SFIA Framework
The Skills Framework for the Information Age (SFIA) is widely used in the tech industry to assess and develop competencies across various roles, including software engineering and IT service management. It offers a comprehensive taxonomy of skills, providing a standardized approach to competence mapping.
The INCOSE Systems Engineering Competence Model
Developed by the International Council on Systems Engineering (INCOSE), this framework focuses on the specific competencies required for systems engineers. It covers technical areas such as system integration, modeling, and verification, providing a structured approach for engineering organizations.
The IEEE Competency Model
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) has developed competence models tailored to the engineering and technology sector. These models outline the knowledge, skills, and abilities needed for various engineering roles, emphasizing technical expertise and ethical considerations.
Lominger Competency Model
Originating from Lominger Limited, Inc., this framework focuses on leadership and management competencies. It offers a broad range of competencies applicable across different industries and organizational levels, providing a foundation for developing leadership development programs.
Find Developers With the Competencies Your Team Needs
Building a high-performing engineering team demands a strategic approach that aligns talent with organizational goals. Competency mapping in training and development is a critical tool in this process, helping organizations identify the specific skills and qualities needed for success.
IntelliSoft specializes in connecting organizations with highly skilled developers who possess the exact competencies needed to drive your projects forward. Our rigorous screening process ensures that our developers not only excel in technical skills, but also demonstrate strong interpersonal and collaborative abilities.
Beyond providing top talent, IntelliSoft offers comprehensive support, including onboarding, payroll, and benefits administration, allowing you to focus on core business operations.
Ready to elevate your engineering team? Contact IntelliSoft today to discover how we can help you find the perfect developers to drive your success.