Team performance management keeps teams running smoothly, making them more efficient and motivated. It’s the key ingredient that enables businesses to hit their goals by ensuring everyone on the team operates at their best.
You’re likely familiar with what effective performance management looks like on an individual level. Well, think of team performance management as the same thing — a continuous cycle of planning, monitoring, assessing, and rewarding — but applied to the whole team.
But strong individual performers aren’t enough today, as companies should learn what is performance management of the development team. Developers must collaborate, communicate clearly, and stay focused on shared objectives. That’s where team performance management steps in, aligning everyone toward the same goals, ready to tackle challenges and succeed together. Check out what is a performance management system on this guide by IntelliSoft.
As Brian Tracy, the famous business coach, said, “The true measure of the value of any business leader and manager is performance.”
Table of Contents
What is Performance Management in IT?
What is performance management? It refers to a structured approach to tracking, evaluating, and enhancing the performance of individuals, teams, and the organization. Aligning everyone’s efforts with technical and strategic objectives is essential. This process involves setting clear goals, consistently reviewing progress, and offering support to help IT professionals achieve short-term and long-term success.
Here are the key components of performance management in IT:
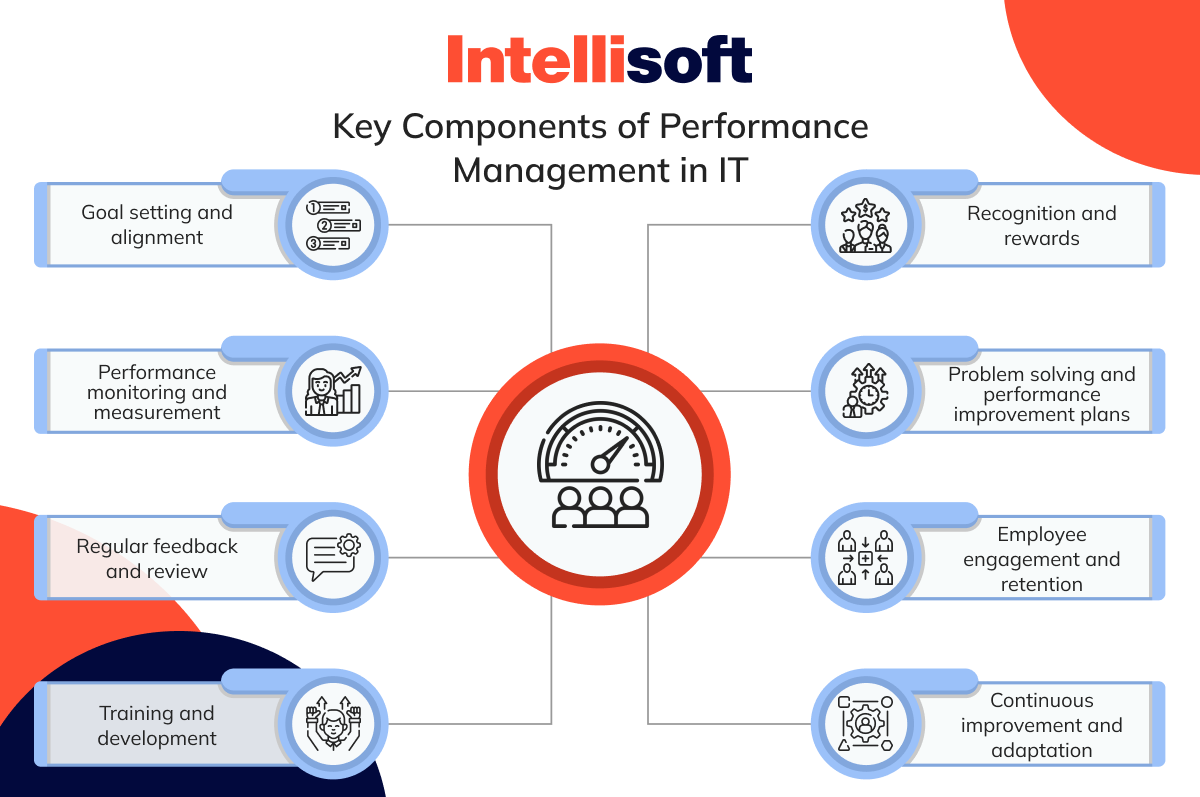
Goal setting and alignment
Defining specific, measurable goals that tie into the company’s broader business strategy starts. These might include meeting project deadlines, ensuring system availability, or driving innovation within the team. Once high-level objectives are set, they’re translated into concrete targets for teams such as development, IT support, and individual roles. This ensures everyone knows how their work contributes to the bigger picture.
Performance monitoring and measurement
KPIs are essential for tracking progress. Metrics can include system uptime, how quickly support tickets are resolved, or how well projects adhere to timelines and budgets. Data gathered from various tools—whether project management platforms, code review systems, or performance monitoring software—help gauge whether individuals and teams are meeting expectations.
Regular feedback and review
Regular, real-time feedback is critical in IT, where projects can change rapidly. This approach helps employees adjust their approach and improve continuously. Alongside ongoing feedback, more formal performance reviews occur at set intervals. These provide a structured opportunity to review progress, address challenges, and plan career development.
Training and development
Performance management also identifies skill gaps and offers training in cloud technologies, AI, or cybersecurity, helping employees stay current and grow professionally. Long-term growth is encouraged through structured development plans, allowing IT professionals to move into leadership roles or become subject-matter experts.
Recognition and rewards
Financial rewards, bonuses, or promotions are often tied to achieving or surpassing performance targets. This drives motivation and continual improvement. Exceptional performance can also be acknowledged through awards, public praise, or by providing new professional growth opportunities.
Problem solving and performance improvement plans
When performance issues arise, structured improvement plans are implemented. These might include additional training, coaching, or other resources to help individuals or teams get back on track. Digging into the causes of underperformance, whether delays in project timelines or issues in code quality, helps identify and address the underlying problems.
Employee engagement and retention
What is application performance management in IT? A solid performance management approach contributes to employee engagement by providing development opportunities, recognizing contributions, and maintaining a healthy work-life balance. Companies can reduce turnover and preserve essential technical knowledge and expertise by ensuring top performers feel valued and supported.
Continuous improvement and adaptation
Change is constant, so effective performance management ensures teams can quickly pivot in response to new technologies or market demands. Organizations can refine their processes by analyzing performance data, enhancing productivity, and fostering innovation within the IT function.
Benefits of Performance Management in IT
Let’s look at the advantages of the performance management process:
- Higher productivity. IT teams can boost their efficiency and output with clear objectives, regular feedback, and access to development resources.
- Improved quality. Ongoing monitoring and continuous feedback help elevate the standard of code, systems, and services delivered by IT professionals.
- Timely project delivery. Performance management ensures projects are completed on time, within budget, and according to clients’ expectations.
- Talent development. A structured approach to performance fosters employee growth and helps retain top talent, ensuring IT teams remain competitive and skilled.
Why Performance Management Is Important for IT Companies?
Performance management plays a pivotal role in IT companies for several reasons:
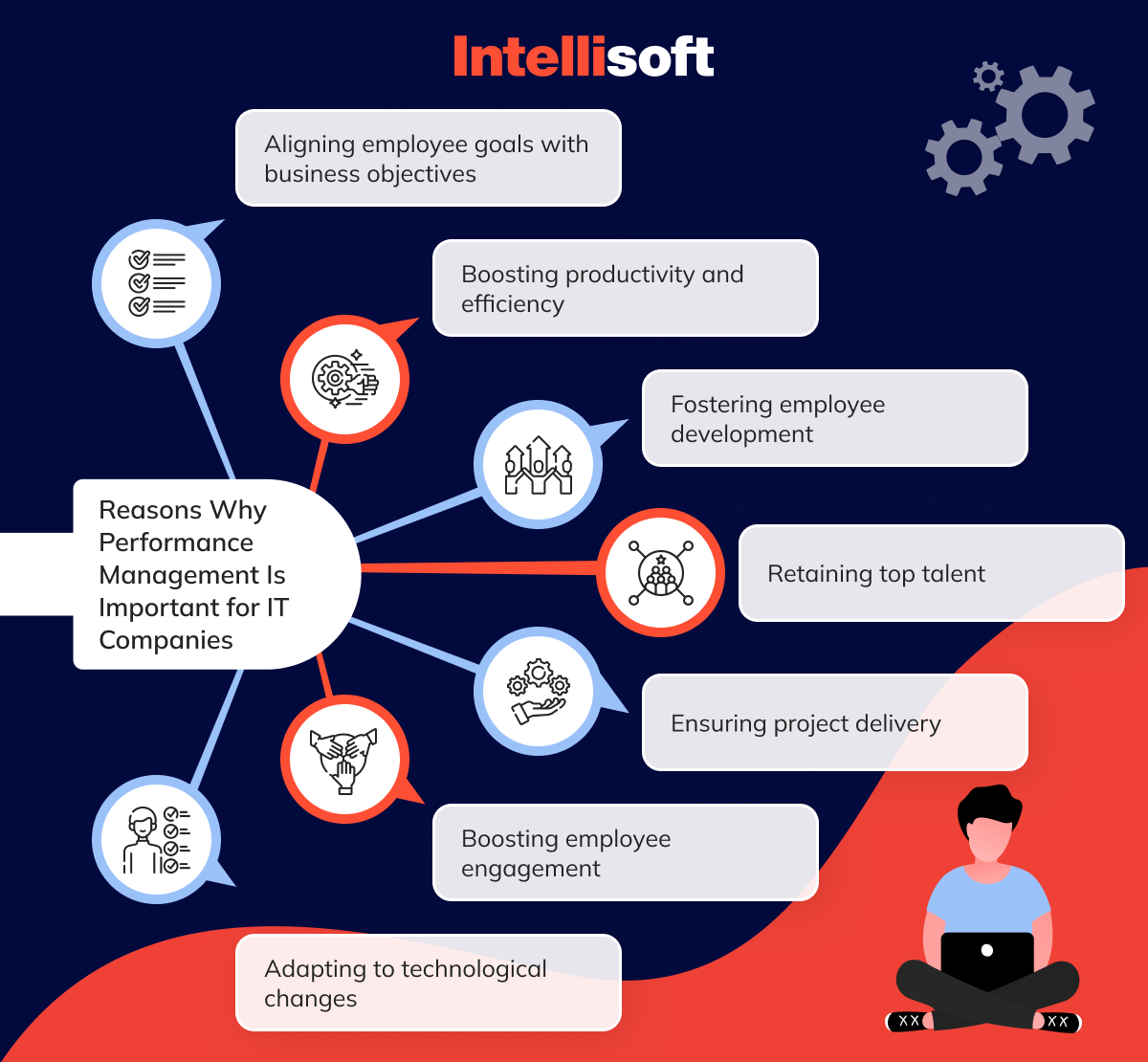
Aligning employee goals with business objectives
Through performance management, individual employee goals can be closely tied to the company’s overarching objectives. This alignment helps IT companies achieve strategic milestones such as project success, client satisfaction, and ongoing innovation.
Boosting productivity and efficiency
Regular monitoring and performance assessments allow IT companies to spot improvement areas, address skill gaps, and fine-tune team workflows. Ultimately, this enhances overall productivity and operational efficiency.
Fostering employee development
A strong performance management system provides employees with continuous feedback and support. This ongoing development is crucial for building new skills, and ensuring teams remain proficient in the latest technologies and methodologies.
Retaining top talent
A well-structured performance management approach keeps employees motivated by recognizing their achievements and creating clear pathways for career progression. This is particularly important in IT, where competition for skilled professionals is fierce.
Ensuring project delivery
Since IT companies often handle high-stakes projects, performance management helps teams meet deadlines, maintain quality standards, and deliver results that meet client expectations.
Boosting employee engagement
Regular feedback, recognition, and defined career growth opportunities are essential for improving employee engagement, which in turn aids in retaining tech talent and fostering innovation.
Adapting to technological changes
The IT industry is characterized by constant technological advancements. Performance management ensures that employees remain flexible and adopt new skills, tools, and practices to remain competitive.
What Is the Business Impact of Performance Management?
What is enterprise performance management for business? Performance management plays a vital role in shaping not just employee success but the overall performance of your business. So, how exactly does it affect your company’s success? Let’s break it down.
- Boost in talent retention. Your employees are the heartbeat of your business, and keeping them engaged is key to long-term success. Replacing an employee can run anywhere from 50% to 200% of their annual salary, underscoring the importance of retention. Interestingly, 52% of voluntary resignations are avoidable. By using effective performance management, you can pinpoint the reasons behind employee disengagement. Offering autonomy and clear goals helps your team feel valued and see a future with your company. Simply put, happy employees are more likely to stay.
- Early identification of potential risks. Underperformance can become a serious issue in any industry, and catching it early is crucial. Performance management equips you with the tools to identify employees who may be struggling, giving you a chance to address issues before they escalate. Whether it’s burnout, personal challenges, or a lack of training, performance data highlights what’s holding someone back. This paves the way for meaningful conversations and an opportunity to offer support and get them back on track.
- Higher employee engagement and motivation. Engaged employees perform better, directly impacting customer satisfaction and your bottom line. A continuous performance management system helps you monitor your team’s goals and progress in real time. Addressing concerns as they arise keeps your team from hitting roadblocks, making them feel more satisfied and motivated. The outcome? A workplace culture that fosters growth and success.
- Clear career progression opportunities. With an agile performance management system, spotting top talent becomes much easier. You can quickly identify employees who excel and may be ready for the next step in their careers. Acknowledging and rewarding hard work keeps your team motivated and clarifies that there’s a path to growth within your organization.
- Better business performance. When all these factors come together, the overall performance of your company improves. Engaged, motivated employees drive innovation and consistent progress, while an effective performance management system ensures everyone stays aligned with company goals. Performance management adds value to individuals and the broader organization when done right.
What Are the Benefits to Employees of a Good Performance Management Process?
But what is performance management in terms of its impact on employees? Well, let’s review this question.
A wellbeing early warning system
Prioritizing wellbeing in the workplace is essential. According to a recent Gallup survey, 61% of employees cited better work-life balance and personal well-being as a key reason for seeking new job opportunities.
When performance management systems identify an employee struggling with motivation or falling behind in their work, it’s crucial to have an open discussion during performance reviews. These conversations allow managers to understand the causes of disengagement and take action to support the employee, helping them feel more valued and less likely to leave or experience burnout.
Boosting engagement and motivation
As the saying goes, “If you love what you do, you’ll never work a day in your life.” Employees naturally want to feel motivated and engaged in their roles. Continuous performance management allows leaders to guide their teams toward goals and objectives in real time, allowing them to maximize their skills and address challenges early on.
Setting clear objectives and expectations
Clarity is key in any job. Performance management systems use SMART goals to provide employees with well-defined objectives that help them focus on their tasks and contribute to their growth. With clear expectations, employees experience less stress and conflict at work, while leaders can be confident everyone is performing at their best.
Identifying growth opportunities
No one wants to remain stagnant in their career. Through performance management, employees can assess their development, identifying areas for growth and progression. Regular check-ins with their managers help them track progress and steer their career paths in their desired direction.
Highlighting training needs
Another advantage of performance management is pinpointing areas where further training would benefit employees. With SMART goals in place, employees can identify specific skills they’d like to develop and communicate their training needs more effectively to managers and leaders.
What Is a Developmental Purpose of Performance Management?
So, what is the developmental purpose of a performance management process? The developmental focus of performance management aims to sharpen employees’ abilities, broaden their knowledge, and boost their overall capacity to contribute more effectively to the organization. Key elements of this developmental purpose include:
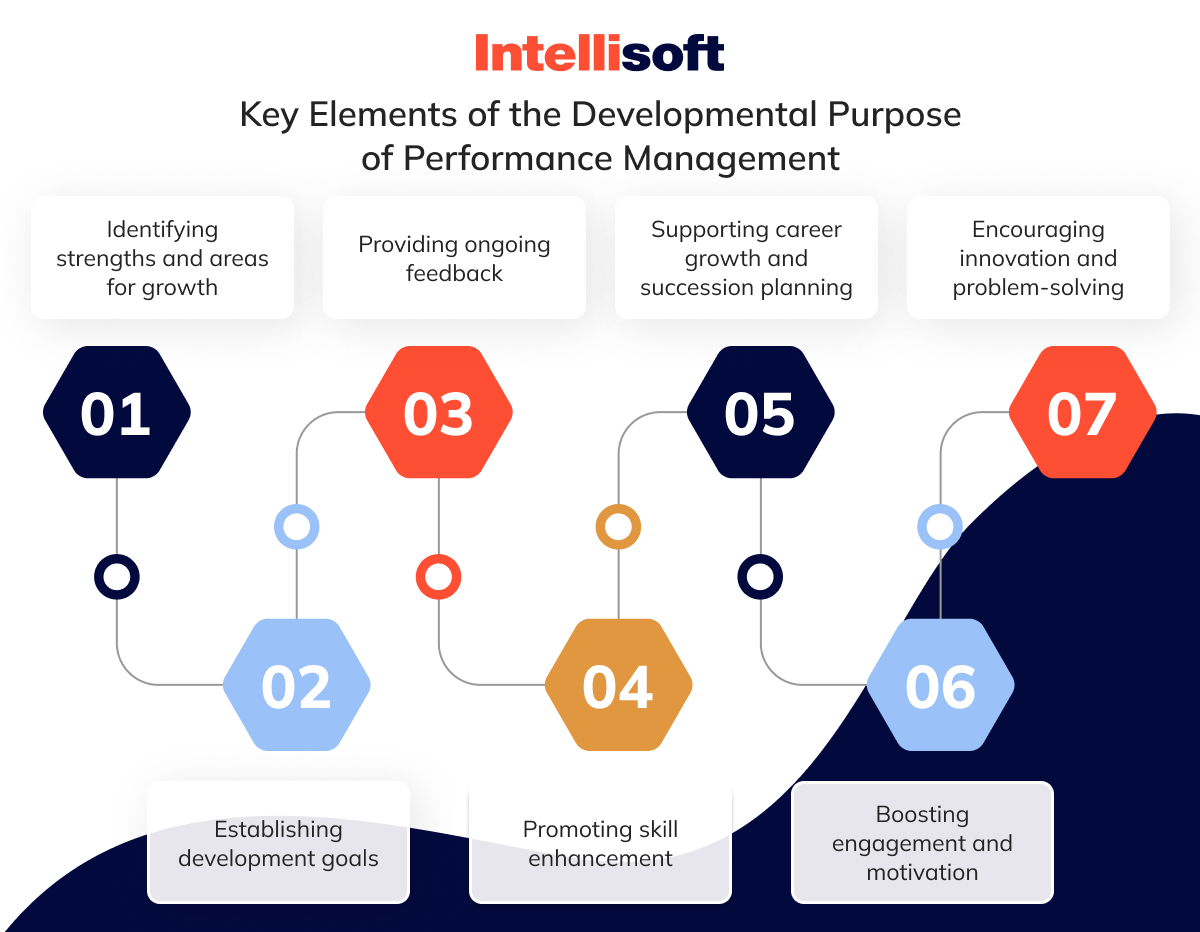
- Identifying strengths and areas for growth. Performance management highlights employees’ strengths that can be maximized while pinpointing areas where development is needed, offering a roadmap for improvement.
- Establishing development goals. It lays out a system for setting career development goals that align with the individual’s career aspirations and the company’s objectives, providing clear guidance for employee growth.
- Providing ongoing feedback. Continuous feedback allows employees to understand their performance in real time, making it easier to adjust, develop new skills, and refine their work processes.
- Promoting skill enhancement. Employees gain access to training, mentorship, and learning opportunities through regular reviews and evaluations that help build technical expertise and soft skills, preparing them for future challenges.
- Supporting career growth and succession planning. Performance management helps the organization identify employees with high potential, grooming them for leadership roles or more complex responsibilities, which is vital for succession planning.
- Boosting engagement and motivation. When employees see paths for personal development and career advancement, they feel more engaged, valued, and motivated to excel, all of which contribute positively to the organization’s overall success.
- Encouraging innovation and problem-solving. A focus on development enables employees to tackle more complex problems, offer creative solutions, and contribute innovative ideas, fostering a more dynamic and adaptive workplace.
What Factors Affect the Performance of IT Company?
Several factors influence an IT company’s performance, affecting its ability to deliver quality services, meet client expectations, and stay competitive. Key elements include:

Skilled workforce
Hiring talented developers, engineers, and IT professionals is crucial for maintaining project quality and fostering innovation. Employee retention is equally important, as high turnover can disrupt ongoing work, create knowledge gaps, and increase recruitment costs. Continuous training and development ensure employees remain proficient with the latest technologies, tools, and methodologies.
Technology & infrastructure
What is asset performance management software in IT? Using up-to-date tools and software significantly enhances productivity, reduces the likelihood of errors, and improves the overall quality of services. A scalable IT infrastructure is essential for accommodating growing workloads and evolving client demands.
Project management
Effective project planning, which includes clear scoping, timeline management, and proper resource allocation, is key to meeting deadlines and staying within budget. Agile methodologies or other project management frameworks enhance team collaboration and adaptability, promoting timely project completion.
Client relationship management
Open and clear communication with clients helps establish a mutual understanding of goals and expectations, which minimizes the risk of misunderstandings or delays. Prioritizing client satisfaction builds long-term relationships, fosters repeat business and generates positive referrals.
Innovation & R&D
Investing in research and development enables IT companies to stay ahead of technological trends and offer cutting-edge solutions. Fostering an innovation-driven culture encourages creative problem-solving and the development of new services or products.
Market competition
The competitive landscape impacts pricing strategies, client acquisition, and the ability to attract top talent. Remaining competitive requires a combination of innovative services, exceptional customer support, and operational efficiency. Additionally, a strong market reputation—bolstered by client testimonials and case studies—is critical in attracting and retaining clients.
Operational efficiency
Streamlining processes, optimizing workflows, and leveraging automation can substantially improve productivity while reducing costs. Managing overhead expenses is essential for profitability and delivering value to clients.
Cybersecurity & data management
Robust cybersecurity protocols safeguard the company and its clients from data breaches, which could damage reputations and result in legal consequences. Efficient data management—encompassing storage, retrieval, and analysis—is essential, especially in IT projects involving big data, cloud computing, and machine learning.
Regulatory compliance
Compliance with industry standards like GDPR and ISO certifications is necessary to maintain client trust and avoid legal penalties.
Economic factors
Global economic shifts, such as recessions or inflation, can impact budgets, client spending, and project opportunities. For IT companies working internationally, fluctuations in currency exchange rates can further affect profitability and cost management.
What Is a Performance Management System?
What is performance management system in IT? A performance management system is a well-organized approach that companies use to evaluate, guide, and improve employee performance. It ensures everyone’s efforts align with the organization’s goals and objectives. Through a set of tools and ongoing processes, this system helps to assess both individual and team performance regularly. It also promotes better communication between managers and their teams, establishes clear expectations, monitors progress, and aids in making decisions about employee development, rewards, and promotions.
What Makes an Effective Performance Management System?
It should be:
- Tailored to your organization. The system should align with your industry, structure, and appraisal processes while accounting for your specific performance cycles.
- Backed by senior management. Without buy-in from the C-suite, a performance management system is doomed to fail. Employees will soon notice that their goals don’t truly reflect the company’s priorities or that their achievements aren’t being adequately recognized.
- Clearly communicated. Employees should have a solid grasp of what’s expected from them and how their role contributes to the broader company objectives.
- Fair, consistent, and ongoing. The system should feel impartial from senior leadership to junior staff, with successes rewarded equitably across the board.
- Accurately measured. Use tried and tested metrics, ideally those validated outside the organization, to minimize any risk of bias or favoritism creeping in.
- Focused on continuous development. If your system becomes just another box-ticking exercise, it won’t deliver the growth and improvements you aim for.
- Tied to rewards. Integrating performance-based rewards can be a powerful motivator, helping to reinforce and acknowledge high-quality work.Trackable. Managers and employees should have access to software that tracks performance over time, offering a clear picture of progress toward goals.
Key Components of a Performance Management System
Now let’s look at the critical components of a performance management system.
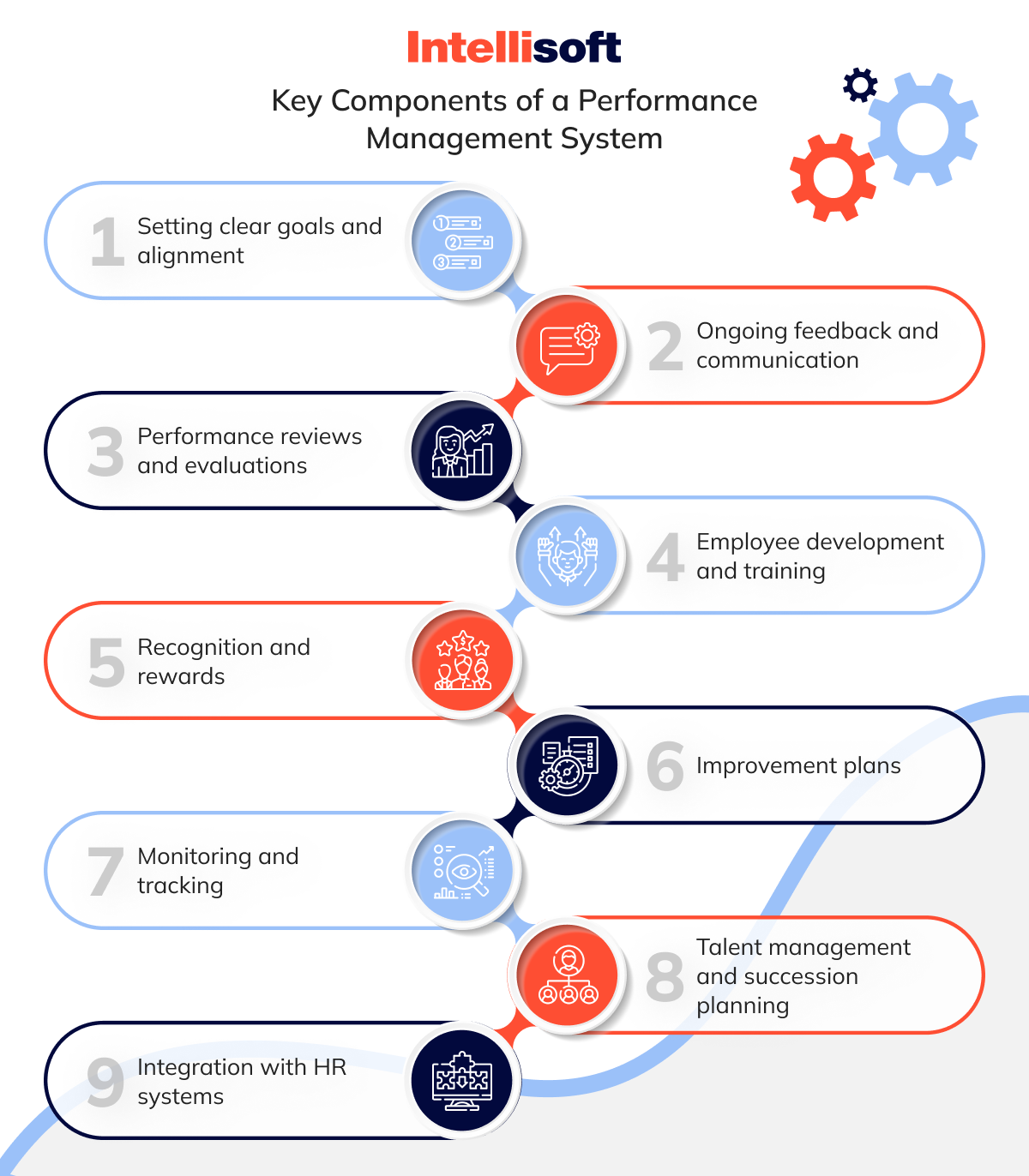
Setting clear goals and alignment
Employees need clear, measurable goals directly connecting to the company’s objectives. These goals may focus on an individual’s role or be specific to their department or team.
Ongoing feedback and communication
Regular feedback, whether through informal check-ins or formal reviews, helps employees understand their performance. This approach ensures they know where they’re meeting expectations and where there’s room for growth.
Performance reviews and evaluations
Employee performance is formally reviewed against established goals at quarterly or annual intervals. These evaluations help determine whether targets are being met.
Employee development and training
Identifying skill gaps and providing opportunities for training and mentorship allows employees to grow in their roles. This not only supports career advancement but also helps the company thrive.
Recognition and rewards
Employees who exceed expectations are rewarded through promotions, pay raises, bonuses, or non-monetary recognition such as awards or career growth opportunities.
Improvement plans
When employees fall short of performance standards, improvement plans are set. These plans involve clear, achievable goals and support to help employees get back on track.
Monitoring and tracking
Performance is tracked in real-time using tools that monitor progress on goals, task completion, and key performance indicators (KPIs). This ensures continuous oversight.
Talent management and succession planning
High-potential employees are identified and groomed for leadership roles. Performance data helps pinpoint candidates for promotions or strategic projects.
Integration with HR systems
Modern performance management tools integrate with systems like payroll, learning management, and recruitment, creating a seamless flow of employee data.
Types of Performance Management Systems
There are three types of performance management systems:
- Traditional annual review systems. These systems focus on a single, formal performance review at the end of the year. While common, they’re often considered outdated due to the absence of ongoing feedback throughout the year.
- Continuous performance management systems. This approach favors regular check-ins, ongoing feedback, and flexible goal-setting, making it more adaptable to shifting business needs and employee development.
- 360-degree feedback systems. This system collects feedback from multiple sources—peers, subordinates, and managers—offering employees a comprehensive view of their performance from different perspectives.
Benefits of a Performance Management System
Let’s dive into some key benefits that can take your organization to the next level.
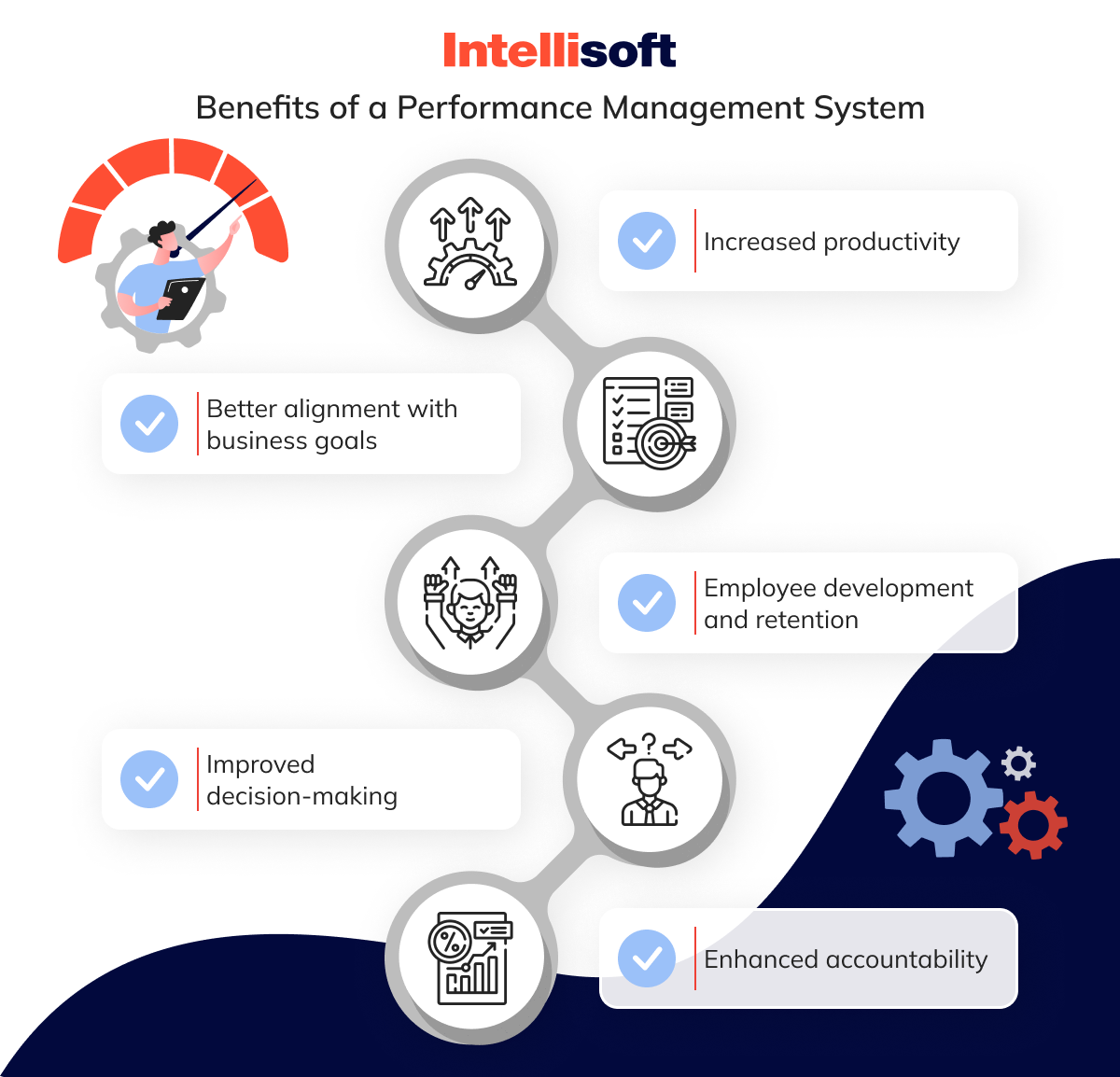
Increased productivity
With clear objectives, consistent feedback, and ample growth opportunities, employees stay focused and enhance their performance.
Better alignment with business goals
A performance management system ensures that individual goals align with company objectives and that everyone works together.
Employee development and retention
Identifying skill gaps and fostering development keeps employees engaged and motivated, which can lead to higher retention rates.
Improved decision-making
The insights from these systems provide a data-driven foundation for decisions about promotions, training, and workforce planning.
Enhanced accountability
When employees know what’s expected and are held accountable, performance naturally improves, leading to stronger results.
Challenges of Performance Management Systems
Still, there are some challenges in using performance management systems:
- Bias in evaluations. Performance reviews often involve personal judgment, which can lead to biases or favoritism.
- Resistance to feedback. Some employees may feel overwhelmed by frequent feedback or struggle to accept constructive criticism.
- Implementation complexity. Creating and sustaining an effective system takes considerable time, resources, and commitment from managers and employees.
- Overemphasis on metrics. Some systems focus too heavily on numbers, which can downplay important factors like creativity or teamwork.
Example in IT Context
An IT company’s performance management system can monitor individual developer goals, such as completing projects on time, fixing bugs efficiently, or following coding best practices. Teams might be tasked with objectives such as ensuring system uptime, enhancing cybersecurity, or driving innovation. Continuous feedback and regular performance reviews help keep IT staff aligned with the company’s goals. Additionally, training programs can be offered to sharpen technical skills and further boost performance.
Related articles:
- 10 Potent Risk Mitigation Strategies in Project Management
- Vendor Management IT. Definition, Features, Advantages, and More
- When Should You Change a Development Team?
- Who Does What? Understanding Roles in a Software Development Startup
- How Much Time Does It Take to Find Outsourcing Team
What Is Results-Oriented Performance Management Method?
The results-oriented performance management approach centers around evaluating and managing employees by focusing on the outcomes they deliver rather than the steps they take to get there. This method prioritizes attaining specific, measurable objectives that align with the organization’s overall success, emphasizing results over the processes involved. Here’s a closer look at how this approach functions:
Key Features of Results-Oriented Performance Management
Below, we’ll dive into the key components that make this method a powerful tool for fostering accountability, continuous improvement, and high performance.

Emphasis on outcomes
In a results-driven approach, employees are assessed based on the outcomes they achieve, not just the tasks they complete or the methods they use. For instance, it could mean evaluating a software developer on the quality and functionality of the code they produce or how effectively they complete projects on schedule and within budget.
Goal-setting with clarity
A major component of this system is setting SMART goals—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. These goals are tied directly to business outcomes, providing clear benchmarks for success. For example, this might involve ensuring system uptime, minimizing bugs, or boosting client satisfaction rates.
Accountability for performance
In this model, employees are held responsible for their results. It promotes a sense of ownership, as meeting or exceeding the predefined goals determines success, not simply following prescribed processes or protocols.
Measuring success
Key metrics and performance indicators (KPIs) are at the heart of this approach. Success is evaluated using measurable data, which can be quantitative or qualitative but always aligned with business goals. Metrics such as customer retention, timely project completions, or revenue growth can serve as performance benchmarks.
Ongoing feedback
Though the primary focus is on results, continuous feedback plays a crucial role. Employees receive regular input to help them track their progress and make adjustments when necessary, keeping them aligned with their goals and ensuring they stay on course.
Alignment with organizational goals
Individual employee goals are closely connected to the company’s larger strategic objectives. This alignment ensures that every person’s efforts contribute to the broader mission, making it easier for the organization to achieve its long-term goals.
Rewarding success
Employees who meet or exceed their goals are often rewarded through bonuses, promotions, or recognition. This system fosters a high-performance culture, encouraging people to focus on outcomes that drive overall business success.
Benefits of Results-Oriented Performance Management
Results-oriented performance management has its fundamental advantages:
- Greater accountability. Employees become more responsible for delivering concrete results, fostering a sense of ownership and accountability in their work.
- Sharper focus and clarity. Well-defined, measurable goals give employees a clearer picture of what’s expected, allowing them to concentrate better and stay on track.
- Stronger alignment with business objectives. Focusing on results means that employees’ efforts are closely tied to the company’s strategic priorities, ensuring their work directly contributes to the broader goals.
- Boosted productivity. A results-driven mindset encourages employees to work more efficiently, knowing their performance is assessed based on tangible outcomes.
Challenges of Results-Oriented Performance Management
What is a disadvantage of using the results-oriented performance management method? Learn more here:
Overemphasis on results
There’s a tendency to prioritize outcomes, which can lead to overlooking the value of collaboration, the work process, or key behaviors that contribute to sustained success, even if they don’t yield immediate returns.
Pressure and stress
Employees might feel intense pressure to meet targets, which, if not properly managed, can result in increased stress or burnout.
Measurement challenges
Some roles, particularly creative or support-oriented, don’t lend themselves easily to quantifiable results, making performance evaluations more complex.
Example in IT
A results-driven performance management system might focus on setting clear, measurable goals in an IT company. For example, targets could include improving system uptime to 99.9% over the next quarter, reducing software release bugs by 20% within a specified period, or delivering a client project on time and within budget while achieving a client satisfaction rating above 90%. Employee performance would then be evaluated based on the achievement of these specific outcomes rather than the methods or processes used to reach them.
What Is the Performance Management Cycle?
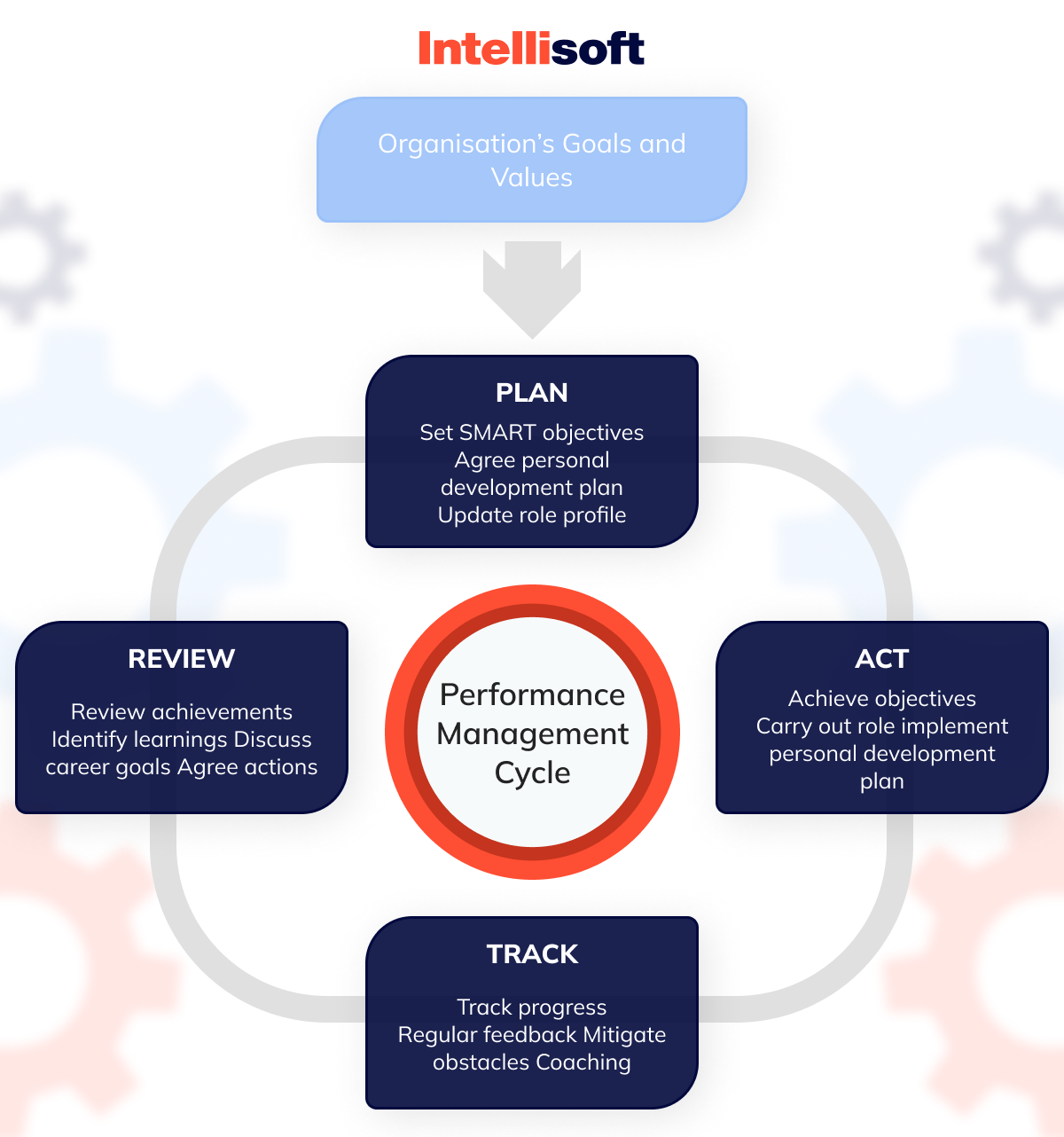
What is performance management process? Traditionally, performance management followed an annual cycle. At the start of the year, an employee would sit down with their manager to set goals, and then, a year later, they’d come together again to evaluate progress. This process typically followed a series of steps:
- Plan. Establish SMART objectives—specific, Measurable, Agreed-upon, Realistic, and Timely—and map out development goals.
- Act. The employee would focus on meeting their objectives with ongoing support and coaching from their manager and the organization.
- Track. Employees could monitor their progress at any point, hitting smaller milestones on the way to their bigger targets.
- Review. A formal appraisal meeting would take place between the manager and employee to assess performance and decide whether to adjust objectives moving forward.
- Reward. High-performing employees were acknowledged for their contributions, often through bonuses, raises, promotions, increased responsibility, or other recognition.
What Is the First Step in the Performance Management Process?
The first stage in the performance management process is goal setting and planning. At this point, it’s crucial to define specific, measurable objectives for individuals and teams, ensuring these targets align with the organization’s overall vision and objectives. Let’s learn what is the first step in the performance management process in more detail.
Setting Organizational Goals
Start by pinpointing the organization’s strategic goals, whether driving revenue growth, fostering innovation, enhancing customer satisfaction, or improving operational efficiency. These high-level objectives provide the groundwork for setting performance goals that align with individual and team efforts.
Translating Business Goals into Team/Individual Objectives
Break down the broader organizational objectives into actionable targets by breaking them down into specific goals for departments, teams, and individuals. This could involve focusing on project delivery deadlines, ensuring high system uptime, or maintaining stringent code quality standards in an IT setting.
When setting these goals, apply the SMART framework—ensuring they are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. For instance, a clear goal for an IT team could be, “Increase system uptime to 99.9% by the end of Q2.”
Role Clarity
Clearly outline each employee’s role and responsibilities, making sure they fully understand how their efforts tie into the overall goals of the team and the company. This clarity lets employees focus on their specific tasks while actively contributing to larger organizational objectives.
Collaborative Goal-Setting
Involve employees in the goal-setting process to foster a sense of ownership and motivation. When individuals actively participate in setting their own goals, they are more likely to stay committed to achieving them. This collaborative approach helps lay a solid foundation for the entire performance management process, ensuring that individual efforts align with the company’s strategic goals.
What Is the Final Step in the Performance Management Process?
The final phase in the performance management cycle is known as the review and renewal stage, often referred to as performance appraisal and feedback. But what is the primary difference between performance appraisals and performance management?
Typically, it involves a detailed assessment of how well goals were met, discussions about strengths and areas for improvement, and crafting strategies for continued development in the upcoming period. What is the final step in performance management process? Let’s find out more.
Performance Review
Evaluating an employee’s performance involves reviewing their achievements against the goals established at the beginning of the cycle. This process can include self-assessments, peer reviews, and manager feedback, all complemented by data-driven insights. By leveraging metrics, key performance indicators (KPIs), and project outcomes, performance can be assessed objectively, ensuring a balanced evaluation combining qualitative input and quantitative results.
Providing Feedback
Provide clear, constructive feedback to the employee, emphasizing their strengths and improvement areas. At the same time, encourage a two-way dialogue where the employee can openly share their perspective on their performance, challenges faced, and future goals, creating a collaborative environment for growth.
Rewarding Performance
Following the performance review, employees who have excelled may be recognized with rewards such as bonuses, salary increases, promotions, or non-monetary acknowledgments. For those who did not meet expectations, this stage involves addressing underperformance by outlining an improvement plan and providing the necessary support or resources to help them succeed.
Development and Goal-Setting for the Future
As part of the review process, create a personal development plan that identifies opportunities for training, skill improvement, and career advancement. This not only helps employees take on new challenges but also aligns with their future aspirations. Additionally, begin setting new or revised goals for the upcoming performance cycle that reflect the employee’s development needs and the company’s evolving objectives.
Cycle Continuation
The performance management process is continuous, renewing after each review cycle, feedback, and development planning. This final step ensures that employees gain valuable insights into their performance, celebrate their achievements, and have a clear path for future growth. The process sets new expectations and fosters continuous improvement by incorporating lessons learned and making necessary adjustments.
What Are Key Steps of Implementing Performance Management in Software Development Teams
Implementing performance management in software development teams requires a well-defined approach that ties individual and team contributions to the organization’s larger objectives while fostering ongoing development. Below are the essential steps to effectively establish performance management within software development teams:

Define Clear Goals and Objectives
Establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for individual developers and the team, ensuring they align with the broader business strategy. For instance, if the company focuses on rapid feature delivery, the team’s goals should include clear timelines and deliverables supporting this objective, such as reducing bug counts, improving code quality, and meeting project deadlines.
Identify Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
When selecting relevant KPIs to evaluate software development performance, focusing on quantitative and qualitative metrics is essential. Key quantitative KPIs may include velocity (work completed per sprint), code quality metrics (such as code coverage and bug density), deployment frequency, customer satisfaction, and system uptime. However, qualitative factors such as collaboration, creativity, and problem-solving skills are equally important and should not be overlooked when assessing team effectiveness.
Establish a Continuous Feedback Loop
To create a robust feedback system, it’s essential to implement ongoing feedback, peer reviews, and regular manager-employee conversations. Rather than waiting for annual reviews, agile development methods encourage continuous feedback through sprint retrospectives and regular check-ins. Peer feedback, particularly during code reviews and pull requests, helps maintain code quality and fosters collaboration. Additionally, consistent one-on-one meetings between managers and team members offer valuable opportunities for guidance, addressing concerns, and discussing professional growth. This integrated approach ensures that feedback is timely, constructive, and actionable.
Leverage Agile Methodologies
In Agile frameworks like Scrum or Kanban, performance management naturally integrates with practices such as sprint planning, daily stand-ups, and retrospectives, which support goal setting, progress tracking, and continuous improvement. These processes are inherently flexible, reflecting the iterative nature of software development, and allowing teams to adapt their goals and workflows as projects evolve.
Provide Training and Development Opportunities
Performance reviews can be a valuable tool for identifying areas where developers need to enhance their skills, whether mastering new programming languages, frameworks, or tools. To address these gaps, providing access to learning resources such as training programs, workshops, or certifications is essential. These enable developers to stay current with the latest technologies like cloud computing or machine learning. Additionally, fostering a culture of mentorship, where senior developers coach junior team members, helps reinforce continuous learning and skill development across the team.
Monitor and Track Performance
To monitor project performance and ensure teams stay on track, use tools like Jira, GitLab, or GitHub to track key metrics such as project progress, code commits, and bug resolution. Combine this with regular quarterly or sprint-based reviews to evaluate how well the team is meeting its objectives and address any gaps in performance.
Recognize and Reward Achievements
Celebrate key milestones and high performance to recognize and reward individual and team achievements. Whether completing major projects, launching new features, or surpassing performance goals, offer incentives such as monetary rewards, promotions, or public acknowledgment to keep motivation high and acknowledge excellence.
Address Underperformance
When dealing with underperformance, whether from an individual or the entire team, start by conducting a root cause analysis to pinpoint the underlying issues—skill gaps, unclear objectives, or external factors such as limited resources. Based on this analysis, develop a targeted performance improvement plan. This plan should outline specific areas for growth, set clear and measurable goals, and provide the necessary support, such as additional training or coaching, to help the team succeed.
Foster a Collaborative Team Culture
Promote a collaborative team environment where developers work together, openly share knowledge, and support one another in achieving common goals. Ensure communication channels remain accessible, encouraging team members to provide input or ask for help when needed freely.
Conduct Regular Performance Appraisals
Conduct periodic formal performance reviews to evaluate individual and team achievements against predefined goals and KPIs. This process should take a balanced approach by combining quantitative metrics, such as code quality and project completion rates, with qualitative assessments, like problem-solving abilities and teamwork.
Adjust and Optimize
Continuously refine the performance management system by leveraging review insights to adjust goals, KPIs, and feedback mechanisms. At the same time, ensure the system remains flexible and scalable, evolving in response to team growth and new projects.
Use Technology for Automation and Tracking
Integrate performance management software with project management tools like Jira or Asana to automate tracking performance metrics, set goals, and streamline feedback collection. Complement this with analytics tools to create real-time dashboards that visualize progress, enabling both managers and developers to monitor and optimize performance effectively.
Measuring Software Engineer Performance
Evaluating how well a software engineer is performing requires both analytical precision and a bit of intuition. To understand their contributions, growth, and overall impact, it’s crucial to look at both quantitative data—like the number of tasks completed or code quality—and qualitative insights, such as teamwork and problem-solving abilities. Each metric type brings a different angle, so combining both provides a fuller picture of the engineer’s true potential. Curious to know more? Read on to dive into the details.
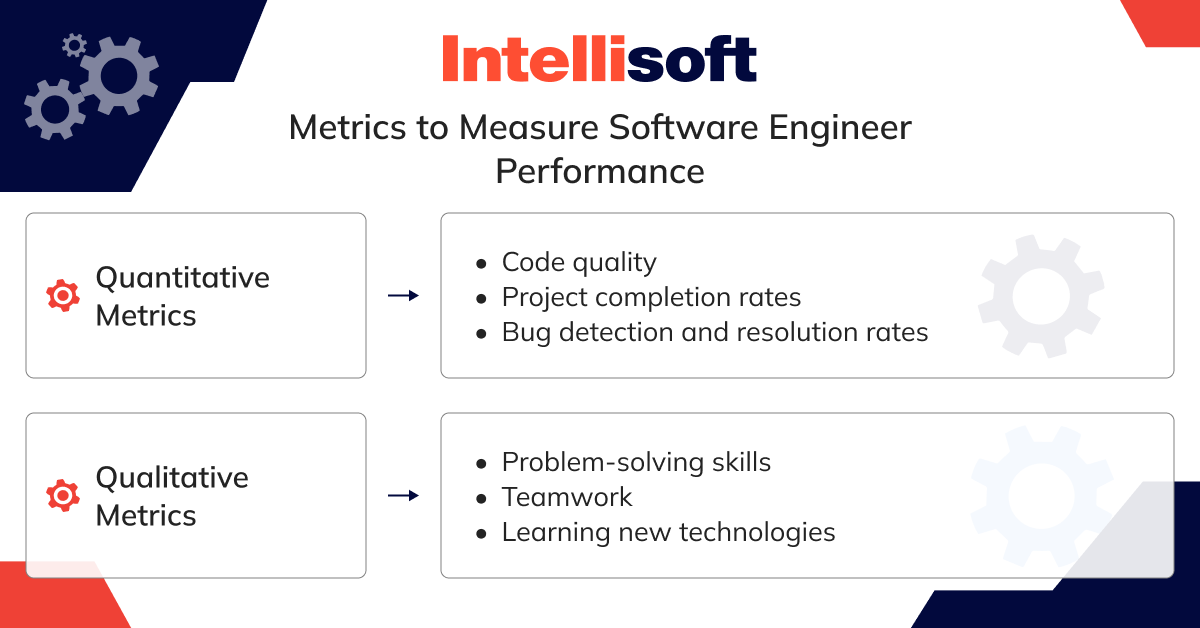
Quantitative Metrics
Performance metrics provide a tangible way to assess a software engineer’s productivity and effectiveness. The main quantitative metrics to consider include:
- Code quality. High-quality code is clean, readable, and maintainable. Evaluating how well-structured and error-free a developer’s code is can give you a sense of its overall quality.
- Project completion rates. Timely delivery is a crucial factor in software development. Monitoring how consistently an engineer meets—or even exceeds—deadlines gives valuable insight into their efficiency and dependability.
- Bug detection and resolution rates. While encountering bugs is inevitable, the real test is how quickly and efficiently an engineer can identify and fix them. This metric highlights their problem-solving ability and attention to detail.
Qualitative Metrics
While numbers can give you some insight, a software engineer’s value often lies beyond measurable metrics. Here are a few personal and qualitative aspects to consider:
- Problem-solving skills. Observing how an engineer approaches issues and devises effective solutions is essential. After all, great developers are often great problem-solvers, creating innovative software to address complex challenges.
- Teamwork. Software development is rarely a solo effort. An engineer’s ability to collaborate, exchange ideas, and contribute positively to a team is just as vital as their technical expertise.
- Learning new technologies. With the ever-evolving tech landscape, it’s essential to gauge how enthusiastic and quick an engineer is at mastering new tools and languages.
How IntelliSoft Implement Performance Management in Development Teams?
When ZyLAB, a prominent name in e-discovery software, aimed to scale and upgrade its platform, IntelliSoft stepped in to provide top-tier development services. They ensured their developers stayed on track by introducing a solid performance management system based on setting SMART objectives, adopting agile methods, and continuously supporting the team with feedback and training. Critical metrics such as code quality and delivery timelines were carefully monitored through advanced tools such as Kubernetes and Docker. This approach allowed the team to successfully containerize services, enhance OCR functionality, and scale the platform seamlessly, resulting in significant performance boosts and improved cost efficiency.
Conclusion
What is performance management in IT? It’s a key to driving both individual and organizational success. By establishing clear objectives, offering regular feedback, and aligning employee efforts with company goals, businesses can promote growth, spark innovation, and boost team engagement. Whether through formal evaluations, ongoing feedback loops, or opportunities for training and development, performance management ensures employees remain focused and contribute meaningfully to the organization’s success. In the end, a robust performance management system enhances productivity and increases employee retention and satisfaction. Contact IntelliSoft today to get a consultation.