The volume of information being produced by businesses and individuals continues to grow at an unprecedented pace. This approach has led to the emergence of big data security intelligence as an opportunity for innovation, as it holds valuable insights about customer behavior, operational performance, and market trends. By analyzing vast amounts of information, organizations can improve their decision-making processes, optimize their business operations, and develop new products to stay ahead of the competition.
However, as processing petabytes of records becomes more prevalent, breaches are also rising. This change poses a potential risk of vulnerabilities, making security a primary concern for organizations. The security big data is vital to ensure that records are protected from unauthorized access and misuse, which could lead to significant losses. Let’s explore the benefits of big data, its challenges, and the best practices for ensuring its safety.
Table of Contents
What Is Big Data and Big Data Security
Organizations are generating massive amounts of information daily. It can be divided into three categories; structured, semi-structured, and unstructured, collectively known as big data. It can be analyzed to extract valuable insights in various advanced analytics applications, including machine learning (ML) and predictive modeling.
To manage hundreds of thousands of records, organizations need to have robust management architectures that can handle the processing and storage of this information. Various tools and technologies are available to users in the big data security market to support big data analytics. Moreover, this aspect is often described using the three Vs:
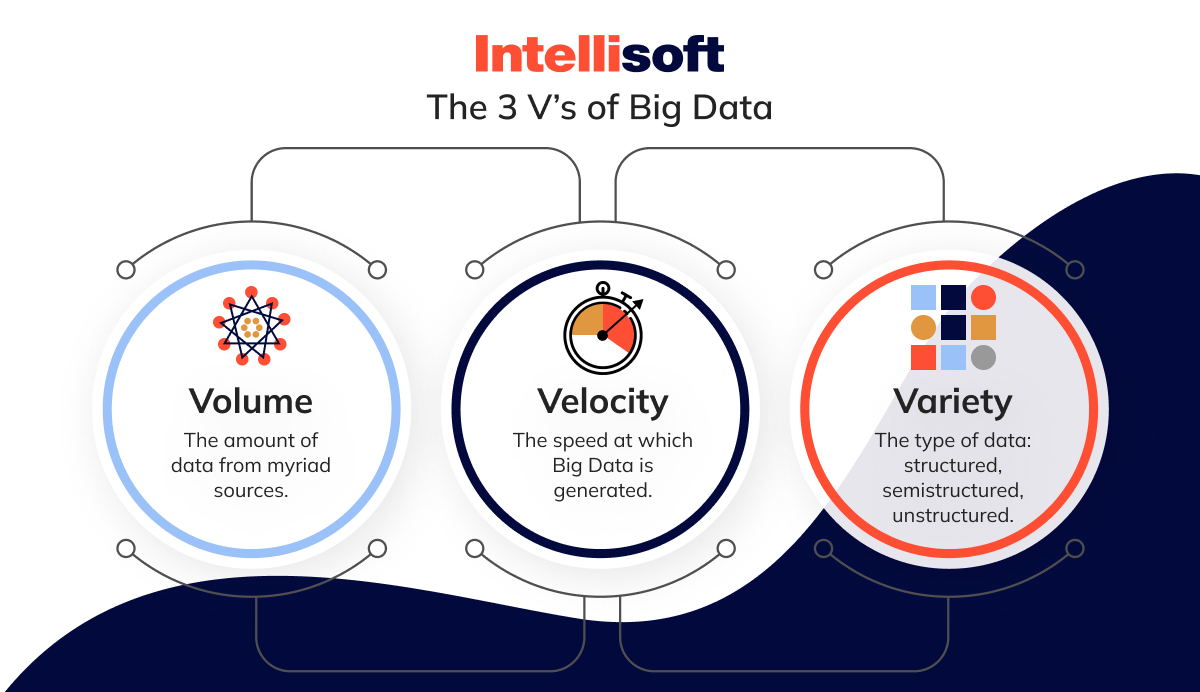
- The volume of information in many environments
- A variety of data types frequently kept in storage systems
- Velocity at which information is generated, collected, and processed.
Big data security intelligence is a set of measures and practices put in place to safeguard extensive collections from unauthorized access, breaches, and other malicious activities. This approach means protecting information against various threats, such as hacking, breaches, insider attacks, and more. The process of securing usually involves three main phases:
- Ensuring secure transfer of information from cloud sources for storage or real-time ingestion.
- Protecting records stored within the layers of the pipeline.
- Maintaining privacy of reports and dashboards with insights from tools like Apache Spark.
Why Is It Important To Secure Big Data
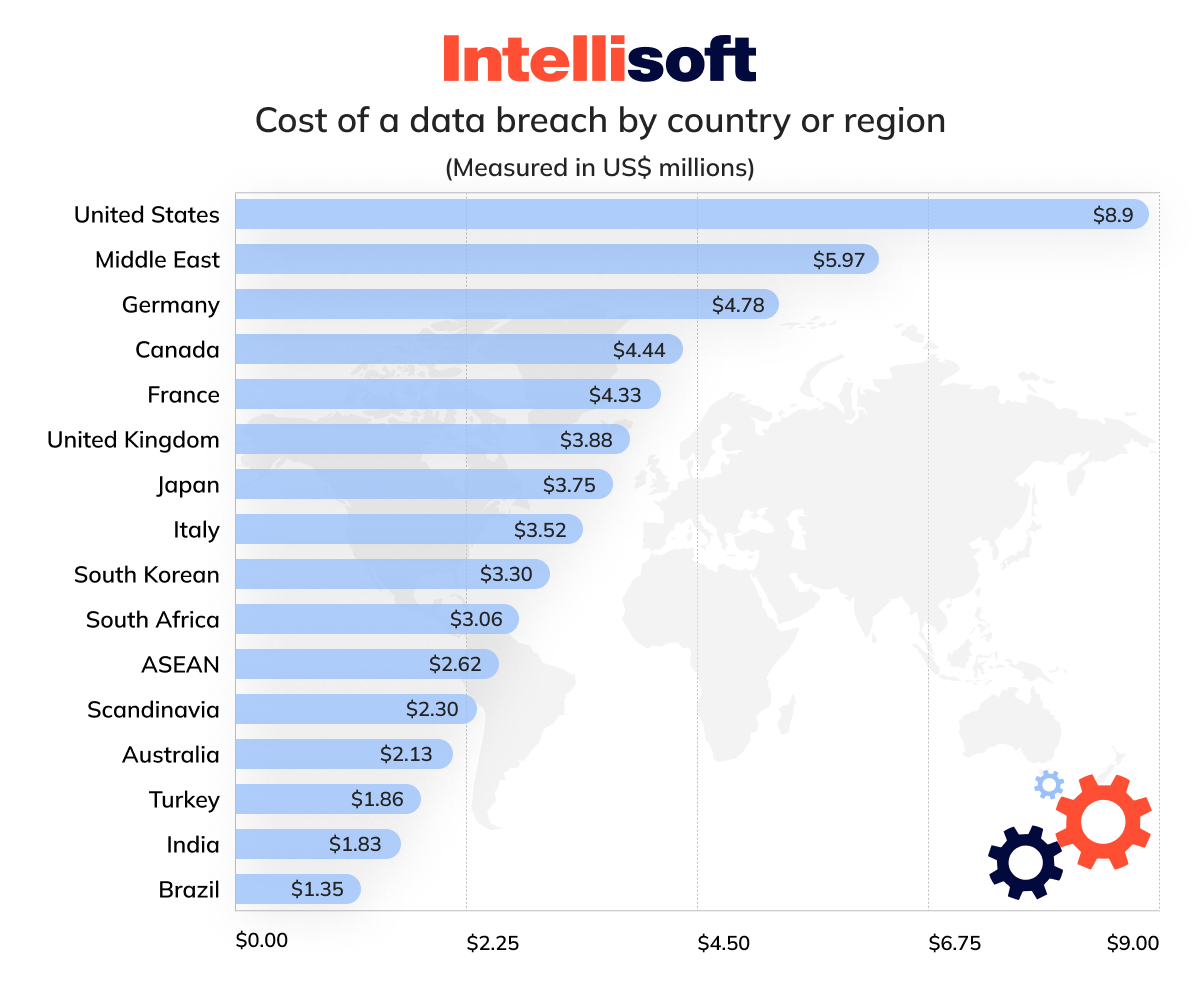
Almost every organization is looking to adopt big data because of its immense potential. However, this shift requires companies to protect sensitive information from potential breaches. As per the IBM and Ponemon Institute’s 2023 report, the average data breach cost is expected to rise by 2% to reach US$4.45 million in 2023, significantly impacting organizations’ finances.
Data breaches have become increasingly frequent, resulting in more legal actions and penalties, especially with stricter privacy regulations in regions like the EU, California, and Australia (e.g., GDPR, CCPA, and CSP234). To ensure the privacy and protection of sensitive information, businesses operating in regulated sectors, such as healthcare and credit card processing, should adhere to industry-specific standards such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) and PCI/DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard).
Safeguarding sensitive information has become increasingly challenging due to the emergence of new and sophisticated threats. These include social engineering tactics, ransomware attacks, and advanced persistent threats (APTs). They are not only difficult to defend against but can also inflict severe damage to records stored. This underscores the critical need for security and tech departments to collaborate and innovate, developing comprehensive solutions to counter these challenges effectively.
In this context, evaluating the cost-effectiveness of current protection measures and assessing the potential returns on further investments becomes essential. Organizations must take a proactive approach toward information protection and ensure their systems are protected from possible threats that may cause severe financial and reputational harm.
What Is The Architecture Of Big Data Security
Let’s begin by reviewing the difference between big data security and management. This is important as some people may need to understand more about these two concepts.
While its architecture and management are related concepts, they are not interchangeable. It’s crucial to understand the difference between them:
The architecture of big data security intelligence is a multifaceted approach that aims to guarantee the safety and security of sensitive data. It comprises various stages and measures that are put in place to minimize risks and protect information from unauthorized access, tampering, and loss. Certain standard components and considerations are essential for ensuring complete protection for an organization.
Data encryption is one of the most crucial components of big data security architecture. It involves converting information into a code that requires decryption to access, thereby enhancing protection specifics during storage, transmission, and processing. This approach serves as a deterrent to unauthorized access or tampering.
Access control is another critical component that governs information access and actions through authentication, user roles, and permissions. This method ensures that only authorized individuals can interact with specific records, minimizing the risk of theft or misuse.
Data masking and anonymization are also essential components that help protect sensitive information by substituting it with fictitious or scrambled details. This method helps prevent unauthorized access and misuse of sensitive records, thus allowing for maintaining confidentiality.
Data loss prevention (DLP) measures involve monitoring, enforcing policies, and using specialized tools to prevent data loss or leaks, whether accidentally or intentionally. DLP solutions help organizations safeguard their records by providing a comprehensive and effective security strategy.
Secure data storage is also critical for safeguarding information at rest. Information stored in databases or servers requires secure systems and encryption to protect against unauthorized access, theft, or misuse. Regular backups and disaster recovery plans are essential in case of unexpected incidents such as system failure, natural disasters, or cyber attacks.
Network security is another vital component of security architecture that protects data during transmission. It involves implementing secure communication protocols, firewalls, intrusion prevention mechanisms, and network configurations to thwart unauthorized access or information interception attempts. Organizations can protect themselves against cyberattacks and safeguard their valuable information assets by employing these measures.
Auditing and monitoring processes are designed to keep track of all data-related activities, identify suspicious actions, enforce security policies for big data, and detect potential breaches. By regularly auditing and monitoring data, organizations can proactively identify and address any security risks and protect sensitive information.
Big data security analytics involves analyzing data patterns and recognizing potential risks to address them proactively. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies, this approach provides a comprehensive solution to safeguard valuable records from any malicious activities.
Big Data Security Challenges And Methods To Mitigate Them
Securing big data requires implementing security protocols that align with an organization’s overall security strategy. This approach involves establishing robust types of security controls and continuously monitoring and maintaining them to ensure optimal protection against potential threats in the long run. Here are some of the big data analytics security and privacy challenges.
Unauthorized Access
There is a possibility that individuals who are not authorized to access sensitive information will be able to gain access to it. This can lead to a breach of confidentiality and potential harm to the organization or individuals associated with the information. Therefore, you should put the following measures in place:
- Implement robust authentication protocols, access controls
- Encrypt records to protect it at rest and in transit
- Regularly revise access privileges
Data Breaches
Security breaches may expose sensitive information, leading to severe consequences such as identity theft, financial losses, and reputational damage. Therefore, companies should implement the following mitigation strategies to prevent such incidents from occurring:
- Use intrusion detection and prevention systems to enhance the security of your system
- Encrypt any sensitive information both in storage and during transmission
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify any vulnerabilities that may exist in your system
Data Privacy Compliance
Handling customer details without appropriate measures in place can result in breaching privacy regulations such as GDPR or CCPA. This can lead to legal penalties, loss of customer trust, and damage to a company’s reputation. In this light, it is crucial to implement necessary measures to mitigate such risks:
- Comprehend and follow all applicable privacy regulations
- Implement anonymization and pseudonymization techniques
- Establish well-defined policies for handling information and provide employee training on data privacy
Insider Threats
Organizations face the risk of employees or contractors mishandling sensitive information. To mitigate this danger, they should implement appropriate types of data security controls and provide adequate training:
- Keep track of the actions and conduct of the user
- Implement role-based access control system and perform background checks
- Properly inform employees about security best practices and the possible outcomes of data breaches.
Data Quality and Integrity
One of the significant risks associated with any data-driven system is the possibility of inaccurate or tampered information that can affect the overall big data analytics for security intelligence and decision-making process. This approach can lead to incorrect conclusions and flawed strategies that can have severe consequences for the business. Implement these practices to mitigate this risk:
- Create a set of quality standards and establish validation procedures
- Use checksums and hashing to verify that the information has not been altered
- Set up a version control system for essential data sets
Scalability Challenges
Organizations need more security measures due to the increasing volume of records. They are necessary to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, theft, or damage:
- Develop security measures that can adapt to the record size and complexity
- Opt for cloud-based solutions that come equipped with built-in security features
- Review and update your security policies regularly for system and information safety
Data Storage Risks
The identified risk pertains to the possibility of information being stored in multiple locations and formats without adequate protection. This approach could make records vulnerable to breaches or unauthorized access. The mitigation strategy would involve taking the following measures:
- Centralize data storage whenever it is possible and apply consistent security measures
- Encrypt all information that is stored and use secure transferring protocols
Third-Party Risks
Outsourcing information to third-party vendors is a significant risk for organizations. Vendors may lack the necessary security measures, leading to data breaches and leaks. Organizations must take proactive measures to mitigate this risk:
Thoroughly vet any third-party providers for compliance with security standards
Establish strong protection agreements and regularly monitor their adherence to high security standards
Data Lifecycle Management
The data may not be adequately managed at all stages of its life cycle, which could lead to various big data analytics security issues such as information loss, security breaches, or compliance violations. To mitigate this risk, establish clear policies and procedures:
- Set well-defined policies for retaining and disposing of sensitive information
- Automate the processes of archiving and deleting data
- Protect all the duplicates of your information
Lack of Security Awareness
There is a risk of employees and stakeholders being unaware of the best security practices, which can increase vulnerability to security threats. Implement certain measures to mitigate this risk:
Provide ongoing security training to employees to identify and prevent security threats
Promote a culture of security within the organization
Related articles:
- SaaS Security Tips and Checklists: Best Practices To Protect Your SaaS Application
- IoT Device Security Concepts: IntelliSoft’s Roadmap to Robust IoT Protection
- What Threatens Your Web Application Security
- What Are the Security Risks of Cloud Computing? Threats & Solutions
- Web Application Penetration Testing: How It Ensures Security
Applying Best Practice Guidelines To Mitigate Big Data Security Risks
With the exponential growth of digital information, security has become a significant concern for organizations. Big data security is a complex issue, but companies can apply several best practice frameworks and guidelines to help mitigate risks effectively. The following 10 frameworks can help businesses safeguard their assets against possible threats.
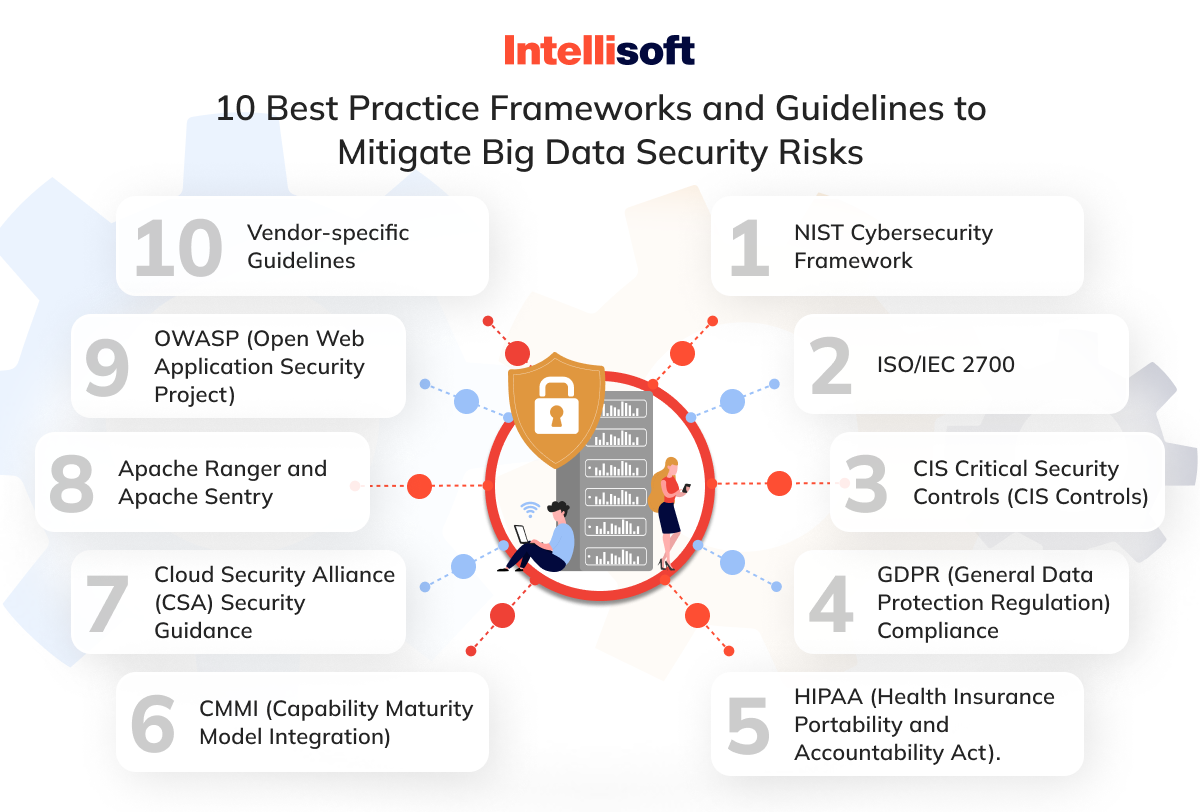
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has created a framework that offers a range of guidelines, standards, and best practices for managing and minimizing cyber security risks, including those associated with big data. This framework comprises five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover.
- ISO/IEC 27001. This globally recognized standard outlines a structured methodology for managing Information Security that IT experts can leverage to create, execute, sustain, and regularly enhance an Information Security Management System (ISMS) customized to their company’s specific requirements and circumstances.
- CIS Critical Security Controls (CIS Controls). The Center for Internet Security (CIS) offers a valuable resource for organizations aiming to bolster their cybersecurity defenses. It provides a comprehensive set of prioritized controls that address various security domains, including data protection. These controls can be effectively employed in big data environments to enhance the organization’s overall cybersecurity posture.
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) Compliance. Adhering to GDPR guidelines is essential for organizations dealing with EU citizens’ personal information. GDPR sets stringent requirements for record protection, privacy, and consent, providing a robust framework for securing big data.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act). If your organization deals with healthcare big data, compliance with HIPAA is crucial due to its specific security standards and safeguards for protecting electronic protected health information (ePHI). It is a mandatory standard for security solutions for big data analytics in healthcare.
- CMMI (Capability Maturity Model Integration). This framework emphasizes process improvement and maturity assessment. Organizations can utilize it to evaluate and enhance their security processes and practices associated with big data.
- Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) Security Guidance. CSA offers comprehensive guidelines and best practices for securing cloud-based solutions, including their helpful Cloud Controls Matrix.
Apache Ranger and Apache Sentry. These open-source projects manage and enforce authorization policies for Hadoop-based ecosystems, allowing IT professionals to control access to sensitive information. - OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project). The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) provides valuable resources that can assist in enhancing the security of your big data applications and web interfaces. By leveraging OWASP’s expertise, you can mitigate the risks associated with vulnerabilities in your web APIs and interfaces and prevent unauthorized access or exposure to sensitive information. With OWASP’s guidance and support, you can bolster the security of your web applications and protect your data from potential threats.
- Vendor-specific Guidelines. Major cloud providers such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud provide security best practice guides. IT professionals should refer to these guides when using specific cloud services.
Big Data Security
This is a crucial aspect of any processing environment. It involves implementing measures and mechanisms to protect the infrastructure, applications, and information involved in big data processing.
This aspect focuses on applying technical security measures to secure various components of an entire ecosystem. These components include storage systems, such as Hadoop clusters and warehouses, processing engines, pipelines, and the data itself.
A comprehensive set of security protocols is implemented to guarantee the maximum protection level. These include information encryption, access controls, authentication, authorization, big data surveillance and security intelligence, threat detection, and data masking, all tailored to the unique demands of the particular ecosystem. Together, these measures create a robust and impenetrable processing environment, preventing any unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Big Data Security Management
Security management is a crucial and complex undertaking beyond implementing technical protection measures in a big data environment. It encompasses a range of policies, procedures, and governance practices that organizations must implement to effectively manage and oversee record safeguarding.
A comprehensive approach that involves multiple facets of security management is needed to ensure the security of big data. This approach includes strategic planning, conducting risk assessments, managing compliance, and coordinating all security efforts related to big data. The process is complex and requires aligning security practices with an organization’s overall security strategy to ensure that security controls are effectively implemented and remain effective over time. A thorough and coordinated approach is critical to protect valuable data assets from potential threats.
In other words, security management involves a holistic approach to security that is proactive and reactive, considering the ever-changing threat landscape and the unique challenges of managing large and complex information sets. By implementing effective practices, organizations can help safeguard their information assets and protect themselves against various threats, including cyber attacks, breaches, and other security incidents.
How Big Data Security Works
Big data presents a unique challenge, as it involves dealing with massive volumes of information that can be accessed and processed from multiple sources. To ensure the safety and integrity of such records, robust security measures are necessary, including firewalls, user authentication, end-user training, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and encryption for both information in transit and at rest.
However, securing big data environments is not a straightforward process. These environments are characterized by three distinct stages (ingestion, storage, and processing), which require different security measures. As a result, securing vast amounts of information requires a more comprehensive and nuanced approach than traditional network security.
Stage 1: Data sources
Big data is the massive volume generated from various sources and formats. This information includes information from user-generated sources such as customer relationship management (CRM) or enterprise resource management (ERM) systems, transactional databases, and a vast amount of unstructured information, such as emails and social media posts.
Moreover, machine-generated records, such as logs and sensor data, further add to the complexity of managing the loads of information. Given the sensitivity and importance of the information within these sets, it is crucial to maintain protection throughout the entire process, from the source to the platform where it is stored.
Stage 2: Stored data
Ensuring the safety of stored information is of utmost importance for businesses, and this requires the implementation of advanced security toolsets. Encryption at rest, robust user authentication protocols, and intrusion prevention systems are key security measures companies must deploy across their distributed clusters with multiple servers and nodes.
In addition, it is crucial to extend the protection of security tools to log files and security big data analytics tools operating within the platform. This comprehensive approach helps safeguard valuable business assets and protect against potential security breaches.
Stage 3: Output data
Modern businesses rely increasingly on unique platforms to gather, process, and analyze vast amounts of information and extract valuable insights. These platforms are designed to perform sophisticated analytics on extensive datasets and generate useful insights through applications, reports, and dashboards.
However, the big data security intelligence generated by these platforms can become a prime target for cyber intrusions, leading to data breaches and other security threats. Therefore, companies should ensure that the output information generated by these platforms is encrypted, alongside data ingress, and that compliance measures are in place at this stage.
What Are the Big Data Security Best Practices
While big data has revolutionized business operations, it also presents unique challenges that demand immediate attention. Organizations must develop a strategic alignment of technology with their objectives to fully harness the power of analytics. Crucially, this strategy should include different types of data security to protect against potential risks. In this context, it is imperative to explore the best practices and methodologies for ensuring security.
Encryption
Ensuring the confidentiality and security of sensitive information is paramount. To this end, robust encryption practices are not just critical, but highly effective. Encryption should be implemented to protect records at rest and during its transit through various stages of the Big Data pipeline.
Scalability is crucial as encryption must extend its protective reach to cover structured and unstructured information and different storage formats such as NoSQL. The strength of encryption lies in its ability to render recourds incomprehensible to unauthorized parties, even if they manage to intercept or access it, providing a robust layer of security.
User access control
Safeguarding sensitive big data is a top priority for organizations. However, protecting it from insider threats and unauthorized access remains a significant challenge. One of the primary causes of data breaches is excessive privileges granted to individuals. Hence, implementing effective access control measures is crucial to mitigate these risks. To accomplish this, organizations rely on role-based access management, which helps manage access across different levels of big data pipelines.
For example, while analysts require access to big data security analytics tools, developers or ETL software don’t have to have the same level of access. By adhering to the principle of least privilege, companies can limit access to the necessary tools and information required for specific tasks. This approach significantly reduces the risk of data breaches, ensuring that sensitive data remains secure.
Cloud security monitoring
The demand for storage and processing capacity in big data workloads has grown significantly. As a result, many enterprises have turned towards cloud computing as a practical solution. With the shift towards cloud computing, new security challenges have arisen, such as exposed API keys and misconfigured cloud environments, which can no longer be ignored.
For instance, leaving an AWS data lake on S3 wide open to the internet can pose a significant risk to an organization’s security. To quickly mitigate potential security flaws, companies should use an automated scanning tool to scan public cloud assets.
Centralized key management
Encryption security is critical to ensure cyber security big data analytics. To handle encryption keys effectively, a centralized key management approach is necessary. This approach controls key governance from key creation to key rotation, which is crucial in maintaining information integrity and confidentiality. Bring Your Own Key (BYOK) is an excellent option for businesses running information workloads in the cloud. It allows for centralized key management and ensures compliance with industry regulations.
Network traffic analysis
In a big data pipeline, a constant flow of information is received from multiple sources, including real-time details from social media platforms and user endpoints. Analyzing network traffic is critical to understanding this data and detecting anomalies or irregularities. For example, this analysis can help identify potentially harmful information from Internet of Things (IoT) devices or unsecured communication protocols being used, which could pose a security risk.
Insider threat detection
The 2021 report has uncovered a startling fact that nearly all organizations, precisely 98%, are worried about being vulnerable to insider attacks. Regarding working with terabytes of records, insider threats can pose a severe risk to the confidentiality of sensitive corporate information. A malicious insider can pose a significant threat by using their access to big data security analytics reports and dashboards to leak valuable insights to competitors or sell their login credentials.
To prevent such incidents proactively, it is highly recommended to examine logs of common business applications such as RDP, VPN, Active Directory, and endpoints. By analyzing these logs, you can detect any unusual activities, such as unexpected downloads or irregular login patterns, that may require further investigation. This approach can help organizations identify insider threats in a timely fashion and prevent potential damage to their critical assets.
Threat hunting
Threat hunting is a big data analytics for cyber security practice that involves proactively identifying and eliminating potential threats in your network. This process, led by a skilled cybersecurity expert, leverages real-world attack data and insights from security tools to formulate hypotheses about potential threats. This practice is critical for uncovering hidden insights within large security information sets. By examining datasets and infrastructure for signs of compromise, threat hunting helps ensure your environment’s security.
Incident investigation
A Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system is employed to collect and analyze a vast amount of information to enhance the security of large-scale records. However, due to the high-speed generation in big data environments, SIEM systems can become overwhelmed, leading to numerous false alarms and alerts for analysts. An incident response tool can address this issue by providing context for security threats and streamlining the investigation process.
User behavior analytics
User behavior analytics is a powerful tool that can help organizations go beyond the traditional approach of insider threat detection. By continuously monitoring user interactions and setting a baseline for normal behaviors, it can quickly identify anomalies or deviations that may indicate potential security threats. This helps organizations detect not only insider threats and compromised accounts but also enhance the overall security of their assets in the big data environment.
Data exfiltration detection
Security leaders face a major challenge in safeguarding their organizations’ sensitive assets from unauthorized data transfers. The large-scale pipelines make it difficult to detect exfiltration, which involves copying vast amounts of information from the system. A comprehensive approach to monitoring outbound traffic, IP addresses, and network activity is required to address this issue.
Prevention involves a combination of tools such as code security, misconfiguration checks, data loss prevention, and next-generation firewalls. However, it’s not enough to rely on technology alone; educating and raising awareness amongst your organization’s employees is essential.
Conclusion
The advantages of big data analytics for security intelligence include gaining valuable insights, predictive analytics, enhanced customer experiences, and improved operational efficiencies. As organizations continue using big data to optimize their operations, drive innovation, and make better decisions, protecting this information has become more critical.
Securing big amounts of information can be challenging, but with the advancement of technology, there are many solutions and best practices to address these challenges. However, choosing the right technology partner is crucial to implementing modern tools to safeguard sensitive details.
At IntelliSoft, we develop custom big data security solutions to help businesses secure their data and reap its benefits. Talk to our experts today and share your needs.