Cloud computing has become a cornerstone for businesses large and small, with 66% of small tech companies and 74% of enterprises already reaping its benefits—think scalability, accessibility, and reliability. However, it’s not all smooth sailing. Despite the advantages, cloud platforms are not impenetrable fortresses. These platforms can be vulnerable to security risks such as insider threats, complex data storage laws, and targeted malware attacks.
The trend toward cloud usage isn’t just continuing; it’s accelerating. According to Grand View Research, the cloud computing market, currently valued at over $602.31 billion, is expected to surge at a 15.7% annual growth rate through 2030.
So, what are the key cloud computing risks? More importantly, how can they safeguard against these potential threats? Let’s dive into the challenges in terms of security in cloud computing and weigh them against its significant benefits.
Table of Contents
How Secure Is the Cloud?
What is cloud computing? Cloud computing is the process of offering various services over the web. These resources include tools and applications such as data storage, servers, databases, networks, and software. Instead of storing files on a hard drive or local storage device, cloud storage allows users to store them in a remote database. As long as an electronic device has access to the network, it has access to the data and programs to run it.
The cloud allows you to upload digital files to a server, and you can retrieve them again whenever you want. If you use a secure cloud service, your information will be password-protected and encrypted, guaranteeing data security and anonymity.
You can’t consider cloud data storage to be 100% secure. Nearly ⅔ of enterprises view cloud computing security as the biggest impediment to adoption. At the same time, many businesses are guilty of data leakage – almost half of them don’t have their cloud databases encrypted, leaving their information vulnerable. What is more worrying is that 29% of enterprises in the cloud have experienced potential account compromises.
While you may think this number is not that dramatic, it is still a catastrophe for healthcare organizations.
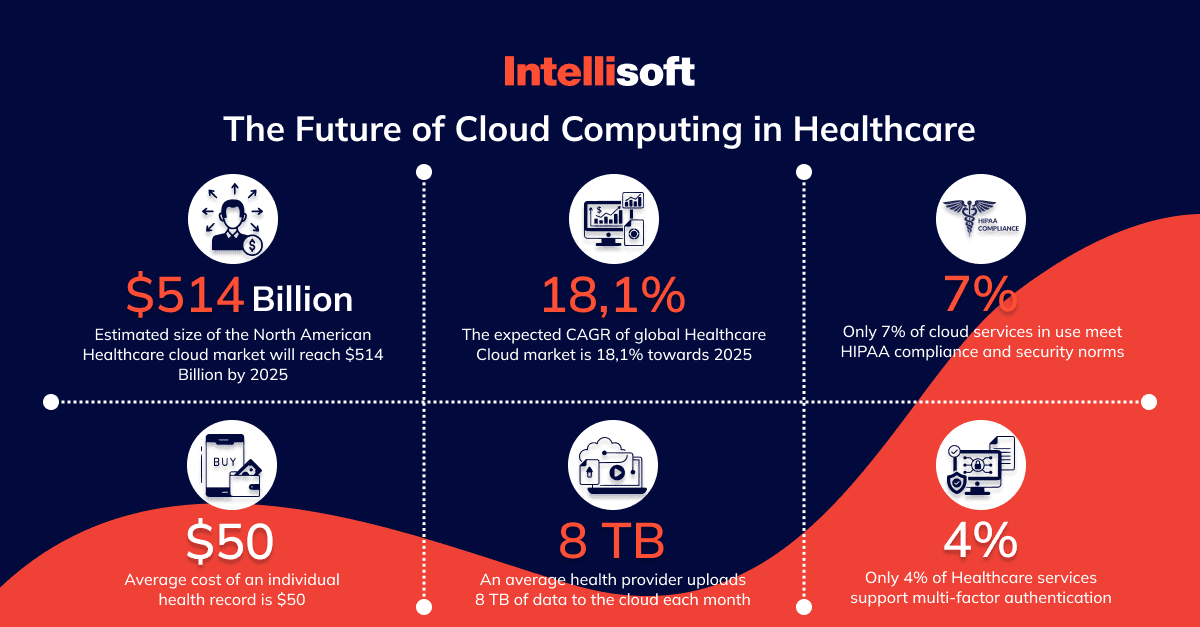
West Monroe Partner’s report shows that 35% of healthcare organizations surveyed held more than 50% of data or infrastructure in the cloud. Interestingly, the average medical company uploads 6.8 TB of data to the cloud monthly, which is more than all of Wikipedia’s archives! The worst thing is that it does not mean each organization knows how to secure information in the cloud.
Some field experts even recommend never storing important information in the cloud, such as passwords for accessing e-wallets and mail. The best place to store sensitive data is in a handwritten notebook or a USB flash drive that no one else can access.
Many professionals forget about the “golden rules” when using cloud storage. If you need to upload an important file to a cloud service, encrypt it with a program before doing so.
If you download files infected with a virus, you could potentially corrupt all your saved data, and the malware could spread throughout your system. This most often happens unknowingly when sharing malicious content among close people. A similar problem can occur if data on a computer system is also automatically synced to the cloud. Thus, malware can get into the cloud storage. The easiest way to avoid this problem is to use antivirus software. It will detect not only viruses but also other malicious programs such as adware and spyware. Antiviruses usually work in the background without slowing down the computer system, removing and preventing viruses from entering the system and, therefore, the cloud.
If you decide to use our cloud services, we’ll help ensure that your cloud computing risks solutions are risk-free and you obtain all the security benefits of cloud computing. Besides, IntelliSoft assists with hiring qualified human resources in the short term, ensuring project regulatory compliance, and creating and adopting standardized processes.
Risk in Cloud Computing #1. Data Privacy
What are the security risks of cloud computing methods? The primary cloud security risk that most companies think about is unauthorized access to confidential information by the service provider. This is because the processing will actually take place on the provider’s equipment, with no ability to control its actions physically.
In assessing security risks of cloud computing, the main threat is unauthorized access to objects such as:
- Database as a service
- Virtual server
- Data transmitted in an unsecured form
- Other objects of a leased cloud involved in information processing (balancers, data storages, source code, etc.).
The simplicity of creating and configuring some services leads to the threat of unauthorized access to published databases and other services for storing information, such as S3 or Object Storage.
Solution 1: Encrypt sensitive data stored in the database
If it is impossible to guarantee the security of the stored data on a physical level, you should make such access meaningless. This measure will also minimize the risk of unauthorized access to the published database.
Encryption can be implemented on the application level or using the built-in database tools.
Solution 2: Remove system users and/or packages created by a provider from virtual servers
Often, the provider adds accounts or programs to virtual servers and other services to enable convenient administration of all services directly from the cloud infrastructure management console. Therefore, this measure should only be used when data privacy is a top priority (e.g., in the bank card processing segment or hospital patient records).
Solution 3: Encrypt data to transmit
If the value of the data is high, it is reasonable to use application-level encryption. The cost of such a measure is relatively small. This measure imposes higher requirements on encryption key and certificate management processes since the service may be disrupted if the certificate suddenly expires.
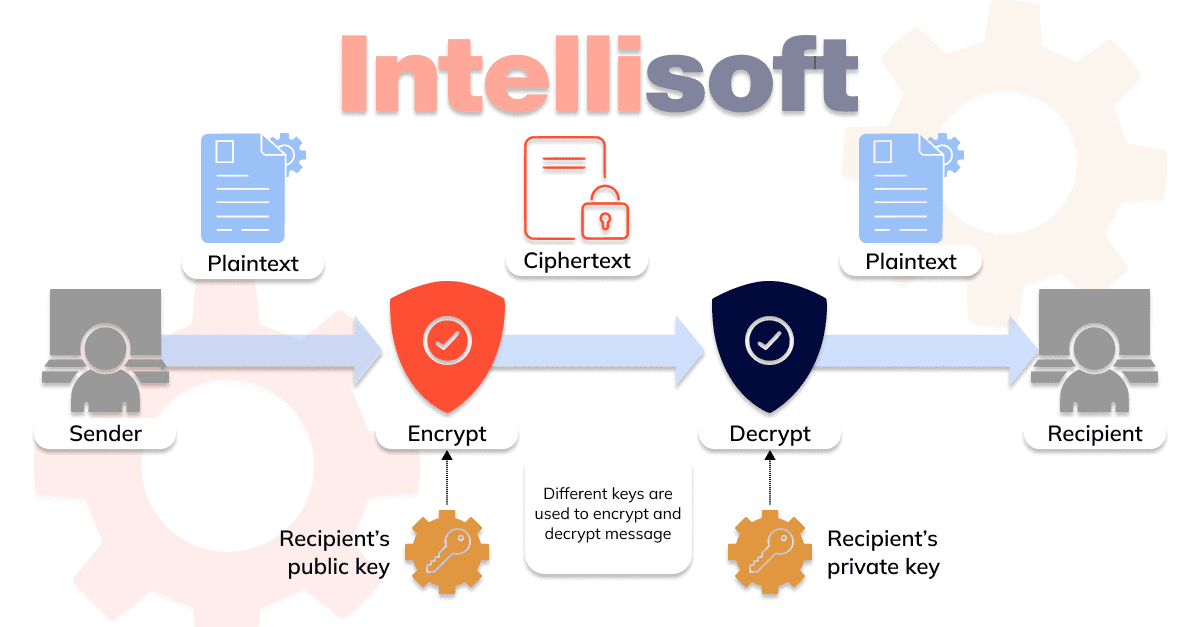
Solution 4: Prohibit public access to databases at the network segment level
It is recommended to use architectural restrictions to eliminate the possibility of accidental publication of the database on the Internet. For example, when access from the web is possible only to one network segment, which is prohibited from placing databases and other similar services.
Solution 5: Must use multifactor authentication to access the cloud
This measure is mandatory when using the cloud. If a privileged account is compromised, you can completely lose control over the cloud and, therefore, all the business processes implemented through cloud services.
To understand how to achieve ultimate cyber security on the example of a healthcare project, feel free to read our exclusive e-Book that includes handy tips on securing IT healthcare projects.
Risk in Cloud Computing #2. Service Availability
The second most important cloud computing security risk is the disruption of service availability because of the provider’s fault. Any tech failures in the provider’s infrastructure or political restrictions can directly impact the dependent service’s operation.
Most often, this risk is a consequence of the implementation of such cloud security threats as:
- Restriction of access due to sanctions restrictions
- Any denial of service by the provider
- Technical failure of the provider’s equipment
In addition, it should be considered that unauthorized access to the control console by an external intruder is very likely to cause a service disruption.
Solution 1: Prohibiting the use of a root account for administration purposes
A root account is an account that was used to sign up for a cloud service. It has the most extensive rights, and if you lose it, it will be tough to regain control of the cloud. Therefore, minimizing the risk of compromising such an account is recommended if it is used for administration or other tasks.
Solution 2: Separate OUs for administrators, security, testers, developers, and core infrastructure
Breaking down functionality is important for at least two reasons. First, the infrastructure used for development or testing changes frequently, and lower security requirements increase the likelihood that services or accounts will be compromised. In that case, separating those segments from the production segment will minimize the impact of those segments on the combat service’s operation. As for splitting security features into separate segments, this is primarily to ensure the security of audit logs.
Solution 3: Monitoring messages from the provider about maintenance or degradation of equipment
The provider performs maintenance of equipment quite often. Sometimes, it is associated with, for example, the degradation of hard drives. There are times when the provider needs to shut down your service to do the job. As a rule, they warn you about this so you can quickly switch to backup equipment. However, if you ignore the ISP’s messages, you may find that the service stops working because the key server suddenly shuts down.
Risk in Cloud Computing #3. Excessive Cost
The simplicity and speed of resource allocation in the cloud is an undeniable advantage of this approach. It allows services to scale quickly as the number of requests from customers increases. On the other hand, remember that if you do not limit resource allocation, the cost of using these resources will eventually exceed the possible profits. The problem of unlimited scaling is particularly acute during DDoS attacks.
If, for example, powerful servers have been rented that are less than 10% utilized, this will lead to cost overruns and lower profits.
Solution 1: Virtual server load control
When renting a virtual server, you pay for its full cost. Consequently, the less loaded the server, the more expensive it eventually costs to operate. Data on resource utilization can be obtained from the server operating system logs.
Solution 2: Limiting scalable services
As a rule, all cloud services allocate resources within quotas. Therefore, it is sufficient to specify such quota values for resources, the cost of which will be acceptable.
Solution 3: Use of application layer defenses
This requirement is mandatory for at least two reasons. First, requests from attackers do not generate any income, meaning there is no point in wasting resources on processing them. Secondly, the absence of app-layer protection significantly increases the risk of a successful attack on the service. Different variants of implementation of application-level protection are possible, ranging from the firewall to traffic cleaning services.
Risk in Cloud Computing #4. The Human Factor
Even if you choose a reliable cloud storage provider, there is still the risk of data loss due to human error. In 9 out of 10 cases, problems arise due to human error. A service technician can get distracted, forget to reset the master password, or connect unprotected devices to the closed circuit of the server. Even a short-term vulnerability can cause cloud computing security risks.
Cloud computing risks can also arise from user error when users leave their devices without VPN protection and do not apply antivirus software. If user errors threaten the user alone, flaws or negligence in the work of company specialists usually affect entire clusters of data under their control.
Solution: Reliable Provider
It is vital to choose a cloud service provider you can trust. Check whether the agency has proven tech expertise in the niche of your interests, positive customer testimonials, a project portfolio, and a point of contact for a recommendation.
Risk in Cloud Computing #5. Unauthorized Changes to Software
Software is responsible for all aspects of Internet services. It is extremely important to ensure the app’s integrity when using cloud services, from writing the source code to running it on a live service. When using external services, additional threats, such as making unauthorized changes to the assembled containers and introducing malicious code during the compilation process, arise.
Solution: Software’s Integrity
To minimize these security risks of cloud computing, ensure that the source code repository and container register are fully controlled and that the integrity of the software is maintained throughout its lifecycle.
How to Bolster Cloud Computing Security?
We have considered several advantages and risks of cloud computing. Now, let’s focus on general problems and solutions.
There is a need for mutual understanding and partnership among enterprises and cloud providers to ensure optimum cloud computing security and data safety onboard. Here are some ways in which they can bolster the same.
Related readings:
- What Is Kubernetes And When to Use It: Key Trends in 2023
- What is Cloud Computing? Understanding the Basics, Services and Benefits
- Docker and Microservices: The Future of Scalable and Resilient Application Development
- Complete Guide to Cloud App Development: Key Steps & Costs
- Monolithic vs Microservices Architecture: Pros and Cons
Risk Assessments
Carrying out a risk assessment involves conducting an audit of your cloud architecture. It helps understand the capabilities of the security controls deployed and how efficiently they are operating presently. It enables the teams to figure out gaps and make requisite decisions to fill them.
User Access Controls
Given that the cloud ecosystem is easier to access, it is imperative for enterprises to establish stringent user access controls. User access controls are necessary to safeguard sensitive leakage by insiders. Access to critical functions should be given to only a handful of individuals to keep the data safe from unauthorized eyes.
Automation
Enterprises need to automate critical initiatives, including real-time monitoring, vendor risk assessments, and more. This would enable the IT department to monitor essential functions instead of being slowed down by a slew of unwanted, repetitive tasks.
Continuous Monitoring
Continuous monitoring is one of the essential functions of the current cloud ecosystem. With the cloud becoming more vulnerable and cybercriminals finding newer ways to breach it, you must loop in real-time assessment to ensure your data remains safe.
The Future Of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has transcended its status as a mere buzzword, emerging as a critical element in the tech world, guiding organizations to take control of their technological destinies. However, with this immense power comes the significant duty of comprehending and managing the cloud computing risks.
As we look ahead, industry visionaries foresee Cloud Service Providers (CSPs) operating almost like ATMs, offering a diverse array of services that businesses can access on demand. This adaptability aims to simplify operations, letting companies utilize services as required. Nevertheless, it demands careful planning and a sharp awareness of the associated risks.
A notable shift in the CSP ecosystem is the rising need for specialized skills to manage substantial system upgrades and migrations. To thrive in this environment, businesses must cultivate a data-driven culture and invest in training their technical teams in good practices for securing cloud environments and data.
Looking forward, we can anticipate CSPs will make significant investments in machine learning and artificial intelligence, enhancing their services with state-of-the-art functionalities. However, integrating AI and ML introduces new security challenges that must be addressed, likely leading to stricter security measures and more regulatory oversight as the market grows.
For businesses, the journey to cloud integration is complex and filled with challenges. It’s not a process to be hurried; it requires meticulous planning, an understanding of potential pitfalls, and strategic execution. By adopting careful management practices and engaging skilled professionals, companies can mitigate cloud computing risks, lower costs, and sidestep common mistakes.
The future of cloud computing involves establishing robust industry standards that tackle regulatory, management, and technological issues, paving the way for sustainable innovation and long-term success in the cloud era.
Final Thoughts
Cloud storage is generally secure, but it can cause some problems that you can prevent. At least, you can avoid them by hiring experts.
You should only use reputable cloud storage providers with a strong track record and reputation. Remember to protect all your devices with a premium VPN like Le VPN and a good antivirus program, and observe basic cyber hygiene. Do not forget about encryption and other types of defense.
Just a few of these simple steps will lead you to have your data protected everywhere. You should be especially careful with cloud computing in healthcare. It’s better to consult specialists from IntelliSoft to see how you can protect all sensitive data for sure. Our company pays extra attention to data protection for our clients and earned a great reputation as an outsourced cloud development service provider among our clients.