In 2024, AI will rapidly reshape architecture, with 41% of architects now using AI tools to enhance their work. From automating mundane tasks to optimizing sustainability, AI in architecture offers exciting possibilities. But with these advancements come pressing questions: Is AI boosting creativity or diluting the human touch that defines architecture? Can data-driven designs truly replace an architect’s unique vision?
AI helps architects explore design alternatives quickly, select eco-friendly materials, and create energy-efficient structures. However, it also raises concerns about how is AI being used in architecture, ethics, privacy, and potential bias.
Our IntelliSoft team, with 15 years of experience in software development, helps architects harness AI to enhance their creativity while tackling these challenges head-on. Dive into the article to explore how to use AI in architecture design.
Table of Contents
AI in Architecture Statistics
What is AI in architecture?
The role of AI in architecture is no longer a distant concept – it’s already here, reshaping the way buildings are designed and constructed.
According to a new study by the Royal Institute of British Architects (RIBA), 41% of UK architects have started using AI in at least some of their projects. Of those embracing AI in architecture, 43% are seeing real results, claiming it’s making the design process more efficient. It’s clear that AI’s potential to transform the industry is undeniable. But are architects really ready to dive into this tech-driven future?
While over half of architects (54%) expect their firms to adopt AI in architecture design in the next two years, and 57% are confident it will streamline their design workflows, there’s a glaring disconnect between this optimism and actual investment.
A surprising 69% of architects admit that their firms haven’t yet invested in AI research and development, and only 41% expect this to change anytime soon. It seems that while the industry is buzzing with excitement, the resources needed to bring AI into full swing are still lacking.
Sustainability is another area where AI could make waves. With 70% of the world’s population projected to live in cities by 2050, architects face enormous pressure to design smarter, greener urban spaces.
AI could be a game-changer here, with 57% of architects planning to use it for environmental sustainability analysis in the near future. Additionally, 49% believe generative AI in architecture and other digital tools will be essential for navigating the growing complexity of building projects, from climate adaptation to smart technology integration.
However, AI’s rise isn’t without its concerns. Over half of architects (58%) worry that AI increases the risk of their work being copied or imitated. And while some fear AI could edge them out of the profession, opinions are split – 36% see AI as a threat, 34% don’t, and 30% are sitting on the fence.
Summing up the pivotal role of AI, RIBA President Muyiwa Oki said, “AI is the most disruptive tool of our time, and we cannot overstate its role in shaping the future of architecture – from the character of our cities to the quality of our built environment.”
The Impact on Architectural Creativity
As AI becomes more integrated into architecture, the question on many minds is; How is AI used in architecture and how does this technology impact creativity? Architecture, long celebrated as a balance of art and science, now faces the challenge of integrating machine-driven tools while maintaining human ingenuity. The good news? AI applications in architecture are not replacing architects – it’s empowering them. By enhancing design workflows and offering new ways to solve problems, AI in architecture is set to expand the creative horizons of the field rather than restrict them.
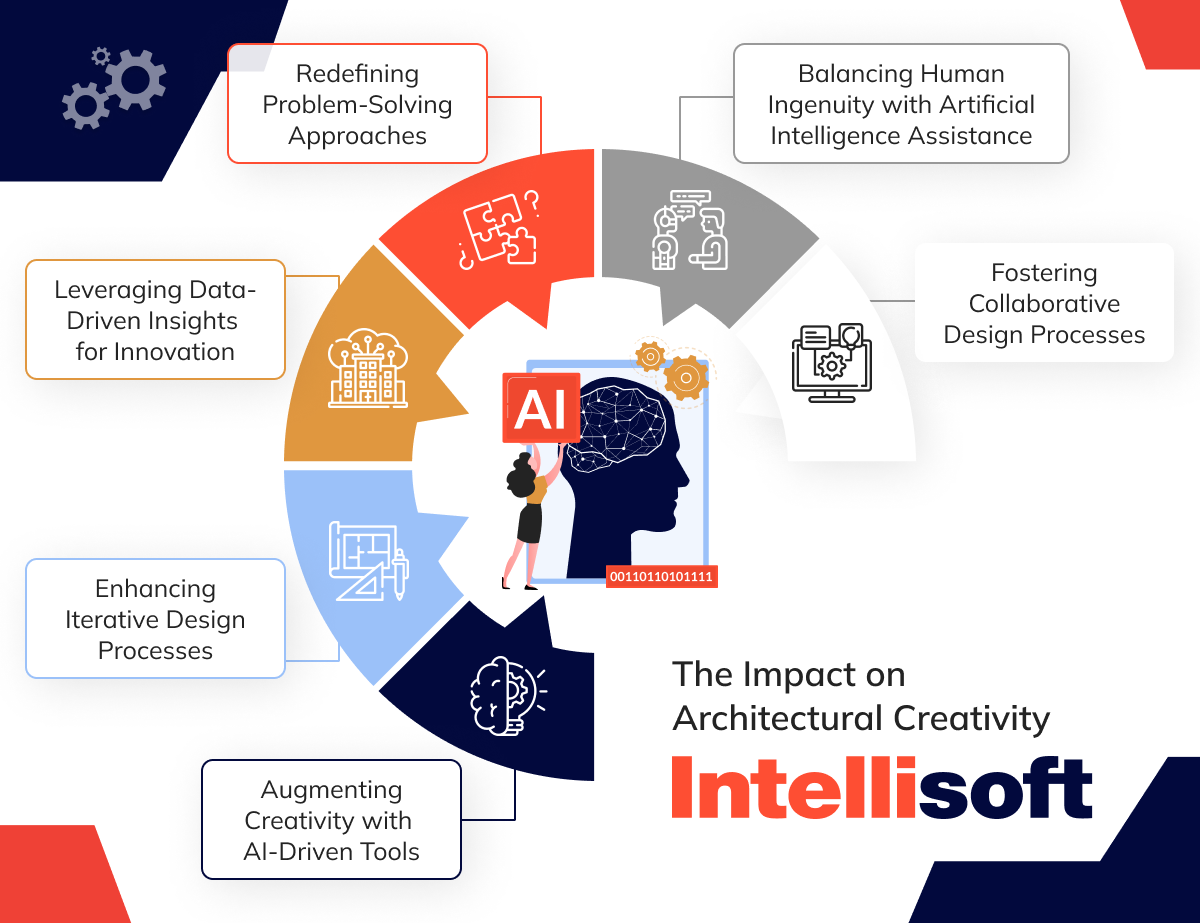
Augmenting Creativity with AI-Driven Tools
AI-driven tools provide architects with unprecedented creative freedom. These tools can generate multiple design variations in minutes, exploring shapes, structures, and layouts that might have otherwise been overlooked. By automating the technical aspects of design, AI allows architects to focus more on the artistic elements, freeing up mental bandwidth for innovation. Whether it’s creating complex parametric designs or optimizing layouts for natural light, AI in architecture and design enhances creativity rather than stifles it.
Enhancing Iterative Design Processes
Traditionally, iterative design can be time-consuming, requiring countless hours of refining and tweaking ideas. AI in enterprise architecture accelerates this process, making it easier to test and visualize different design concepts quickly. Architects can run simulations, adjust parameters, and explore design alternatives in real time. This speed and flexibility allow for more experimentation, making room for creative breakthroughs that might not emerge through conventional methods.
Leveraging Data-Driven Insights for Innovation
Artificial intelligence in architecture doesn’t just generate designs; it also analyzes vast amounts of data to offer insights that drive innovation. By evaluating environmental factors, material choices, and energy efficiency, AI can inform architects on how to optimize their designs for sustainability and functionality. This data-driven approach enables architects to push the boundaries of design, combining artistic vision with scientific precision to create buildings that are not only beautiful but also practical and sustainable.
Redefining Problem-Solving Approaches
Architects have always been problem-solvers, but AI takes this capability to a new level. By processing complex datasets and offering predictive analytics, AI helps architects tackle challenges like urbanization, climate adaptation, and energy efficiency with greater precision. It offers suggestions architects might not have considered, turning problems into opportunities for creative, forward-thinking solutions.
Balancing Human Ingenuity with Artificial Intelligence Assistance
While AI in architecture and construction can handle technical tasks and offer data-driven insights, the human touch is irreplaceable when it comes to creativity. AI assists, but it doesn’t dictate. Architects still hold the reins in determining the vision and final direction of a project. The key lies in finding the right balance – letting AI take care of the repetitive tasks while using human ingenuity to bring the design to life.
Fostering Collaborative Design Processes
AI is also reshaping collaboration within the architecture field. By making it easier to visualize and share ideas, AI tools foster more inclusive design processes. Architects, engineers, and clients can collaborate more effectively, with AI helping to bridge communication gaps through real-time design visualization and feedback. This collaborative environment not only enhances creativity but ensures that projects align with the vision of all stakeholders involved.
Success Stories of AI Used in Architecture
How to use AI in architecture? AI is already making a significant impact on some of the most innovative architectural projects around the world. From sustainability to generative design, these success stories showcase how AI is helping architects push boundaries and create structures that are both functional and visionary.
The Edge Building in Amsterdam

Known as the world’s most sustainable office building, The Edge in Amsterdam is a shining example of how AI can transform architecture. Gen AI in architecture monitors energy usage, adjust lighting, and control heating and cooling based on occupancy and environmental conditions. The building’s AI-driven smart design not only maximizes energy efficiency but also creates a highly personalized and comfortable working environment for its occupants. It’s a glimpse into the future of sustainable architecture powered by AI.
AI-Assisted Parametric Design at Zaha Hadid Architects

Zaha Hadid Architects has long been at the forefront of architectural innovation, and their use of AI-assisted parametric design is no exception. With the use of AI in architecture, the firm has been able to create complex, fluid structures that would be nearly impossible to design manually. AI tools help generate, test, and refine intricate geometric forms, enabling the creation of buildings that are as functional as they are visually stunning. Projects like the Beijing Daxing International Airport showcase the power of AI in pushing the limits of modern design.
Hudson Yards, New York

Hudson Yards, one of the largest real estate developments in U.S. history, has integrated AI to optimize design and construction processes. AI played a key role in managing the logistics of this sprawling project, from scheduling and resource allocation to ensuring sustainability goals were met. The result is a sleek, futuristic complex that marries architectural beauty with cutting-edge technology. AI has also been used in ongoing management, helping improve energy efficiency and operations across the entire development.
AI-Driven Sustainability at Foster + Partners

Foster + Partners, another global leader in architecture, has embraced AI to drive sustainable building design. In their projects, machine learning architecture in the age of artificial intelligence is used to analyze data on sunlight, wind flow, and energy use, which allows architects to make informed decisions on material selection and building orientation. This AI-driven approach ensures that buildings are optimized for energy efficiency, reducing their carbon footprint. Notably, the firm’s work on Apple Park in Cupertino, California, showcases how AI can blend sustainability with stunning architectural design.
Generative Design at Autodesk

Autodesk, a pioneer in the use of generative design, uses AI to explore design possibilities based on specified constraints like materials, budget, and performance. Their tools allow architects to quickly generate and evaluate thousands of design alternatives, leading to innovative solutions that are finely tuned to both aesthetic and functional requirements. AI-driven generative design not only speeds up the creative process but also opens up new possibilities for unique and efficient architectural forms, as seen in Autodesk’s own office spaces and collaborations with other architectural firms.
What Are the Most Common Machine Learning Models Used in Architecture?
Artificial intelligence in architecture design is revolutionizing architecture by offering advanced tools to analyze data, optimize designs, and streamline processes. Several machine learning models are frequently used in the field, each bringing unique capabilities to architectural challenges. Below are some of the most common types of architecture in AI used to enhance creativity, efficiency, and problem-solving. Here’s how architects use AI:
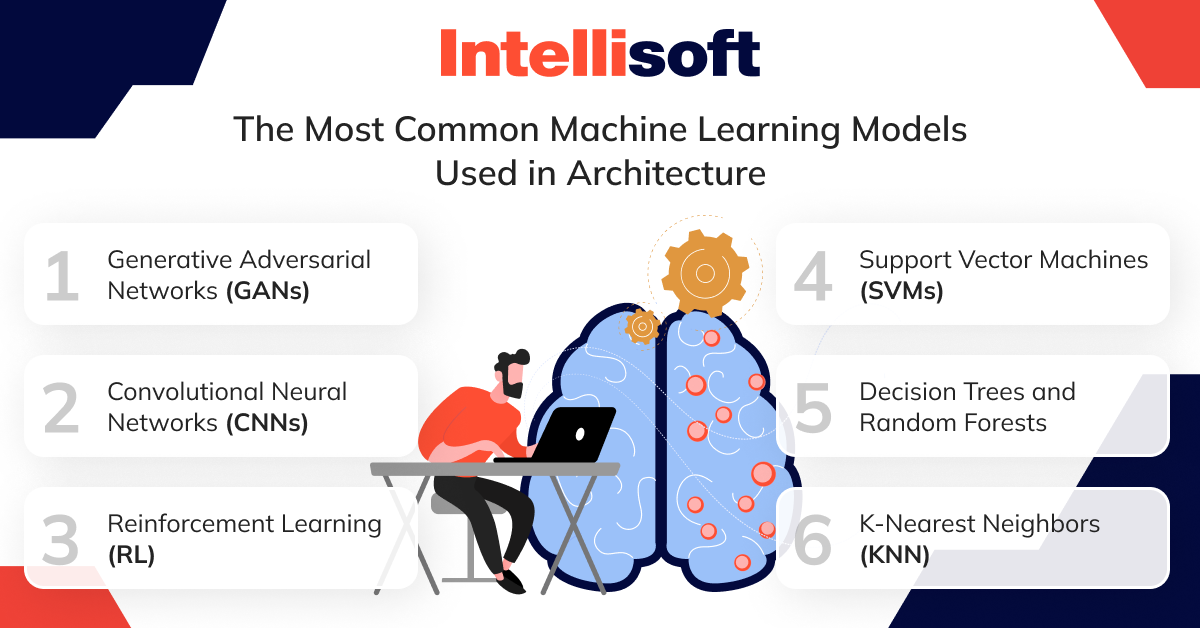
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are a powerful tool for creating new designs based on existing data. In architecture, GANs can generate realistic architectural forms, layouts, or even entire buildings by learning from previous designs.
By pitting two neural networks against each other (one generating designs and the other evaluating them), GANs refine their outputs over time, helping architects explore multiple creative possibilities without manual intervention. This is especially useful for generative design and rapid prototyping.
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are primarily used in image recognition, but they have found applications in architecture for analyzing visual data such as floor plans, building facades, and 3D models. CNNs can automate the identification of design features or detect structural anomalies in construction, helping architects and engineers make data-driven decisions. The ability to process large-scale visual information makes CNNs invaluable for tasks like site analysis, architectural detailing, and even historical building restoration.
Reinforcement Learning (RL)
Reinforcement Learning (RL) models are designed to optimize outcomes through trial and error. In architecture, RL can be used to optimize design decisions such as spatial layouts, energy efficiency, or structural stability. By setting specific goals (like minimizing material use or maximizing natural light), the RL model explores various design iterations and learns which ones provide the best results. This makes RL an excellent tool for sustainable design and large-scale urban planning, where balancing numerous factors is essential.
Support Vector Machines (SVMs)
Support Vector Machines (SVMs) are commonly used for classification tasks in architecture. For instance, SVMs can help classify different types of architectural elements, such as windows, walls, and doors, based on design data. This classification ability is useful for organizing large design databases or automatically sorting elements in 3D models. SVMs can also be applied in predictive analysis, such as assessing whether certain design features will meet performance standards.
Decision Trees and Random Forests
Decision Trees and Random Forests are models that help architects make structured, logical decisions based on multiple factors. These models can be used for project management tasks, such as estimating the costs and timelines of construction projects or predicting the energy efficiency of a building. Random Forests, in particular, are effective at handling large datasets and providing more accurate predictions by combining the outputs of multiple decision trees. This makes them a valuable tool for both design optimization and operational efficiency in architecture.
K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN)
K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) is a simple yet effective model for pattern recognition and prediction. In architecture, KNN can be applied to identify similar design patterns, suggest material choices based on past projects, or cluster building types for urban development. By comparing a new design or building feature to its “nearest neighbors” in a dataset, KNN can offer insights and recommendations that align with both historical data and emerging trends. Its simplicity and adaptability make it a versatile tool in early-stage design analysis.
AI Implementation in Architecture: Key Steps
Bringing AI into your architectural practice is more than just adopting new software – it’s about transforming the way you approach design, efficiency, and innovation. If you’re ready to harness the power of AI in landscape architecture, here are the essential steps to ensure a smooth, impactful integration.
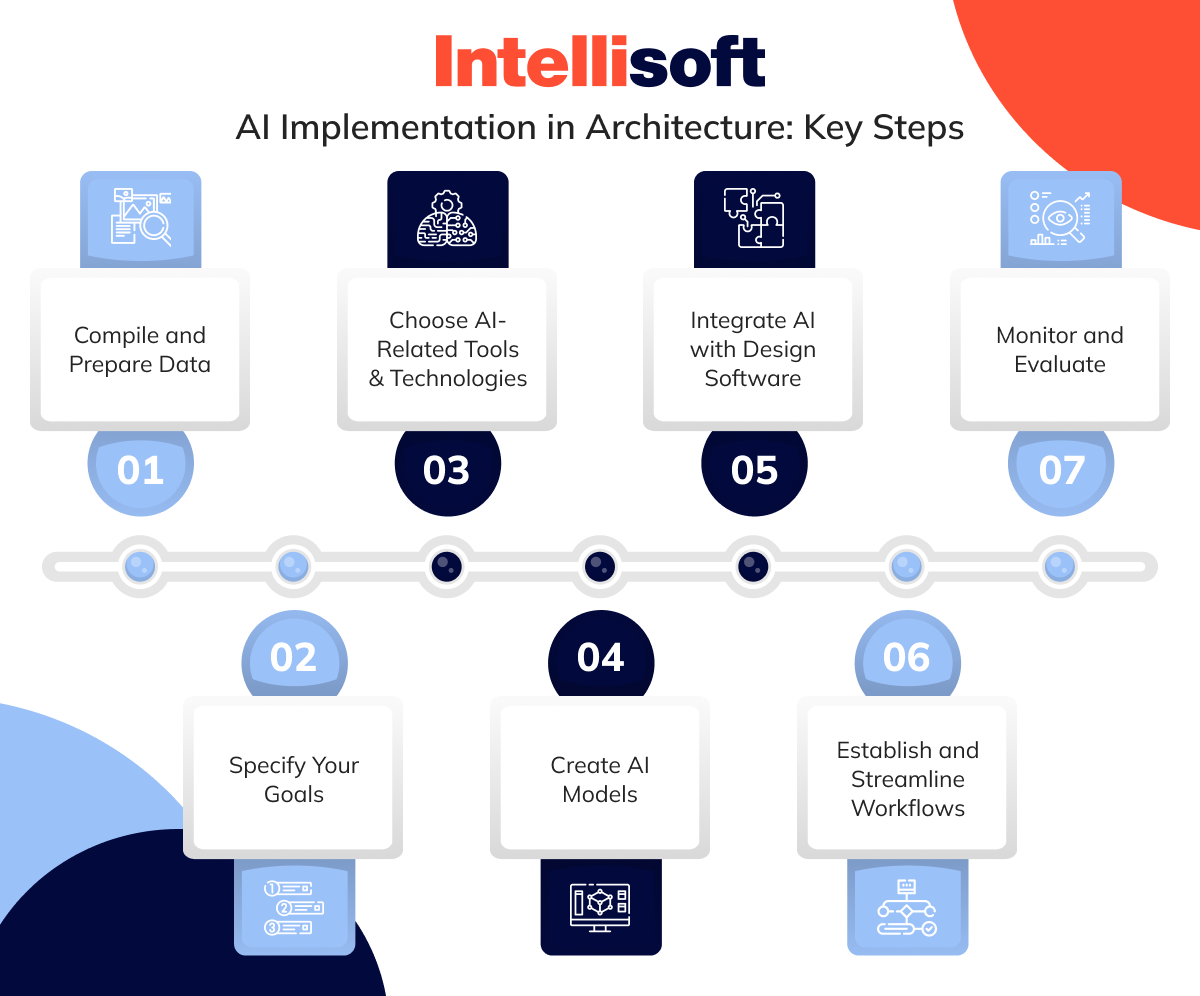
Compile and Prepare Data
Data is the foundation of AI in architecture and engineering. Begin by gathering all relevant design data, including blueprints, client feedback, material specifications, and environmental factors. The more data you collect, the better equipped your AI will be to generate insightful recommendations.
However, this isn’t just about quantity – quality matters. Ensure your data is clean, relevant, and well-organized so that your AI can learn and provide meaningful outputs. Think of this step as laying the groundwork for an intelligent assistant that will help you make more informed decisions.
Specify Your Goals
Before diving into AI tools, it’s essential to know what you’re aiming for. Do you want to streamline design iterations, improve sustainability, or optimize project management? Clearly defining your goals will help guide the AI implementation process. By specifying what you want AI to achieve – whether it’s reducing energy consumption or enhancing material efficiency—you can tailor your approach to align with your practice’s needs and vision.
Choose AI-Related Tools & Technologies
With so many AI tools available, choosing the right technology for your practice can feel overwhelming. Whether it’s AI-driven design platforms like Autodesk’s generative design tools or machine learning algorithms to analyze sustainability metrics, the key is selecting tools that align with your goals. Focus on technologies that integrate easily into your existing workflows and enhance – not complicate – your design processes.
Create AI Models
Creating an AI model tailored to your architectural needs is where the real magic happens. This is where you train AI to understand your data and deliver actionable insights. Depending on your goals, this could mean developing machine learning models to predict structural integrity or using AI to suggest energy-efficient materials based on climate data. Don’t be afraid to experiment with various models – each project may require a different approach to find the best fit.
Integrate AI with Design Software
For AI to truly elevate your practice, it needs to work seamlessly with your current design software. Integration is key – whether it’s linking AI models with CAD tools or incorporating generative design into your 3D modeling process. This step ensures that your AI-driven insights can be directly applied to your design work, enhancing both creativity and precision.
Establish and Streamline Workflows
AI thrives in a well-organized environment. To get the most out of your new tools, streamline your workflows so that AI-generated insights are easily accessible throughout the project lifecycle. Whether it’s automated reports on design performance or real-time updates on energy usage, make sure your team knows how to interact with the AI and incorporate its feedback into their processes. Effective workflows make AI a natural extension of your architectural practice rather than an isolated tool.
Monitor and Evaluate
The AI journey doesn’t end with implementation – it’s an ongoing process. Regularly monitor the effectiveness of your AI systems and make adjustments where needed. Is the AI improving your design efficiency? Are its sustainability recommendations aligning with your goals? Stay proactive in evaluating how AI is impacting your projects, and continuously refine your approach to ensure your practice stays at the forefront of architectural innovation.
Related articles:
- Generative AI Use Cases: Benefits and Real-life Examples
- How to Build an AI App from Scratch
- How to Choose between Machine Learning vs Predictive Analytics
- Best programming languages for AI and machine learning solutions
- Why GPT-3 Chatbot from OpenAI Is A Game Changer for Businesses?
Challenges and Concerns of Using AI and Machine Learning in Architecture
While the potential of AI and machine learning in architecture is undeniable, the integration of these technologies comes with its own set of challenges. Addressing these concerns is essential to ensure AI is used responsibly and effectively in the industry.

Ethical Concerns
AI raises significant ethical questions in architecture, particularly when it comes to creativity and originality. How much should we rely on machines to make creative decisions that traditionally belonged to humans? Some fear that AI-generated designs may lack the emotional depth and human intuition that have long been at the heart of architecture. Additionally, concerns about biases in AI algorithms – whether cultural, aesthetic, or environmental – pose a real risk to fairness in design.
Data Privacy and Security
AI-driven architecture relies heavily on data, and with that comes the critical issue of data privacy and security. When architects and firms gather vast amounts of data on user behavior, energy consumption, and urban environments, questions arise about how this data is protected. Ensuring that sensitive data is stored and used responsibly is crucial to preventing breaches and protecting clients’ privacy.
Job Displacement
The fear that AI might replace jobs is not limited to factory floors – it has made its way into the architectural world. As AI takes on more tasks, such as generating design variations or automating project management, there are concerns about job displacement. While AI can boost efficiency and creativity, it also prompts questions about the role of human architects and whether certain positions might become obsolete. Balancing AI’s contributions with preserving the human element in architecture remains a key challenge.
Technical Challenges
AI implementation in architecture is not without technical hurdles. Developing, training, and maintaining AI systems can be complex and costly. Integrating AI with existing design software, ensuring accuracy in AI-driven designs, and troubleshooting when AI-generated suggestions don’t align with real-world needs are just a few of the technical issues firms may face. For smaller firms, the cost and expertise required to adopt AI technologies can be prohibitive.
Regulatory and Legal Issues
As AI takes on more significant roles in architectural design and construction, regulatory and legal challenges become more pressing. Who is responsible when an AI-generated design fails to meet safety standards? How do you ensure that AI-driven buildings comply with local building codes? The legal frameworks surrounding AI in architecture are still evolving, and navigating this uncharted territory poses challenges for architects and firms.
Dependence and Over-Reliance
A key concern in the adoption of AI in architecture is the potential for over-reliance. While AI can assist in decision-making, there’s a danger that architects might become too dependent on these tools, stifling their own creativity and critical thinking. Over-reliance on AI could lead to standardized, cookie-cutter designs, reducing the unique and innovative flair that architects bring to each project. Ensuring that AI remains a tool rather than a crutch is vital to maintaining the balance between technology and human ingenuity.
Wrapping Up
AI is reshaping architecture, opening up new possibilities for creativity, sustainability, and efficiency. From generative design to smarter workflows, the potential is immense – but it comes with challenges like data privacy, ethics, and finding the right balance between human intuition and machine-driven insights.
As the industry moves forward, architects have the chance to harness AI for better designs and more sustainable solutions. If you’re ready to explore how AI can elevate your practice, IntelliSoft is here to guide you. With 15 years of experience, we can help you integrate AI seamlessly into your workflow – contact us today to get started!