The healthcare industry is open to innovation, constantly adopting new technologies and tools to enhance patient care and optimize processes. Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, big data, IoT, and other technologies are reshaping how healthcare institutions operate and how people receive care. Mobile health, or mHealth apps, are currently a trend in healthcare, reshaping how people access and manage their health and well-being.
In 2022, the global mHealth market surged to $87 billion. Forecasts suggest it could grow to $640 billion by 2031, indicating a projected Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of over 29.6% from 2023 to 2031.
In this article, we will explore why mHealth apps are on the rise, discuss their types and use cases, and help you decide whether you need one. Moreover, if you’ve been looking for a development partner to help you develop your first mHealth app, IntelliSoft is here to help. With more than 13 years of experience in the healthcare industry, we know where the industry is headed and how to stay on top of the competition, providing top-notch patient care.
Table of Contents
mHealth Apps Market Overview
Based on insights from Grand View Research, the global mHealth apps market was valued at USD 43.5 billion in 2022 and is anticipated to maintain a steady growth trajectory with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 11.6% from 2023 to 2030. This growth of the top mHealth apps is fueled by several factors, including the rising adoption of fitness and medical apps for health data monitoring via smartphones, increased internet and smartphone penetration, and heightened awareness about the importance of maintaining overall well-being.
With over 350,000 health applications available across app stores, users are increasingly inclined towards managing chronic conditions, while healthcare professionals advocate for mobile app integration to enhance patient care.
However, there are a lot of challenges, particularly concerning data security and privacy. Experts underscore concerns such as unauthorized data access, breaches, and regulatory compliance hurdles. To tackle these obstacles, collaborative efforts among healthcare entities and technology firms are underway to devise secure and user-friendly solutions, ensuring seamless mobile patient care while mitigating potential risks.
mHealth Apps for Patients: Types, Use Cases, and Trends
What are mHealth apps? These apps help revolutionize patient care and make it easier to access and receive care. Let’s discuss the main app types, the best mHealth apps use cases, and market trends.
Types of mHealth Apps
Professional Solutions
These apps are designed for healthcare professionals, such as doctors, nurses, clinicians, pharmacists, administrators, etc. They help improve communication between various healthcare teams, facilitate better decision-making, and streamline patient care.
Main features include:
- EHR integration
- Telemedicine for remote consultations
- Secure messaging
- Clinical decision support systems
- Prescription tools and medication management
Applications for Patients
These mHealth apps for patients are created for patients to use, helping them manage their health more effectively. These applications have user-friendly interfaces, provide personalized health insights, remind patients about medications, help track symptoms, and grant direct access to their medical records. They also help connect with healthcare providers and receive help instantly.
Key features include:
- Health and wellness tracking
- Appointment scheduling
- Medication reminders
- Symptom tracking
- Access to medical records
mHealth Apps Use Cases
Let’s take a look at mHealth apps for patients use cases and where they make the most impact in the healthcare sector.
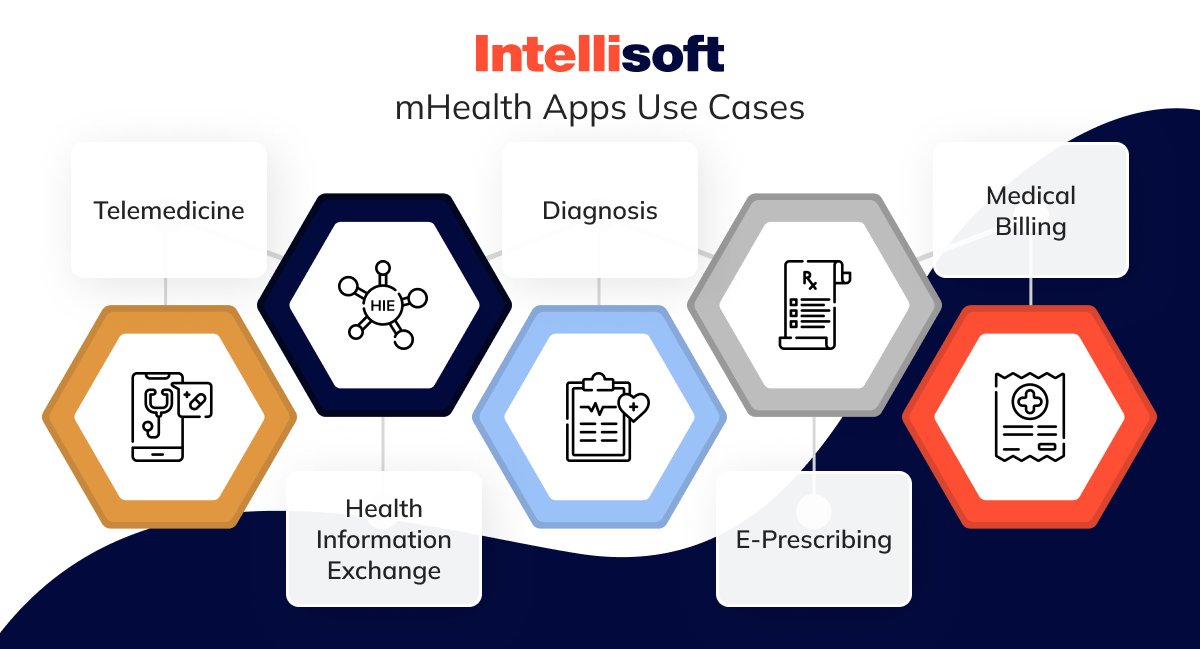
Telemedicine
During the Covid-19 pandemic, mHealth apps became a necessity rather than an option. They were used to schedule appointments, connect with doctors, and grant people access to high-quality care regardless of their location. Now, mHealth apps are still used for the same purpose, revolutionizing how people receive care.
Health Information Exchange
The best mHealth apps are also used to store and exchange patient data. For instance, EHR systems allow accessing and updating patient records on the go, so the management process becomes more effective and accurate. These apps also allow healthcare providers to share patient data in a secure way, ensuring that everyone involved in patient care in well-informed.
Diagnosis
Some examples of mHealth apps include diagnostic tools and algorithms that help healthcare practitioners diagnose accurately. This is a must-have feature for preliminary assessments and decision support.
E-Prescribing
mHealth apps streamline the prescription process through electronic prescribing functionalities. This feature enables healthcare providers to electronically transmit prescriptions to pharmacies, minimizing errors, enhancing efficiency, and improving medication adherence for patients.
Medical Billing
mHealth apps facilitate seamless medical billing processes by automating billing tasks and streamlining reimbursement procedures. Healthcare providers can efficiently manage billing workflows, submit claims electronically, and track payment statuses, optimizing revenue cycle management and reducing administrative burdens.
Current Trends in Mobile Health Apps
The technology used in healthcare is constantly changing, and so are the mobile apps developed for healthcare institutions. To stay ahead of the competition and deliver top-notch patient care, you should be aware of the latest trends in the market and how technology is shaping healthcare. Let’s dive in.
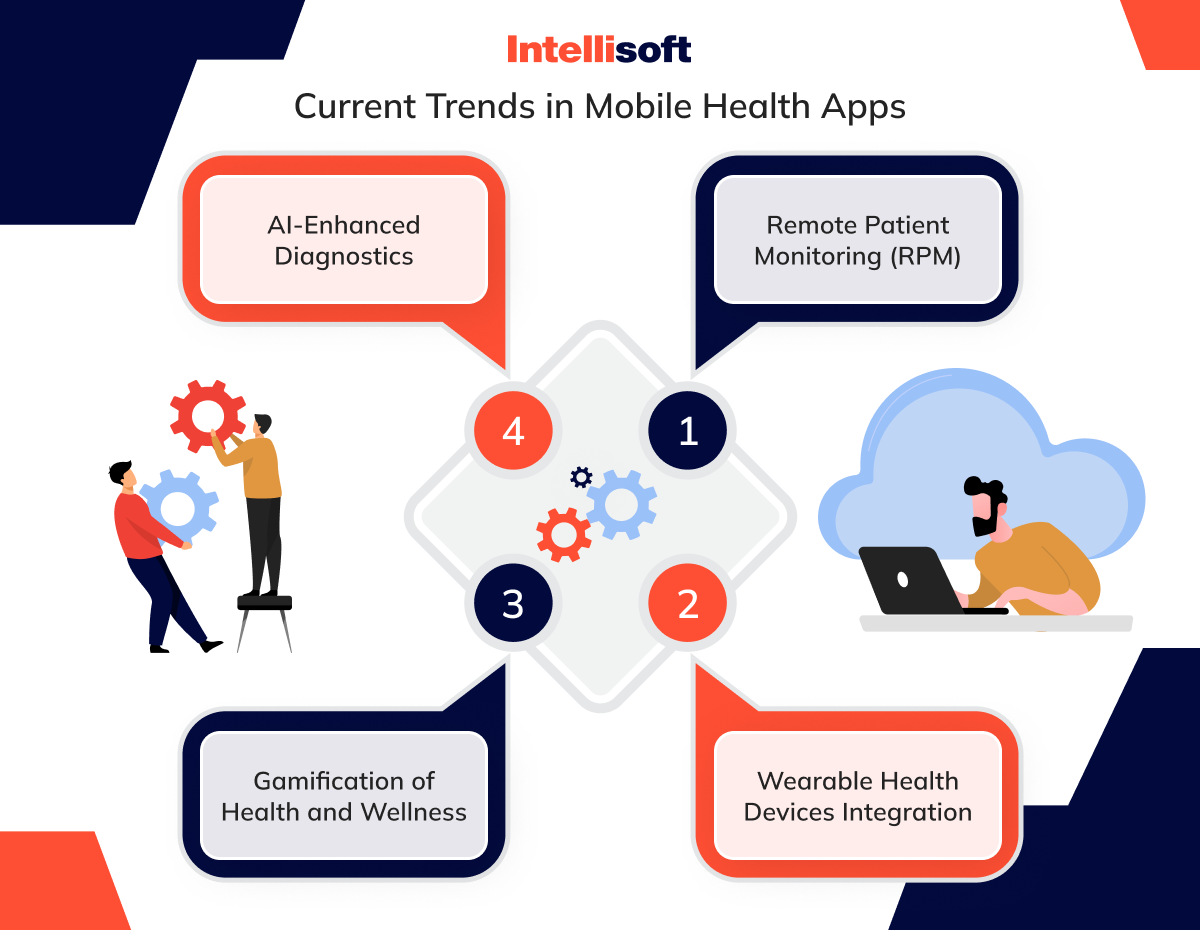
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
The demand for remote healthcare solutions is growing, and remote patient monitoring systems have emerged as one of the main trends in mHealth apps. These applications allow healthcare practitioners to monitor patients’ vital signs remotely, keep track of their symptoms and medication adherence, and facilitate early intervention.
Wearable Health Devices Integration
mHealth apps can be integrated with wearable devices such as fitness trackers and smartwatches. This integration of mHealth apps for exercise allows the synchronization of data and tracking of the health and wellness of patients wearing smart devices.
Gamification of Health and Wellness
Gamification techniques are reshaping health and wellness apps, making behavioral change more engaging and sustainable. By incorporating game elements such as challenges, rewards, and social interactions, these apps motivate users to adopt healthier habits and achieve their wellness goals.
AI-Enhanced Diagnostics
AI is revolutionizing diagnostics through mobile apps, enhancing accuracy and efficiency. These apps leverage AI algorithms to analyze medical data, images, and symptoms, assisting healthcare professionals in diagnosis and treatment planning, ultimately improving patient outcomes, for example, thanks to mHealth apps for diabetes.
Related readings:
- App for Doctor Appointment Development: A Comprehensive Guide
- Transforming Healthcare Communication: Integration of HL7 Interface Engine
- Prescription Management Software: The Future of Pharmacy
- Hospital App Development: Innovate, Integrate, and Provide Better Care
- Automation in the Industry of Healthcare: Main Benefits for Business
Benefits of Mobile Health Apps for Healthcare Professionals and Patients
As practice has shown, mHealth apps have a lot to offer for practitioners, caregivers, healthcare organizations, and patients. The benefits of mHealth apps are incredible, spanning from better diagnosis to convenient bill payments. Let’s explore all the advantages of mHealth apps.

Reduced Risk of Misdiagnosis
Handling patient records manually can increase the risk of diagnostic errors. In the US alone, more than 12 million people are affected by diagnostic errors yearly. mHealth apps help practitioners improve diagnosis by keeping track of prescriptions, treatment options, and communications. As a result, the risk of misdiagnosis is reduced, and patients receive timely and accurate care.
Access to Medical Records
mHealth apps allow healthcare practitioners and patients to access medical records more easily. Now people don’t have to rush to the hospital to get their medical records; they can access them from their mobile phones. The records are always with them, ready to be accessed anytime from anywhere.
Optimized Person-Hours
Unfortunately, long working hours are a common case among healthcare practitioners. They work unregulated hours, which causes stress, negatively affects their performance, and can influence patient care. mHealth apps help practitioners keep all documentation in one place, monitor treatment procedures, and keep in touch with patients, saving time and effort.
Timely Care at Remote Locations
A lot of people living in remote locations can’t receive timely care and treatment. mHealth apps help these patients connect with caregivers by video calls and receive help no matter their location. Moreover, it helps people avoid the need to commute to hospitals for regular visits, saving time and money.
Real-Time Communication
Instant messaging, video consultations, and telemedicine features empower seamless collaboration and rapid response to patient needs, fostering better healthcare outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Convenient Bill Payments
With integrated billing functionalities, mHealth apps simplify the payment process for patients. From insurance claims to copayments, these apps offer convenient options for managing healthcare expenses, enhancing financial transparency and accountability for both patients and healthcare providers.
mHealth App Development Features
When you decide to develop a mHealth app, remember that it can include multiple features and functionalities, depending on your healthcare organization’s needs and capabilities. However, some features are most common, including:
- Appointment Scheduling and Reminders. People can schedule appointments online and receive reminders to help them manage their time and healthcare journey.
- Symptom Tracking. People can track symptoms, medication, and other information to monitor their conditions and ensure that they receive effective treatment. Practitioners can check this information as well.
- Personalized Health Information and Recommendations. Mobile health apps can provide users with personalized health info and recommendations based on their health history, symptoms, and other factors.
- Virtual Consultations. This feature facilitates remote consultations between patients and healthcare professionals, offering convenient access to expert advice and medical services from any location.
- Fitness Tracking and Monitoring. With these features, patients will be able to monitor their physical activity, set goals, and track progress.
- Medication Tracking and Reminders. Help users manage medication schedules with reminders and tracking functionalities, ensuring adherence to prescribed treatments and reducing the risk of errors.
- Electronic Health Records. This feature provides secure storage and access to electronic health records, enabling users and healthcare providers to access comprehensive medical histories and streamline care delivery.
- Health Education and Resources. This feature offers a wealth of health-related information, educational resources, and wellness tips to empower users with knowledge and promote health literacy, fostering informed decision-making and proactive healthcare behaviors.
- Wearable Device Integration. With the help of this feature, it is possible to integrate mHealth apps with various wearable devices such as fitness trackers and smartwatches. It helps gather real-time data, enhance user engagement, and provide valuable insights for monitoring patients’ wellbeing and health.
- Emergency Contact and Health Information. Users can store emergency contacts and critical health information in their app, ensuring a quick response in case of emergencies.
mHealth App Development Process
Developing an mHealth app is not that different from developing any other type of mobile applications. The only major difference is that some mHealth apps need compliance with HIPAA.
In general, the development process consists of 5 main stages: discovery, UI/UX design, development, testing, and support and maintenance.
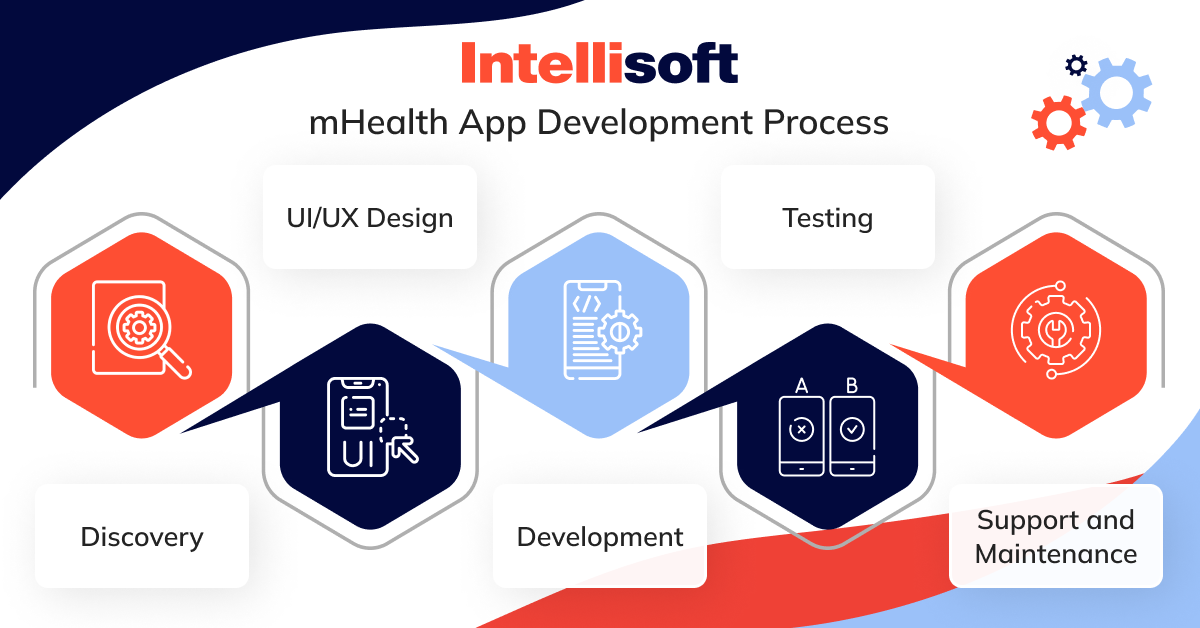
Discovery
During this stage, it is essential to gather requirements for the future product as well as identify target audience, key features, and technical requirements. During the discovery phase, you will attend stakeholder meetings, conduct market research, and analyze competitors to shape the roadmap and set the foundation for future development.
UI/UX Design
User interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design are critical for creating an intuitive and engaging app interface. Wireframing, prototyping, and usability testing ensure that the app meets user expectations and provides a seamless experience across devices.
Development
Here comes the main stage of the process; development itself. It involves the actual building of your app through code, according to the specifications outlined in the design phase. Development usually includes the front-end development (client-side), back-end development (server-side), and integration with external APIs or databases. For mHealth apps, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards like HIPAA is essential at this stage.
Testing
Thorough testing is conducted to identify and address any bugs, errors, or usability issues before the app is launched. This includes functional testing, performance testing, security testing, and user acceptance testing. Compliance testing for regulations such as HIPAA is also crucial to ensure data privacy and security for mHealth apps.
Support and Maintenance
This may involve monitoring app performance, addressing user feedback, implementing updates or patches, and addressing any issues that arise post-launch.
How Much Does It Cost to Develop mHealth App?
The first thing you might be intered in when you embark on mHealth app development journey is the cost. The question “How much will it cost?” is totally valid – you must now what to expect and how to plan your expenses accordingly. Well, we can’t tell you the exact price but we have prepared rough estimates to help you have a clearer picture.
On average, the cost of developing a mobile health app ranges from $45.000 to $80.000, depending on factors like features, developers’ location, and project complexity.
If you want to go big and integrate AI, ML, and other advanced technologies in your app, the price will rise to $100.000-$150.000. Again, the prices are just estimates, based on our experience of working with various clients and prices for healthcare development in the market.
If you are interred in a more accurate estimate, don’t hesitate to contact us or check our pricing page; our experts will calculate the cost of your project promptly.
Factors Influencing mHealth App Development Costs
Again, there are numerous factors that influence the cost of mHealth app development. Understanding them is vital for careful planning and budgeting, so let’s dive in.
- Platform Choice. Deciding whether to develop the app for iOS, Android, or both platforms significantly impacts development costs. Each platform has its own set of development tools, programming languages, and design guidelines, requiring separate development efforts for each platform.
- Features Set. The number and complexity of features also influence the final cost. The basic essential features such as registration and appointment scheduling are less expensive; however, if you need advanced functionality like telemedicine, AI tools, or live medical data monitoring, the price will go up.
- UI/UX. Intuitive and appealing design will be more expensive, but it’s essential if you want to increase customer satisfaction and engagement. The more customized the design – the higher the cost.
- Integration with Third-Party APIs. Integrating with external APIs for functionalities such as payment processing, location services, or health data interoperability can streamline app development but may incur additional costs. Licensing fees, API usage charges, and development efforts for seamless integration contribute to overall project expenses.
- Performance and Compliance with Regulations. Ensuring optimal app performance and compliance with regulatory standards, such as HIPAA for healthcare data security and privacy, is paramount but can increase development costs. Implementing robust security measures, data encryption, and compliance audits require specialized expertise and resources.
- Testing and QA. It is essential to create a secure, high-quality app protected against breaches. Thus, investing in thorough testing and quality assurance is a must. You should test the app across multiple platforms, devices, and scenarios, uncovering potential issues and bottlenecks that may affect performance or influence patient data.
- Maintenance and Support. Post-launch maintenance and support are ongoing costs associated with mHealth app development. This includes addressing user feedback, implementing updates or patches, monitoring app performance, and ensuring compliance with evolving regulations.
Challenges Prevalent In The mHealth Sector
As the mHealth sector continues to grow and evolve, it faces several challenges that impact its development and adoption. Let’s explore some of the most prominent issues:

Compliance & Regulations Issues
One of the biggest issues with mHealth apps is following compliances since every country has its own set of regulations that must be followed. Here are the regulations you should follow in major countries:
- The USA. Compliance with HIPAA for data protection and FDA regulations for medical devices.
- Canada. Adherence to PIPEDA for personal data and Health Canada regulations for medical devices.
- The UK. Compliance with GDPR for data privacy and MHRA oversight for medical devices.
- European Union. Adherence to GDPR and EU medical devices regulations (MDR, IVDR).
Presence of Multiple Devices
New devices and channels keep entering the healthcare sector, including Smart TVs, smartphones, voice-powered devices, etc. Thus, interoperability is a huge problem in healthcare as it is difficult to connect all these devices and ensure that they operate correctly. It is essential to keep track of the number of devices and ensure security and interoperability across platforms.
Lack of Security
In an era marked by increasing cyber threats and sophisticated attacks, the security of mHealth apps and platforms is of paramount importance. The sensitive nature of health data, including personal medical records, diagnostic information, and treatment histories, makes mHealth systems lucrative targets for malicious actors seeking to exploit vulnerabilities for financial gain or other malicious purposes.
One of the primary challenges in addressing the lack of security in mHealth apps is the complex and dynamic nature of the threat landscape. Cybercriminals continuously evolve their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) to circumvent security measures and exploit vulnerabilities in software and systems.
Wrapping Up
mHealth apps are revolutionizing the healthcare sector, changing the way both caregivers and patients operate in the healthcare industry. By harnessing the power of technology, mHealth apps facilitate seamless communication, streamline processes, and empower individuals to take charge of their health and wellness like never before.
As the demand for mHealth solutions continues to rise, it is essential for healthcare organizations, developers, and stakeholders to prioritize security, compliance, and user-centric design to ensure the efficacy, safety, and trustworthiness of these apps.
For cutting-edge solutions and expert guidance in mHealth app development, contact Intellisoft today and embark on a journey towards transforming healthcare for the better.