Like any other industry today, the healthcare sphere continues to evolve, implementing digital solutions into day-to-day operations. Today, we want to discuss electronic health information exchange (HIE). So, what is health information exchange? HIE fundamentally transforms patient care. It connects medical facilities, health organizations, and government agencies through a network adhering to national standards. This interconnectedness enhances healthcare quality, safety, and efficiency, ensuring that vital health information is exactly where and when it’s needed.
Since the launch of the Nationwide Health Information Network (NHIN) in 2004, this initiative, now known as the eHealth Exchange, has set the benchmark for secure and efficient electronic health information exchange across the U.S. At IntelliSoft, thanks to our extensive experience in the healthcare field, we lead the way in the seamless, secure electronic transmission of healthcare-related data. We enable secure data exchange without needing a national identifier by accurately matching patients to their records.
If you aim to enhance your organization’s health IT infrastructure, read this article. Mastering HIE with IntelliSoft can unlock the full potential of your healthcare operations, significantly improving the speed and quality of patient care.
Table of Contents
What is HIE in Modern Healthcare?
What is health information exchange designed to do? HIE (Health Information Exchange) forms a pivotal part of modern healthcare, revolutionizing how medical information is exchanged between various healthcare systems and stakeholders. Health Information Exchange definition is in the name. HIE allows healthcare professionals like doctors, nurses, pharmacists, and even patients to access and securely share vital medical information electronically. This shift allows us to move away from outdated paper records and represents a fundamental enhancement in patient care’s speed, quality, safety, and cost-effectiveness.
Picture the old-school doctor’s office, crammed with filing cabinets stuffed with paper records. This traditional method is outdated and riddled with inefficiencies. Many Americans’ medical records are trapped in these outdated systems, or worse, in homes, only to be laboriously sorted through at each medical visit. When these records need to be shared among different healthcare providers, they’re typically mailed, faxed, or personally delivered by patients. This process is slow and error-prone.
With the advent of HIE, this disjointed information landscape has been transformed into a seamless, secure, and comprehensive electronic network. HIE doesn’t seek to replace the crucial interactions between patients and healthcare providers. Instead, it enhances these interactions by making complete medical histories readily accessible at the click of a button. Such immediate access to comprehensive medical records means that all relevant information, from previous treatments to ongoing medications, is readily available for consultation during visits, significantly improving decision-making and overall patient care.
To finalize the definition, health information exchange is the backbone of integrated healthcare systems, offering a more informed and cohesive approach to managing patient care. As the healthcare sector continues to advance, the role of HIE becomes increasingly critical for a future where all healthcare providers are armed with the necessary information to offer the best care possible.
Why Health Information Exchanges are Important?
Health Information Exchange HIE has become an indispensable tool that enhances the efficiency and quality of healthcare delivery. HIE provides healthcare providers with a complete overview of a patient’s health history by ensuring seamless communication among caregivers. This comprehensive integration is crucial for effective care coordination, which the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality defines as the organization of patient care activities by multiple parties to ensure the optimal delivery of healthcare services.
What is HIE role in improving patient care? It is immense. With access to more complete patient information, healthcare providers can minimize medical errors, avoid redundant treatments or tests, and reduce hospital readmissions. These benefits improve patient safety and significantly enhance health outcomes. As one of the best use case health information exchange examples, a robust HIE system can identify potential issues in treatment plans early on, ensuring that patients receive appropriate care precisely when needed.
Beyond individual care, HIE also positively impacts population health. A notable instance is the contribution of Healthix, a leading HIE in New York. Healthix was instrumental in supporting the New York State Department of Health’s AIDS Institute in overseeing the healthcare of the HIV-positive population. The data shared through HIE enabled the Department of Health to carry out targeted public health surveillance and interventions, ensuring consistent care and access to necessary treatments for those living with HIV.
Which Federal Act Mandated that Physicians Use the Health Information Exchange (HIE)?
The mandate for physicians to use electronic Health Information Exchange primarily stems from the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act. Enacted in 2009 as part of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA), the HITECH Act was designed to promote and expand the adoption of health information technology, specifically the use of electronic health records (EHRs) by healthcare providers.
While the HITECH Act itself does not explicitly mandate the use of HIE, it set the stage for significant enhancements in the electronic exchange of health information. One of its key components is the Meaningful Use program, which was later evolved into the Promoting Interoperability Programs. These programs offer financial incentives to healthcare providers who demonstrate the meaningful use of certified EHR technology, including the electronic exchange of health information to improve patient care.
The requirement to exchange information is a core component of these programs, effectively making it a federal expectation for physicians to participate in HIE to some extent. The aim is to ensure that health information is available wherever and whenever it is needed, improving the quality, safety, and efficiency of health care delivery across the United States.
Patients greatly benefit from HIE. Health Information Exchange empowers them to manage their health. Consumer-mediated exchange is an essential aspect of modern Health Information Exchange systems, empowering patients to actively manage and control the sharing of their health information among providers.
By facilitating consumer mediated exchange, HIE systems improve patient engagement and support a more informed and personalized healthcare experience. In addition, the implementation of consumer mediated exchange mechanisms within HIEs helps ensure compliance with privacy regulations and fosters greater trust between patients and healthcare providers, making it a cornerstone of patient-centered healthcare strategies.
How Data is Stored and Shared
Managing health information effectively in a Health Information Exchange (HIE) is key to giving healthcare providers quick and correct information to best care for patients. This process involves three main steps: collecting health information, keeping it safe, and sharing it correctly with those allowed to see it.
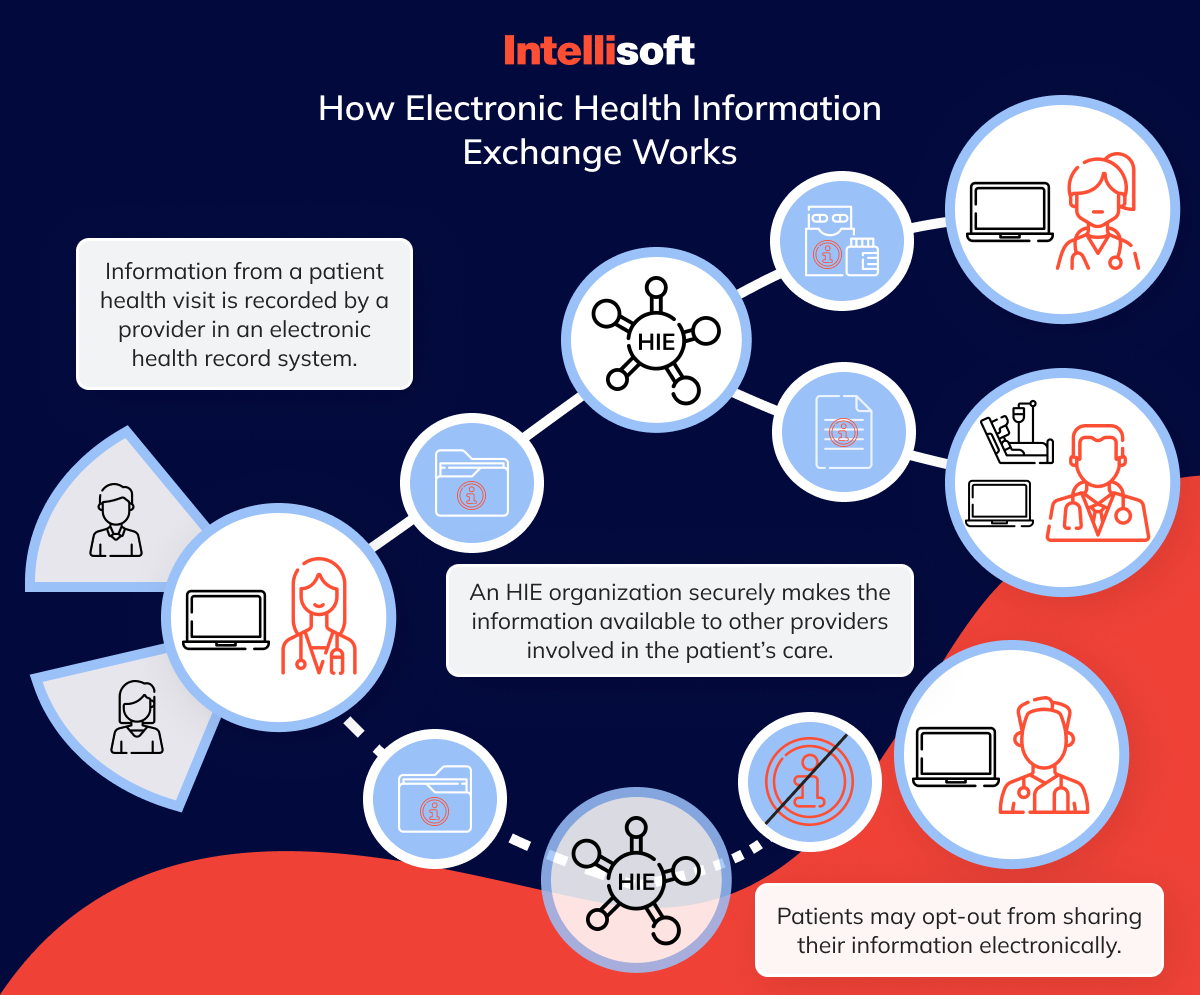
How Health Information is Gathered
Health data is collected at the point of care, mainly through digital systems called electronic health records (EHRs) or electronic medical records (EMRs). These systems gather all details about a patient’s medical history, like diagnosis, treatments, medications, lab tests, and scans. As patients visit different healthcare providers, their digital records are updated. This electronic way of gathering data is more efficient and reduces mistakes often made when things are written down by hand.
How Health Information is Stored
After health information is collected, it must be stored securely to keep it safe and private. HIE systems use advanced data centers with the latest technology to ensure the data is always available and protected. They store data in a well-organized manner, which makes it easy to find and access patient information quickly when needed.
HIE systems have multiple backup systems to prevent data loss or damage. These backups ensure the information can be accessed, even if technical problems or natural disasters occur. The strong storage systems show HIEs’ commitment to keeping patient information safe and always available.
How Health Information is Exchanged
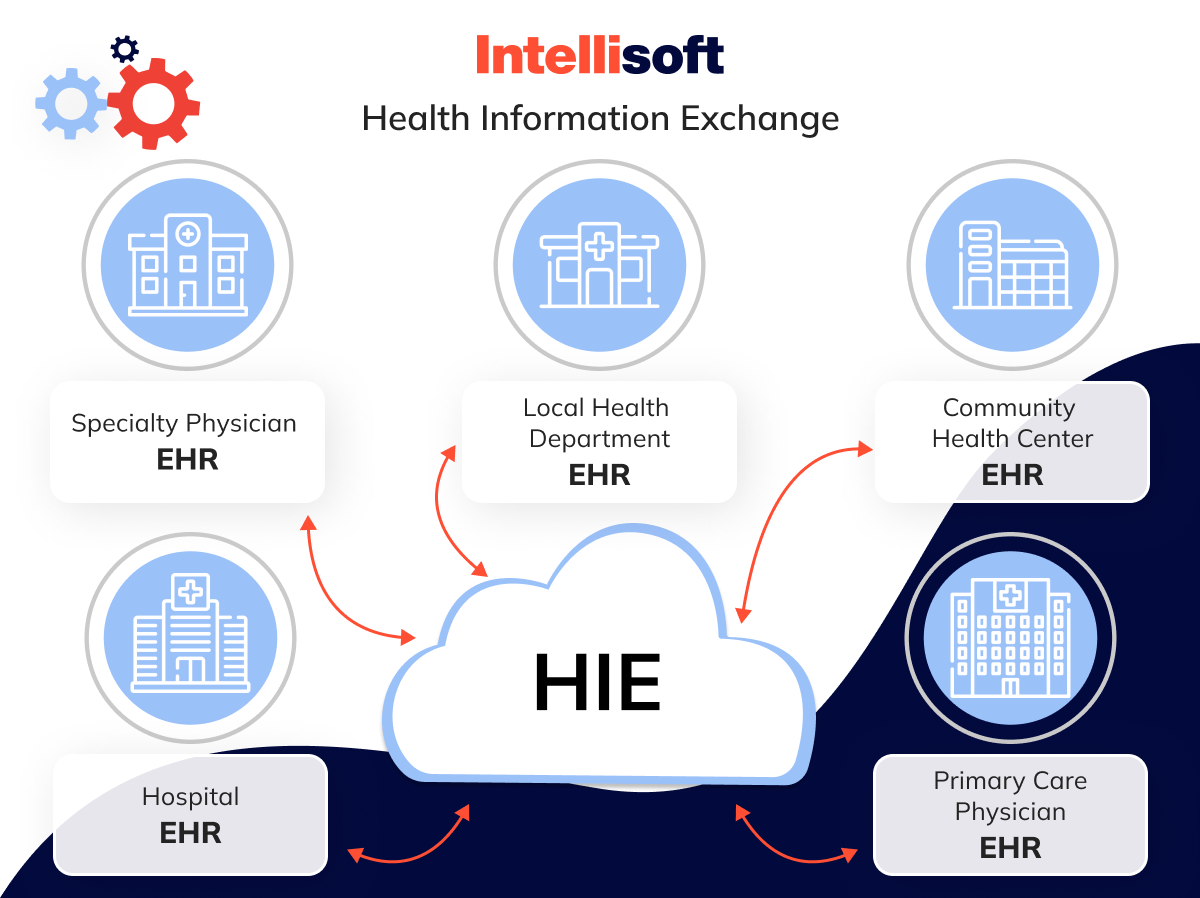
Sharing health information can be done in two ways: push and pull. In a push exchange, specific pieces of information, such as a lab result, are sent directly from one healthcare provider to another. In a pull exchange, a healthcare provider looks up and pulls out the patient information they need from the HIE. Health Information Exchange is especially useful when a complete patient history is required for ongoing treatment or a new diagnosis.
HIEs can be set up in different ways, including federated (where each place keeps its own records), centralized (where all data is kept in one place), and hybrid (a mix of both). Each setup affects how easily data can be accessed and shared.
HIEs handle clinical data, insurance claims, public health information, and data for reporting and quality checks. Every data exchange is protected by strong security measures to ensure that only authorized people can access the information, keeping it private and secure.
Related readings:
- App for Doctor Appointment Development: A Comprehensive Guide
- Transforming Healthcare Communication: Integration of HL7 Interface Engine
- Prescription Management Software: The Future of Pharmacy
- Hospital App Development: Innovate, Integrate, and Provide Better Care
- Automation in the Industry of Healthcare: Main Benefits for Business
Benefits of Health Information Exchange
Health Information Exchange (HIE) marks a significant step forward in the medical world, enhancing how patients deliver, coordinate, and receive healthcare. This essential system offers major benefits, including saving time and costs, improving care coordination, and enhancing patient care.
Time and Cost Savings
HIE systems bring substantial efficiency improvements that save time and money for healthcare providers and patients. By automating tasks like record retrieval and reducing reliance on manual processes like faxing, HIE allows healthcare workers to focus more on patient care rather than paperwork. This makes operations more efficient and improves the quality of care patients receive.
Additionally, HIE reduces the costs of paper-based systems, such as printing, postage, and storage. Less paperwork and reduced need for storage space lead to significant cost savings. HIE also supports cost-effective telehealth services by allowing real-time access to patient data during virtual visits, which can lower the costs associated with in-person consultations, like travel and facility use.
Enhanced Care Coordination
HIE provides a complete view of a patient’s medical history, which is crucial for effective care. Access to detailed records, including diagnoses, medications, allergies, and lab results, helps healthcare providers make informed decisions. This prevents unnecessary tests and promotes patient-centered care. HIE ensures that all healthcare providers involved in a patient’s care, from general practitioners to specialists, have the information they need to provide coordinated and informed care.
For example, in elderly care, HIE lets healthcare providers like primary care physicians and specialists share updates about treatments, medication changes, and test results easily. This coordinated approach helps manage complex health issues, reduces the risk of medication errors, and ensures the best possible interventions, improving the patient’s overall health.
Improved Patient Care
The main benefit of HIE is its ability to improve patient care. Immediate access to a patient’s complete medical history enables quicker and more accurate diagnoses, avoids unnecessary treatments, and can reduce hospital stays. This creates a safer and more efficient healthcare system with better patient outcomes.
Patients also experience fewer redundant tests since their complete medical records are easily accessible, saving time and money. Better medication management is another advantage, as access to a full medication history decreases the risk of prescription errors. Efficient referral management, facilitated by HIE, allows primary care doctors to quickly and electronically share necessary patient information with specialists, speeding up the referral process and enhancing the overall healthcare experience.
As you can see, Health Information Exchange streamlines the operational aspects of healthcare and fundamentally improves how care is delivered and experienced. With the help of a partner with expertise in robust HIE solutions, like IntelliSoft, your healthcare organization can realize these advantages, leading to a more effective, efficient, and patient-centered healthcare system.
Key HIE Usages
Health Information Exchange (HIE) does more than just improve patient care; it is crucial for enhancing various operational aspects of healthcare. Here’s a look at how HIE systems streamline provider operations, improve revenue cycles, and increase overall efficiency in managing healthcare.
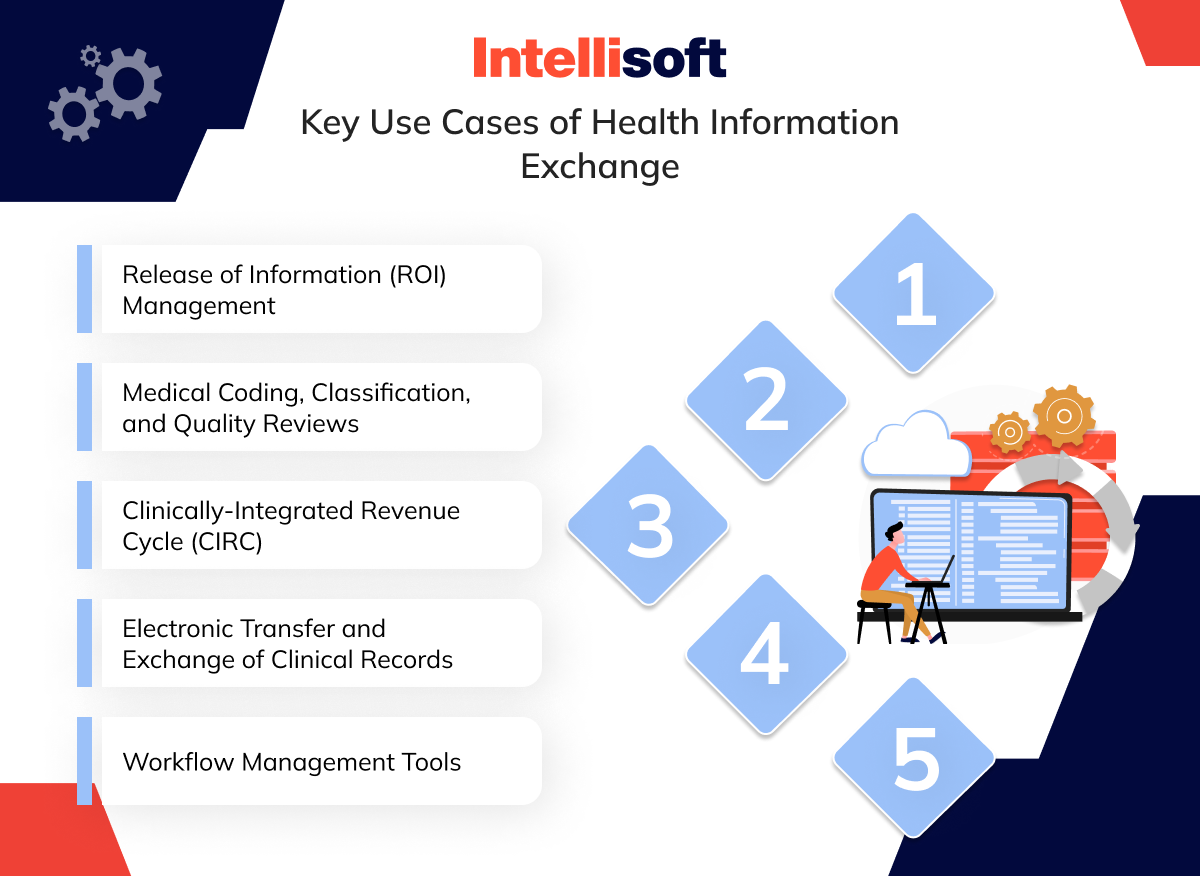
Release of Information (ROI) Management
HIE simplifies the secure and efficient release of medical information to authorized parties. By moving requests for medical records online, HIE allows patients and authorized requesters to use secure web portals instead of handling physical paperwork or making in-person visits.
This digital process is supported by Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), which standardize access while securing data and ensuring compliance with regulations. These systems provide real-time access to updated patient information, aiding in more informed decisions during patient consultations and boosting patient satisfaction by speeding up information delivery.
Medical Coding, Classification, and Quality Reviews
Accurate medical coding and classification are vital for correct billing and optimal reimbursement. HIE gives healthcare providers access to comprehensive patient data, leading to more precise coding and fewer claim denials. Providers can use this data to conduct detailed quality reviews of medical coding.
By checking the accuracy of codes and spotting potential errors, providers can make necessary corrections, ensuring adherence to coding standards and minimizing financial risk. This proactive approach improves financial outcomes and maintains compliance with healthcare regulations.
Clinically-Integrated Revenue Cycle (CIRC)
HIE helps integrate clinical and financial data, facilitating a Clinically-Integrated Revenue Cycle (CIRC). This integration connects patient health information with billing systems to optimize revenue processes, reducing revenue leakage and speeding up claims processing.
The CIRC approach encourages collaboration between clinical and financial staff, enhancing the quality of clinical documentation. This synergy, in turn, leads to fewer denials and better reimbursement rates. Consequently, CIRC strengthens financial performance and improves patient care by aligning clinical practices with financial operations.
Electronic Transfer and Exchange of Clinical Records
HIE is essential for electronically transferring clinical records, ensuring consistent and informed care across healthcare providers. For example, when patients move between providers, their records are transferred securely and efficiently, preventing any care disruptions. This capability lowers the risk of medical errors and improves care quality, underscoring HIE’s critical role in managing patient health information across various care settings.
Workflow Management Tools
When integrated with workflow management tools, HIE significantly enhances healthcare organization efficiency. These tools automate routine tasks such as scheduling appointments, ordering tests, reporting results, streamlining operations, and reducing error likelihood. Improved workflow management through HIE not only quickens the delivery of healthcare services but also elevates patient satisfaction by cutting down on wait times and enhancing the overall healthcare experience.
Health Information Exchange has the potential to revolutionize your healthcare operations. You can utilize the power of HIE to help your healthcare organization achieve operational excellence.
Implementing Health Information Exchange in Medical Practice
Setting up a Health Information Exchange (HIE) within a medical practice is a meticulous process that demands careful planning and execution. This step-by-step guide aims to ensure that the integration of patient health information sharing is smooth and secure and enhances healthcare efficiency.
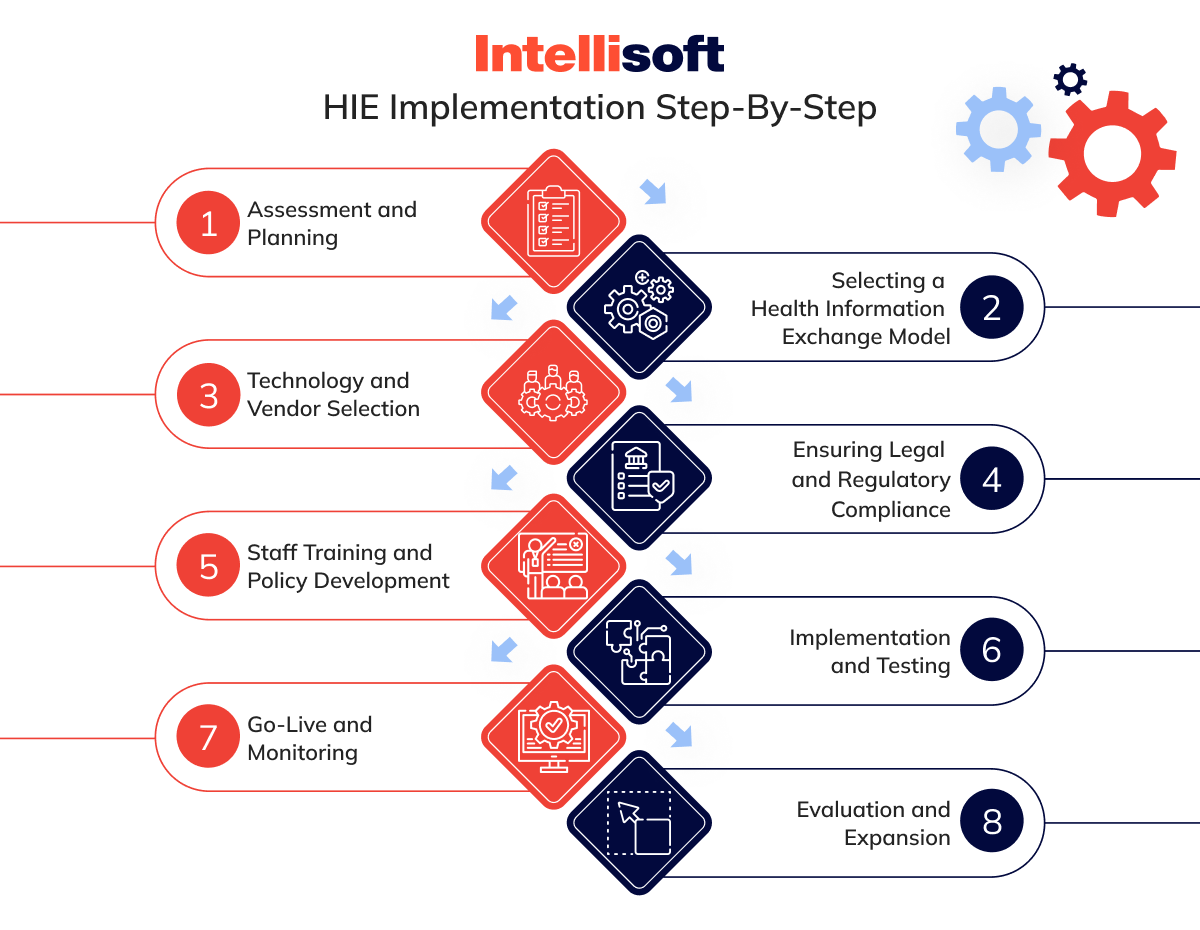
Step 1. Assessment and Planning
Start by thoroughly assessing the specific needs of your practice. Determine the types of health information essential for effective patient care and which need to be shared and received. After pinpointing these needs, explore local, regional, or national HIE organizations that can fulfill them. Armed with this information, you can develop a comprehensive implementation plan. This plan should outline crucial elements such as timelines, budgets, training needs, and any policy adjustments required to seamlessly integrate HIE into your existing systems.
Step 2. Selecting a Health Information Exchange Model
Choosing the appropriate HIE model is crucial and should match your practice’s needs, resources, and objectives. Consider one of the following models:
Centralized Model
All data is stored in a single, central repository accessible by all participants. This model is ideal for practices seeking streamlined data access and management.
Decentralized (Federated) Model
Data remains at each participant’s location, with the HIE enabling sharing among them without centralizing storage. This model provides more control over data.
Hybrid Model
This model combines elements of both centralized and decentralized models. It often includes a central directory to facilitate locating information across the network, offering a balance of data control and accessibility.
Step 3. Technology and Vendor Selection
After selecting an HIE model, it is vital to ensure your electronic health records (EHR) system is compatible. You must plan for the necessary upgrades or changes if compatibility issues occur. Choosing the right technology vendors is also crucial; opt for those with a strong track record in HIE integration and substantial support and training.
The right vendor selection can significantly influence the successful implementation of HIE, as these vendors provide the tools and expertise needed to integrate the system effectively into your practice’s operations.
Step 4. Ensuring Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Understanding and complying with federal and state regulations related to patient data exchange and privacy is imperative. Become familiar with laws such as HIPAA, which dictate the privacy and security of patient information. Moreover, forming contracts with chosen HIE organizations is crucial to fully addressing all legal and compliance issues. These agreements should clearly define the responsibilities of all involved parties and guarantee that data exchange adheres to strict security protocols.
Step 5. Staff Training and Policy Development
The foundation of a successful Health Information Exchange (HIE) implementation includes well-trained staff and clear, comprehensive policies. It is crucial to develop or revise policies that cover data sharing, privacy, and security within your practice. These policies must clearly define how patient information is handled and ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
It is equally important to train all staff members on how to use the HIE system. Training sessions should focus on the importance of data security and patient privacy and provide detailed instructions on how to use the system securely and efficiently. This ensures everyone understands how to access and share patient data properly.
Step 6. Implementation and Testing
After preparing your staff and policies, the next step is setting up the HIE system’s technical infrastructure. This phase involves working closely with your chosen vendors to ensure the technology integrates seamlessly with your existing electronic health records (EHR) system.
Once installed, it’s critical to thoroughly test the HIE system to verify that it meets your practice’s needs and functions correctly. Test scenarios should mimic real-world use to identify potential issues affecting daily operations or data security. Addressing these issues before the system goes live is essential for a smooth transition.
Step 7. Go-Live and Monitoring
When testing confirms the system’s readiness, begin the live launch, ideally starting with a smaller pilot group. This controlled approach helps manage the scale of the initial deployment and address unexpected challenges efficiently.
Continuous monitoring of the HIE system after going live is crucial. Monitor how well the system integrates with daily operations and actively seek user feedback. This monitoring should assess the system’s technical performance and usability, making necessary adjustments to optimize workflows and ensure data exchange meets healthcare standards.
Step 8. Evaluation and Expansion
Regularly evaluate the performance of the HIE system against the goals set for improving information exchange within your practice. This evaluation should determine if the HIE enhances care quality, boosts efficiency, and upholds data security. Based on these evaluations, decide how to proceed with the HIE system’s future.
If the initial implementation proves successful, consider expanding the HIE. Health Information Exchange may require including more data types, adding more healthcare providers to the network, or enhancing the system’s capabilities to support more complex services. Each expansion phase should be carefully managed to maintain the integrity and efficiency of the HIE system.
These are the steps that will help your practice maximize the benefits of Health Information Exchange, ensuring effective and efficient patient care.
Challenges with Health Information Exchange
While Health Information Exchange (HIE) brings many benefits to healthcare delivery, its implementation comes with significant challenges. As outlined in a 2014 report to Congress by the U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO), these challenges can affect the effectiveness and reach of HIE initiatives. Here, we delve into these issues and their implications for healthcare providers.
Insufficient Standards
A primary challenge in HIE is the lack of comprehensive standards for the electronic exchange of information. Existing standards often do not cover all aspects of information exchange, leading to inconsistencies in data interpretation across different electronic health record (EHR) systems. The exchanged information must adhere to uniform standards for HIE to function effectively. These standards must ensure that information can be accurately understood and integrated into the recipient’s EHR system without further modifications or clarifications.
Variations in Privacy Rules
The exchange of health information across state lines introduces complexity due to differing state privacy regulations. Healthcare providers frequently encounter challenges when sharing information with entities in other states, mainly due to limited knowledge of these legal differences. This complicates compliance efforts and impacts the efficiency of health information exchanges. Navigating through a mosaic of varying regulations can slow down and complicate data transfers, affecting the overall speed and ease of healthcare coordination.
Difficulty of Accurately Matching Patients to Their Health Records
Another significant operational challenge in HIE is accurately matching patients to their health records. Ensuring that the exchanged health information corresponds accurately to the right patient is crucial to prevent errors that could result in inappropriate care decisions. Many providers experience difficulties with this aspect of HIE, highlighting the need for more sophisticated systems and processes to improve the accuracy of patient data matching.
Cost of Exchanging Health Information
The costs associated with setting up and maintaining HIE systems also pose a substantial barrier. These costs include the initial investment required to join state or local health information organizations and ongoing expenses, such as per-transaction fees charged by some HIE vendors. These costs can be prohibitive for smaller practices or underfunded healthcare facilities, limiting their ability to participate in health information exchanges effectively.
These challenges underscore the complexity of implementing and maintaining a successful HIE system. To address these issues, healthcare providers, policymakers, and technology vendors must coordinate their efforts. Together, they should work to develop more robust standards, streamline regulatory complexities, enhance patient matching accuracy, and make HIE more affordable.
The Future of Health Information Exchange
The Health Information Exchange (HIE) technology continues advancing. The future of HIE looks bright, with new technological developments expected to improve how medical providers store, maintain, and share patient information. There’s a significant move toward greater integration of HIE systems across local, regional, and national healthcare organizations.
A key trend in the evolution of HIE technology is the creation of single-platform resources. These platforms are designed to simplify the data transfer process, making it easier for healthcare providers to access and share information effectively.
However, several challenges need to be overcome to fully unlock HIE’s potential. Current systems often face issues with interoperability, especially when integrating seamlessly with diagnostic tools and new medical treatments. The rapid introduction of new drugs and treatment protocols can outpace HIE systems’ ability to adapt, underscoring the need for more flexible and responsive technologies.
Additionally, global variations in standards complicate the creation of a universally accessible HIE, while concerns over data ownership and confidentiality remain significant challenges.
Despite these obstacles, HIE is increasingly becoming the industry standard for managing medical records and transferring data. This shift highlights the need for skilled IT and healthcare information professionals to manage and maintain these systems effectively. As technology continues to drive these changes, HIE is poised to become a central component of a broader revolution transforming the healthcare industry.
At IntelliSoft, we are leading this transformation. Our HIE system implementation services are designed to provide healthcare organizations with advanced, robust, and secure HIE solutions. By partnering with IntelliSoft, you can ensure that your organization is prepared for the future of healthcare and become a leader in adopting innovative health information technologies.
Our expert teams are dedicated to offering the support and expertise needed to integrate HIE systems seamlessly into your operations, enhancing your ability to deliver exceptional patient care. Discover the future of healthcare with IntelliSoft’s HIE solutions, where cutting-edge technology and exceptional care converge to redefine the possibilities in health information management.